Transcription
v1.2Earned Value Management(EVM)Tracking cost and scheduleperformance on projects“What are my chances?” / “Not good.” / “You mean, not good like oneout of a hundred?” / “I’d say more like one out of a million.” / “Soyou’re telling me there’s a chance!”- Jim Carrey as Lloyd Christmas to Lauren Holly as Mary SwansonDumb and Dumber, http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0109686/.Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.1
v1.2Acknowledgments ICEAA is indebted to TASC, Inc., for thedevelopment and maintenance of theCost Estimating Body of Knowledge (CEBoK )– ICEAA is also indebted to Technomics, Inc., for theindependent review and maintenance of CEBoK ICEAA is also indebted to the following individuals who have madesignificant contributions to the development, review, and maintenance ofCostPROF and CEBoK Module 15 Earned Value Management (EVM)– Lead authors: Jennifer M. Rose, Maureen L. Tedford– Senior reviewers: Richard L. Coleman, Brian L. Octeau, Fred K. Blackburn,Colleen M. Craig– Managing editor: Peter J. BraxtonUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.2
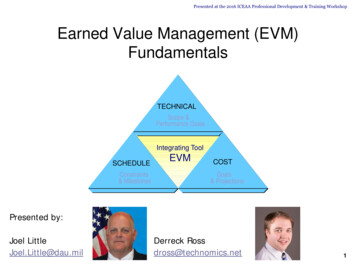
v1.2EVM Overview Key Ideas Practical Applications– Integrated baseline Resource-loaded schedule– Earned value Objective progressing– EACs – risk-adjusted rollups– EACs – alternative formulae– Performance measurement Contract vs. technical– Extrapolation from Actuals– Cost and scheduleperformance Analytical Constructs Related Topics– AC (Actual Cost) actuals to– Risk Managementdate– Project Management– EV (Earned Value) value of– Schedule Analysis / Riskwork performed– PV (Planned Value) budget– EAC AC (BAC-EV)/PI Tip: This formula, while intuitive, may not be theBCWRbest predictor of EAC!Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.3
EVM within theCost Estimating Frameworkv1.2PastPresentFutureUnderstanding yourhistorical dataDevelopingestimating toolsEstimating the newsystem3000.03000.0Management Reserve2500.0VACManagement Reserve2500.0PMBEAC or LRECBBCBBBACPMB2000.02000.0Schedule DelayCost Variance500.0Earned Valuedata elementsEstimate AtComplete (EAC)formulaeUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.EAC ost 1500.0AprScheduleVariance1500.0
v1.2EVM and Cost Estimating How should Cost Estimators beinvolved in EVM? Verify Realistic Baselines20– Control Accounts that trace to BOEs– Cost Estimator participation in IBRs Develop Accurate EACs– Statistical and risk-based methods Gather Cost Data to Support Estimating– IPMR and other EV data serve as datasources for estimating analogous effortsUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.5
v1.2Earned Value Data Elements Earned Value has five basic data elements:ElementTitleCommon TerminologyBCWSBudgeted Cost of WorkScheduledPlanned Value (PV), PerformanceMeasurement Baseline (PMB), plan,baselineBCWPBudgeted Cost of WorkPerformedEarned Value (EV)ACWPActual Cost of Work PerformedActual Cost (AC), actualsBACBudget at CompletePlanned CostEAC / LREEstimate at Complete / LatestRevised EstimateForecasted CostTip: EAC generally refers to the Government’s independent assessment of theestimate at complete while LRE refers to the Contractor’s estimate at completeUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.6
v1.2BCWS (The Plan) Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS): The sum ofthe budgets for all work packages, planning packagesscheduled to be accomplished within a given time period– The value of the work scheduled– The baseline used to measure all performance– The resource-loaded scheduleAKA PlannedValue (PV) Picture a Gantt chart17 BCWSBACTimeUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.7
v1.2BCWP (What Work Was Performed?) Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP): Thesum of all budgets for completed work packagesand completed portions of open work packagesAKA Earned– The value of the work performedValue (EV)– Dependent on BCWS – can only earnas much as is loaded in the completed BCWS tasksTime now BACBCWSBCWPTimeUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.8
v1.2ACWP (Cost Incurred) Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP): The costsactually incurred to accomplish the work earnedwithin a specified time frameAKA Actuals (AC),Actual ValueLaborMaterialGeneral LedgerContractor’sAccounting SystemSubcontractInvoicesExport actualsto EVM databaseInvoicesTravelODCsACWP BCWSBACBCWPTimeUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.9
v1.2BAC and LRE (End of Work) Budget At Complete (BAC): Cumulative BCWS atthe end of the contract Latest Revised Estimate (LRE): The contractor’sbest guess at how much the effort will actually costat the end of the contractLREACWP BCWSBACBCWPTimeUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.10
v1.2Basic EVM Example Managing projects without earned valueprovides only part of the picture Traditional approach:– Budget work– Record Actual expenses Example:– Budgeted for 4 Aquaria to be built inNovember at 100 each– At end of November, spent 300– Great! I am 100 under budget or am I?Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.11
v1.2Basic EVM Example Example (continued):– Did I accomplish 400 worth of work whilespending only 300?– Earned value adds a new dimension – whatis the VALUE of work accomplishedEarnedValueBudget 400vsActual 300Variance 100Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.12
