Transcription
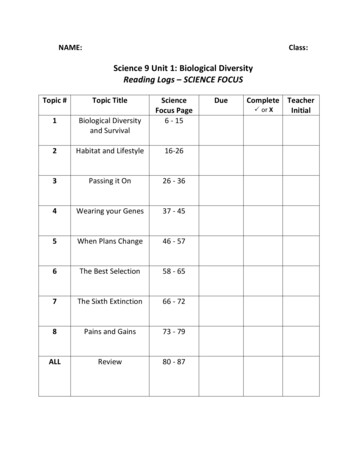
NAME:Class:Science 9 Unit 1: Biological DiversityReading Logs – SCIENCE FOCUSTopic #Topic TitleScienceFocus Page6 - 151Biological Diversityand Survival2Habitat and Lifestyle16-263Passing it On26 - 364Wearing your Genes37 - 455When Plans Change46 - 576The Best Selection58 - 657The Sixth Extinction66 - 728Pains and Gains73 - 79ALLReview80 - 87DueCompleteP or XTeacherInitial
Science Focus 9Biological Diversity2
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityBiological Diversity and SurvivalPage 6 – 15The and of organisms is called Biological Diversity.Define Variation, and then give an example of a variation between you and a classmate (variationwithin a species) and an example of a variation between two different mammals (variationbetween species).Variation –Example 1 –Example 2 –“Species” refers to one type of plant or animal. Organisms are grouped as species if:1–2-Explain why lions and tigers are not the same species:What is SPECIATION? Define and give an example:3
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityProvide a definition and example of each:AdaptationBehavioural AdaptationStructural AdaptationWhy is variation important? Convince me.Formula for calculating Diversity IndexGood Diversity Index Bad Diversity Index Who came up with the system we use to classify animal populations?A Mnemonic is a learning technique that aids information retention. Come up with amnemonic that will help you memorize:Kingdom – Phylum – Class – Order – Family – Genus - Species4
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityTopic 1 Review:Species diversity – occurs within individual organisms of the same species.Genetic diversity – occurs within organisms at a cellular level, as it describes the variety of geneticmaterial in all living things.Species Distribution – Plant and animal species are not distributed evenly throughout the various ecoregions of the world. Most of the different species of plants and animals can be found in tropicalregions and, more specifically, in the rainforests. As you move closer to the poles of the Earth, thereis less biological diversity.Topic 2: Habitat and Lifestyle16-26PagesAn organism’s niche includes two parts:1. –2. –Give an example (not the deer example from your text) of how a variation betweenspecies may give one of them an advantage when competing for food or habitat:The warblers on page18 share a habitat byresource partitioning.Using diagrams ANDwords, explain whatresource portioningis.5
Science Focus 9Niche TypeBroadBiological DiversityResident SpeciesSpecies ExampleHabitat ExampleSpecialistExplain “the trap of specialization” so that a grade 4 student could understand:A relationship is one in which two organisms live indirect contact. List the 3 types we discussed in class.TypeExplainExampleWhat is an Invasive species?Are invasive species typically GENERALISTS or SPECIALISTS?(circle one)Give 3 examples of invasive species in Canada, include 1 that is invasive to Alberta:(bonus points of diagrams)6
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityTopic 3: Passing it OnPages 26 – 36What are Heritable Traits? Give 2 Examples.Asexual ReproductionSexual Reproduction# of ParentsVariation (Y/N)FormsBinary Fission:In Animals:Fertilization:Budding: Spores:a zygote develops into aNew life develops either:What is Vegetative Reproduction?INEX-Briefly describe the following and give anexample of a plant that does it.CuttingsRunnersTubers/BulbsIn Plants:Pollination:Fertilization:Cross Pollination:What structures make up a seed?7
Science Focus 9Biological DiversitySuckersBacterial Conjugation:DiagramExplanationPlant dite:Monotremes:8
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityTopic 4: Wearing your GenesPages 37 – 45Mendel’s Laws of Heredity1. Each trait is controlled by two factors-genes (one from each parent)2. Each gene has two forms (alleles) – dominant or recessive3. For each trait an organism could inherit either:Ø Two dominant allelesØ Two recessive allelesØ One dominant and one recessive allele4. The distribution of dominant and recessive genes from the parents to the offspring is determined by chanceVariationContinuous VariationDefinition3 Distinct Examples-Discrete Variation-Environmental InfluencesTrue or False: Variations can result from interactions with the environment. (supportyour choice)9
