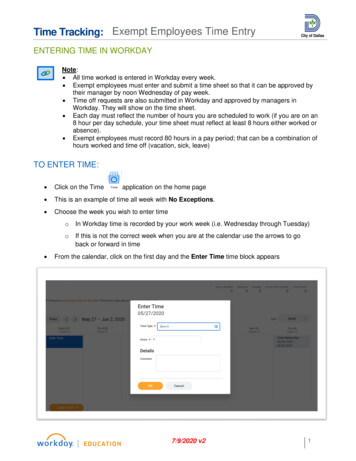
Transcription
Keep it plumb. Becauseof soil obstructions andthe way the machine’sgeometry changes asthe boom lowers, theoperator needs to makeregular adjustments toplumb the pile.It’s Time to ConsiderHelical-PileFootingsSteel piles screwed into the ground can supportanything from mailboxes to housesBy Jeremy Hess50FINE HOMEBUILDINGCOPYRIGHT 2016 by The Taunton Press, Inc. Copying and distribution of this article is not permitted.Drawing: Don Mannes
After almost 20 years in construction,I became a dealer for TechnoMetal Post (TMP), a helical-pile manufacturer. Helical pilescan be driven almost anywhere, install inminutes, don’t make a mess, and come insizes that can support an enormous varietyof structures. Since becoming a dealer, I’veinstalled piles to support decks, porches,boardwalks across wetlands, industrialequipment, and business signs; to shoreup failing house footings; and to underpin concrete slabs that were settling. Someof the machines used to drive the piles aresmall enough that they can be used inside ahouse—for example, to add a footing to abasement. It is not uncommon for my helperand me to pull up to a job site first thing inthe morning, install 10 or 12 piles for a largedeck, and leave by midafternoon with noevi dence of our having been there besidesthe piles themselves.Helical piles are essentially large steelscrews that thread into the ground to serveas footings, and they have been in use sincethe early 1830s. The machines used to drivethe modern versions come in many sizes,from the walk-behind machine I use to versions that are mounted on excavators. All ofthem work pretty much the same way. Agas or diesel engine drives a hydraulic pumpthat provides the power to spin the pile intothe ground.The first project I ever did—a 30-ft. by80-ft. deck for a winery—exemplifies someadvantages of helical piles. The originaldesign called for concrete footings. However,because the deck was to be built over uncompacted fill, those footings needed to be 14 ft.deep to reach bearing soil. The owner almostabandoned the project after finding that concrete footings would cost 20,000. I was ableto save him 8000 with helical piles. And evenon the steep slope of that site, the installationtook a couple of days instead of a week.When you account for all the costs ofconventional footings, helical piles are surprisingly affordable. Consider these costs:renting an auger or hiring an excavator, orthe time it takes to dig by hand; removingspoils from the excavation; and repairing sitedamage from heavy equipment. If the concrete will come from a truck, how will it bemoved to the hole? How do you know thatthe soil will support the structure? What if itrains between the time of the excavation andthe footing inspection so that the hole haswww.finehomebuilding.comNO MESSThe helix simply threads intothe ground, leaving virtuallyno surface disturbance.6 in. of water in the bottom? Helical pilesovercome all of these concerns. Althoughpricing for piles can vary widely based onavailability, contractor, and location, mycompany can install four piles for a typicalresidential deck for 600 to 900.While there are other helical-pile installers, most don’t focus on residential worklike TMP does. That said, you may have alocal contractor who does residential workusing other manufacturer’s products. Manyof the advantages I discuss here are commonamong manufacturers.What are helical piles?A helical pile consists of three main parts.The shaft is either a hollow square bar, a solid square bar, or a hollow pipe. The helixis a deformed round plate resembling a section of screw thread that is welded to the bottom of the shaft. Once the pile is installed, acap attached to the top of the shaft connectsthe structure to the pile.The first section of shaft with the helix isreferred to as the lead section. The length ofthe lead section varies by manufacturer andapplication, but it’s typically between 5 ft.and 7 ft. For greater depths, extensions areadded as necessary. Extensions are just shaftswithout a helix that are welded or bolted tothe installed pile. In poor soils, additionallead sections with their helices sometimesare added to improve bearing.The size of the helix used is determined bya number of factors, but the load to be carried and the soil type are the main considerations. In soft soils, a larger helix is needed tospread the load over a wider area. In rockyor very dense soils, a smaller helix is typically used. Most helical-pile manufacturersoffer helix sizes ranging from 6 in. dia. to24 in. dia. The helix sizes my company usesin residential work range from 6 in. to 12 in.,but we’ve used helices as large as 18 in. whenworking in very soft ground. Larger sizes areavailable but are used typically in heavy commercial or industrial applications.Every helical-pile manufacturer has its ownselection of pile caps for attaching to wood,concrete, and steel. Typical pile-to-wood connections are made through U-brackets or flatplates. Usually called heads, they either arefixed, meaning there is no adjustment afterinstallation, or are adjustable by means of athreaded stalk so that the elevation may befine-tuned. Heads used to support slabs andgrade beams are flat plates with short piecesjune/july 2016COPYRIGHT 2016 by The Taunton Press, Inc. Copying and distribution of this article is not permitted.51