v1.2Basic EVM Example Example (continued):– At the end of November I spent 300 butonly completed 2 AquariaBudget 400EarnedValue 200Actual 300CostVariance- 100– So I am not only overrunning Cost, I amalso behind schedule!Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.13
Integrated Baseline Overview Key component of EVM is the ResourceLoaded Schedule– Elements of the Performance MeasurementBaseline (PMB) defined early in acquisitionprocess by Government and Contractor WBS Structure Schedule BOEs (justification for time phased costs and effort)– Time-Phased Budget / Resource LoadedSchedule initially defined for proposal andrefined/baselined post negotiations Government review of PMB occurs viaIntegrated Baseline Review (IBR)Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.1514v1.2
v1.2WBS Definition/Overview Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Product1oriented division of material and work tasks Used to organize and define product/work tobe accomplished Different forms:– Program Summary WBS (Government), usuallyreferred to as WBS– Contractor WBS, usually referred to as CWBS– Cost Element Structure (CES) Level and scope may depend on the underlying data andmethodology used in developing the estimate– WBS typically several levels higher than CWBSOSD EVM Website: http://www.acq.osd.mil/evm/Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.15
v1.2WBS Importance to EVM WBS provides framework within which allEarned Value planning is accomplished WBS must be:– Comprehensive Matches program content– Hierarchical– “Sufficient” level of detail Sufficiency depends on size, complexity, risk, and otherfactors For EVM, level of detail for tracking costs usually lowerthan level for reporting costsUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.16
v1.2WBS Example WBS Sample layout for the aquaria example1.0 Aquarium Development Program1.1 Program Management / Systems Engineering1.2 Design AquariumNOTE: Example1.3 Develop/Integrate AquariumWBS is not1.3.1 Material Acquisitioncomprehensive or1.3.2 Material Integrationextensively detailed.1.3.3 Development Documentation1.4 Test Aquarium1.5 Deploy Aquarium2.0 Aquarium Maintenance Program2.1 Maintain Environment2.2 Replace Material2.3 Maintain/replace Fish PopulationUnit V - Module 15This WBS does notadhere toMIL-STD-881C andtherefore needs acomprehensive WBSDictionary.4 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.17
Organizational BreakdownStructure (OBS) Definitionv1.2 Functional breakdown of Organization16– Identifies the program’s organizational structure– Supports the identification of the functionresponsible for controlling overhead costs Typically aligns with Company’s Org Chart One piece of the framework used for planningresources One popular organization technique involvedIntegrated Product Teams (IPTs)– Multi-disciplined– Overarching IPT and Working-level IPT(s)Defense Acquisition w document&rf GuideBook\IG c10.3.asp.Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.18
Assignment of Work –Control Accountsv1.2 WBS cross-walked to OBS Control Accounts– Identifies Responsibility– Result is Control Account (sometimes called a Cost Account) Control Account is the focal point for integration ofscope, cost, and schedule Control Account Manager (CAM) is personresponsible for:– Developing plan for Control Account (Technical Scope,Schedule Tasks, Budget/Resources) Work Authorization Document (WAD)– Managing Earned Value performance within Control Account Monitoring EVM metrics Analyzing control account performance status Reporting variances– Conducting risk management/mitigation as requiredUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.19
Assignment of Work –Work Packagesv1.2 Work Packages are the lowest level at whichresources are allocated Within Control Accounts, work and planningpackages defined at lowest level of detail– Work packages for near-term workTip: Typically 4-6weeks long– Planning packages for far-term work– Planning packages become more detailed work packages astime progressesTip: Detail plantypically 6 months out Resources allocated to each work/planning package– Direct Labor– Material– Other Direct Charges (ODCs)Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.20
Assignment of Work IllustrationAquariumDevelopmentProgramProgram WBSElementsProgramMgmt/SystemsEngineeringContract WBSReportingElementsMaterialAcquisitionContract tControlAccountPlanningPackagesGraphic adapted from EVMS Basics Concepts, Sean Alexander, MeridianetOBS DATA SUMMARIZATIONUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.21v1.2
v1.2Baseline DevelopmentPriceContract BudgetBaseMR coversunanticipated,in scopechangesCost (CBB)ManagementReserve 10MControl Accounts arethe managementcontrol point for theintegration of scope,schedule & cost 110Mf 100MPerformance MeasurementBaseline (PMB) 90MDistributed Budget(Control Accounts) 85MWorkPackages 40MFeeUndistributedBudget 5M 10MEarned Value ismeasured againstthe PMBWork is tied toan activity, butis not detailplannedPlanningPackages 45MUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.22
v1.2Baseline Development – PMB18 Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB)developed– Sum of all Work/Planning Package Budgets UB– Undistributed Budget (UB) is: Work tied to an activity, but not detail-planned Used most often when new work added to contract Earned Value is Measured against the PMB Work packages and related budget (BCWS)are time phased using logic-driven schedule– e.g., PERT chart showing dependenciesTip: UB usually distributed within 60 daysUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.23