Science Focus 9ChromosomesBiological DiversityGenesAllelesUse the terms dominant, recessive and alleles to define:HomozygousHeterozygousis known as the Father of Genetics.Let’s say that in seals the gene for the length of whiskers has two alleles. The dominant allele (W)codes long whiskers and the recessive allele (w) codes for short whiskers. Use a Punnett Square toanswer the following questions.What percentage of offspring would be expectedto have short whiskers from the cross of two longwhiskered seals, one that is homozygousdominant and one that is heterozygous?%If one parent seal is pure long-whiskered and theother is short-whiskered, what percent ofoffspring would have short whiskers?%10
Science Focus 9Biological Diversity1.5 When Plans ChangePages 46 – 57First identified by:StructureDiscovered by (no relation):DNA:Deoxyribonucleic AcidDetailed/labelled structure of a DNAMolecule:Why are the terms “blueprint” and “code” used todescribe DNA?Where is DNA found?Nitrogen Base PairsHumans have PAIRS ofChromosomes for a total of .Cells of multicellular organisms (like us) divide for growth of the organism and repairand replacement of tissues.Somatic Cells (all cells other than sex cells) undergoSex Cells undergoThe major difference between the two processes is that to form sex cells, cell divisionoccurs times. The final result is that the gametes have only theoriginal number of chromosomes.The process of randomly dividing 23 pairs of chromosomes in half creates thepossibility of 223 different combinations of chromosomes! That’s a lot of variation!11
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityMost Cats have 19 pairs of chromosomes (Meow). Draw and label the process forcellular division of a somatic and a sex cell in Fluffy:Somatic Cell Division:Sex Cell Division:Super Happy Fun Definition Time:BiotechnologyGenetic EngineeringArtificialInseminationIn Vitro FertilizationDraw a picture to demonstrate your understanding of the hierarchyof the following: Gene, Chromosome, DNA, Allele, Cell, Nucleus, DNAFun Fact - If you took the DNAfrom all the cells in your bodyand lined it up, end to end, itwould form a strand 6000 millionmiles long (but very, very thin)!To store this important material,DNA molecules are tightlypacked around proteins calledhistones to make chromosomes.12
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityTopic 6: The Best SelectionArtificial selectionPages 58 – 65ExampleProsConsExampleProsConsDefinitionNatural selectionDefinitionThe Theory of Natural Selection can be summed up in four statements:1.2.3.4.How did humans influence the natural selection of peppered moths?Topic 7: The Sixth ExtinctionPages 66 – 72Some areas in the word support greater biological diversity than others: why?13
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityWhat other factors influence biological diversity over the globe?TermDefinitionExampleCanadian ExampleExtinctionExtirpationBioindicator Species1.8 Pains and GainsPages 73 – 79How do Zoos and Seed Banks help prevent the decline of biodiversity?ZoosSeed BanksWhat happened in 1992?14
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityWhat does COSEWIC stand for?Complete the following table for COSEWICs classification of wildlife species: (hint- you need to lookthis up online!)XXTETSCNARTell me about your favourite topic in this unit and why you enjoyed learning aboutit!15
Science Focus 9Biological DiversityBiological Diversity Review – Key TermsVariationMeristemMutationBiological nSexual reproductionChromosomeStructural AdaptationZygosporeGene somatic cellsBehavioural AdaptationBacterial conjugationGenetic engineeringDiversity cCompetitionStamenAquacultureBroad NicheOvuleArtificial selectionGeneralistPollen TubeSelective breedingSpecialistEmbryoNatural selectionNarrow ationBioindicator speciesSymbiotic AssociationGeneticsSeed bankHeritableContinuous VariationGlobal treatiesAsexual reproductionDiscrete variationProtected areasBinary fissionDominant traitSporeRecessive trait16
Science Focus 9 Biological Diversity 5 Topic 1 Review: Species diversity - occurs within individual organisms of the same species. Genetic diversity - occurs within organisms at a cellular level, as it describes the variety of genetic material in all living things. Species Distribution - Plant and animal species are not distributed evenly throughout the various eco-