Verifying a pile’s bearing capacityThere aretwo ways toverify bearing:a high-techapproach basedon hydraulicpressure, and alow-tech approachthat involveswhackingthe pile with asledgehammer.of rebar attached. Custom heads can be madefor attaching almost anything imaginable.Piles can last a lifetime or longerHydraulic pressureequates to torqueand bearing capacity.The more torqueneeded to drive apile, the greater itsbearing capacity.Think of a woodscrew. The harder it isto spin the screw intothe wood, the harderit will be to pry thescrew out or tohammer it farther in.OrHelical piles are made of either black steelor hot-dipped galvanized steel. Used properly, both should last several lifetimes. Igenerally install galvanized piles for decks,boardwalks, light posts, or other applicationswhere the shaft is exposed. (People don’t liketo see rust.) For grade beams, foundation repairs, and other applications where the pilewill be encased in concrete or buried deeply,I typically use black steel. When the piles areburied or encased in concrete, air can’t get tothem as easily, so corrosion isn’t as much of aconcern. However, some local codes requireall steel in the ground to be galvanized.Additional corrosion-protection systemscan be used if clients request it. In placeswhere piles are to support a whole building,the extra peace of mind from the corrosionprotection can be considered cheap. Thereare both passive and active systems. Passivesystems use magnesium anodes that attachto the piles and work the same way a sacrificial anode does on a boat or buried propane tank—that is, the anode corrodes first,leaving the steel intact. Eventually, though,oxidation will consume a sacrificial anode.An active kind of corrosion-protection system known as an impressed-current systemworks by connecting all the piles in a foundation and passing a small electrical currentthrough them to prevent corrosion.Verifiable bearing capacityAn alternative test measures how farthe pile sinks under impact loads. Slicksoils such as wet clay don’t require muchtorque to drive a pile, and when the pileis stopped by ledge rock, torque ceasesto be a factor. In those cases, a benchmarkis made on the shaft using a laser leveland a permanent marker.52FINE HOMEBUILDINGSwing like John Henry. A steel bumperplaced in the shaft is hit hard with asledge, and the benchmark is checkedagainst the level to see if the pile wentdown. Depending on how far it sinks, upto 5000 lb. of bearing can be assumed.The capacity of an installed pile dependson its size and on the soil. Dense, gravelysoils generally have a much higher bearingcapacity than clay or sand. To carry greaterloads, piles may need to have additionallengths of shaft so that they can be drivendeeper to reach better soils. Helical pileshave excellent uplift resistance because thesoil above the helix is not disturbed. As arule of thumb, uplift resis tance is one-halfof compression resistance.One of the chief benefits of helical piles isthat the installer can verify the capacity of theinstalled pile. Building codes cover helicalpiles, but most inspectors haven’t dealt withthem in person. Inspectors may be skeptical, but once they learn about the productand see engineer-stamped documentationof the bearing capacity, they become receptive. When a building department requiresBottom photos, facing page: courtesy of TechnoMetalPost.comCOPYRIGHT 2016 by The Taunton Press, Inc. Copying and distribution of this article is not permitted.
Weld thehead tothe pile.A weldedconnectiontransferslateral anduplift loadsfrom thestructure tothe pile.Where the metal hits the woodProviding bearing and uplift resistance is only half the battle. You also needto attach the helical pile to the structure, and that requires some kind of cap.Saddle up. This U-shaped bracket makes astout attachment for a deck beam.www.finehomebuilding.comAdjustable height. In some jurisdictions, athreaded stalk can be used to fine-tune theheight of column bases.Hold the house down. Steel plates arelined up and welded to the piles. Thevertical legs provide attachment forperimeter beams.june/july 2016COPYRIGHT 2016 by The Taunton Press, Inc. Copying and distribution of this article is not permitted.53
Go-Anywhere MachinesHelical piles are versatile, and the smaller machinescan even retrofit footings inside an existing house.Stabilizing house footingsJacking up a houseOn lake iceIn wetlandsSourcesMost helical-pile installers are regional, butyou can find links to multiple contractors atthese websites.In a kitchenan installation report, I submit a sketch ofthe footprint of the structure, the pile layout,and the installation data for each pile to ourengineer. He reviews the building loads andthe pile data to verify that the pile will support the design weight. He then stamps andsigns this report and submits it to the building department.Accurate placementRocks did not prevent the installation of anyof the hundreds of piles my company did lastyear, although they made a few of them difficult. Except for in very rocky soils, a pilecan be installed within 1 4 in. of its designedlocation and made plumb in all directions.54FINE HOMEBUILDINGOver a bankA skilled installer can manipulate the pilearound rocks the size of a basketball. Smallerrocks are no more than an inconvenience.In soils with larger rocks, helical piles area little more challenging to place accurately.A boulder may have to be removed with abackhoe, or the pile may need to be relo cated. Sometimes, though, I’ve been able toattach a cable winch between the boom ofthe pile machine and a stationary object tosteer a pile through very rocky soils.If a pile lands on ledge or on a large rockthat is below the frost line, and if lateral stability is achieved through the framing of thestructure and not the soil’s resistance to pilemovement, it may be fine to rest the pile onhelicalpileworld.commyfoundationsolutions.comtop of the rock. This situation requires hammer testing the pile to be sure it won’t sinkonce the structure is built and is generallyonly an option for light structures such asdecks and sunrooms.Winter doesn’t have to halt construction. Helical piles can be installed in frozenground. To do that, I drill a hole through thefrost with an electric demolition hammer.Then I insert a 3000w electric heater intothe hole. It takes 10 to 15 minutes to thawenough ground to install a pile. Jeremy Hess is a contractor in Elizabethtown, Pa. Photos by Andy Engel, exceptwhere noted.Photos this page: courtesy of TechnoMetalPost.comCOPYRIGHT 2016 by The Taunton Press, Inc. Copying and distribution of this article is not permitted.
50 FINE HOMEBUILDING Drawing: Don Mannes. A fter almost 20 years in construction, I became a dealer for Techno Metal Post (TMP), a helical-pile manufacturer. Helical piles can be driven almost anywhere, install in minutes, don’t make a mess, and come in sizes that can support an enormous variety of structures. Since becoming a dealer, I’ve installed piles to support decks, porches .