v1.2Baseline Development – MR Management Reserve (MR) set asidewhile developing PMB19– Covers unanticipated, in scope changes– MR % tied to level of risk and type ofcontract14 2-4% low risk and/or Cost Plus 15% high risk and/or Firm Fixed Price– More discussion on MR and its use iscovered under the Analysis of PastPerformance sectionTip: MR is most commonly 7-9% of CBBUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.24
v1.2Baseline Development – CBB PMB and MR together form the Contract3Budget Base (CBB) (“Cost”) CBB plus fee yields the Total Contract Value(“Price”) A time-phased graphic illustrating PMB andMR forming CBB is on the next slide EVM should be complemented by adisciplined Risk Management (RM) approachto identifying, quantifying, and addressingunknown future events“Integrating EVM and RM: A Statistical Analysis of Survey Results,” Alissa C. Kumley, Northrop Grumman Corporation,ISPA/SCEA Joint International Conference, 2005Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.25
PerformanceMeasurement – EV Methodsv1.2EV MethodDescriptionType of Tasks that Use MethodMilestone(Weighted)Take performance as definedMilestones (MS) are accomplished.MSs can be weighted if one or moreare considered more importantTasks that can be planned usinginterim MilestonesPercentCompletePerformance is taken based onPercent of task completedWork that does not have anyreasonable interim measurable MSs0/100All performance is taken when task iscompleteShort duration tasks - one month orless50/50Or X%/Y%50% (X%) performance taken whentask starts; 50% (Y%) performancetaken when task is completeShort duration tasks - two months orlessLOEPlan based on resource expenditureplan – Performance always equalsPlanUsed for tasks that are more timeoriented vice task oriented, such asProgram ManagementBest Method for EVMUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.26
Example –Performance Measurementv1.2 Determine the best earned valuemeasurement technique:– Aquarium System Program Management– Aquarium Design– Aquarium Deployment to Site ATLANTIC4Unit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.27
Example –Performance Measurementv1.2 Valid earned value measurement techniques:– Aquarium System Program Management LOE – most common method Milestone– Aquarium Design Most likely Design will be divided into smaller workpackages and multiple methods will be employed Milestone / Weighted Milestone – most common method Percent Complete– Aquarium Deployment to Site ATLANTIC 0/100 X%/Y% MilestoneMultiple Answers are JustifiableUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.28
v1.2Earned Value Analysis Elementary EV AnalysisAnalysis of Past PerformanceVariance ReportsProjection of Future PerformanceEarned Value Review ProcessUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.29
v1.2Elementary EV Analysis Common calculated Data Elements:– Schedule Variance (SV) BCWP – BCWS– Cost Variance (CV) BCWP – ACWPAKAAccomplishmentVariance3000.0CBBManagement Cost VarianceBCWSACWP500.0BCWPUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.AugJunAprFebDecOctAugJunAprFeb0.030
v1.2Elementary EV Analysis Common calculated Data Elements:– Variance at Complete (VAC) BAC – LRE– Estimate at Complete (EAC) Forecasting measure Various methods applicable Discussed in more detail later– Budgeted Cost of Work Remaining (BCWR) BAC – BCWP Analysis of data, including sampleproblems, in next sectionUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.31
v1.2Elementary EV Analysis3000.0EAC or LRECBBVACManagement Reserve2500.0BACPMB2000.0Schedule DelayScheduleVariance1500.0BCWS500.0ACWPUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights .0Cost Variance32
Projection of Future Performance Strength of EV is it enables the identification ofproblems early Recall that final CV will be worse than the cumulativeCV at the 20% completion point– Look for tendency to circumvent EVM's purpose as an “earlywarning system”– Delays in admitting/discovering cost growth is likely to resultin even greater cost overrun Various ways to analyze and project futureperformance– TCPI metric designed to lend credibility (or not) to contractorEAC (see future slide for more details)– Formula-derived EAC Example: EAC ACWP (BAC-BCWP)/CPI Based on EVM performance to date Equivalent to CPI Forecast on next slideUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.33v1.2
v1.2Future Performance – EAC Objective, mathematical Estimates AtComplete (EACs) can be calculated Most common are CPI and CPI * SPI– CPI ForecastEstimate ToCompletion(ETC) ACWP BCWR / CPI BAC / CPI Assumes even cost performance across the entireproject equal to performance experienced to date Referred to as “best case” EAC– CPI * SPI Forecast ACWP BCWR / (CPI*SPI) Also assumes that past cost and schedule performanceare indicative of future performance Adjusts estimate to account for schedule performanceexperienced to date Referred to as “worst case” EACUnit V - Module 15 2002-2013 ICEAA. All rights reserved.34
BAC Schedule Delay . EVM within the Cost Estimating Framework. Past. Understanding your historical data. Present. Developing estimating tools. Future. Estimating the new system. Earned Value data elements Estimate At Complete (EAC) formulae EAC and Predicted Schedule. 0.0 500.0 1000.0 1500.0 2000.0 2500.0 3000.0. b r n g Oct c b r n g. Management Reserve. CBB PMB BCWS ACWP BCWP Cost Variance .