Transcription
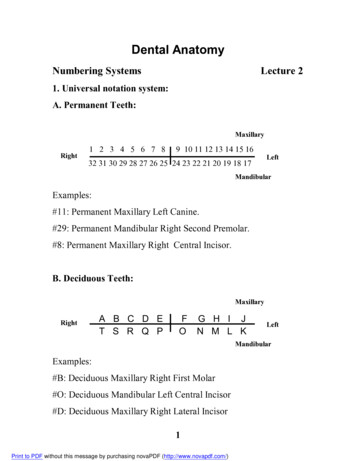
Dental AnatomyNumbering SystemsLecture 21. Universal notation system:A. Permanent Teeth:MaxillaryRight1 2 3 4 5 6 7 89 10 11 12 13 14 15 1632 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17LeftMandibularExamples:#11: Permanent Maxillary Left Canine.#29: Permanent Mandibular Right Second Premolar.#8: Permanent Maxillary Right Central Incisor.B. Deciduous Teeth:MaxillaryRightA B C D ET S R Q PFOG H I JN M L KLeftMandibularExamples:#B: Deciduous Maxillary Right First Molar#O: Deciduous Mandibular Left Central Incisor#D: Deciduous Maxillary Right Lateral Incisor1Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
2. Palmer notation system:A. Permanent Teeth:MaxillaryRight8 7 6 5 4 3 2 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 88 7 6 5 4 3 2 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8LeftMandibularExamples:6Permanent Maxillary Right First Molar3Permanent Mandibular Left Canine8Permanent Maxillary Left Third MolarB. Deciduous Teeth:MaxillaryRightE D C B AE D C B AA B C D EA B C D ELeftMandibularExamples:BDeciduous Mandibular Left Lateral IncisorEDeciduous Maxillary Right Second MolarCDeciduous Mandibular Right Canine2Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
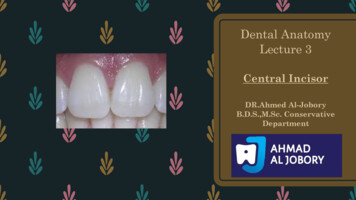
Crown and RootEach tooth has a crown and root. Thecrown is covered with enamel. The root iscovered with cementum and they join at thecemento-enamel junction (CEJ) or cervicalline.The enamel, cementum and dentin arethe hard tissues of the tooth. The majorbulk of the tooth is dentin.Dental pulp: is the soft tissue of thetooth and present in the pulp chamber andpulp canal.Pulp chamber: is the part of dental pulpin the crown.Pulp canal: is the part of dental pulp inthe root.Anatomical crown: is the portion of thetooth which is covered by enamel.Clinical crown: is the portion of thetooth which is visible in the mouth.In healthy person, the anatomical crown is larger than theclinical crown.3Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
The number of roots:1. Single root: in all anterior teeth, mandibular premolars andmaxillary second premolar.2. Two roots with bifurcation: in mandibular molars andmaxillary first premolar.3. Three roots with trifurcation: in maxillary molars.Surfaces and RidgesThe crowns of incisors and canines have 4 surfaces and a ridgeand the crowns of the premolars and molars have 5 surfaces.The surfaces are:1. Labial surface: is the surface which is towards the lip inincisors and canines ( in anterior teeth).2. Buccal surface: is the surface which is towards the cheek inpremolars and molars ( in posterior teeth).The labial and buccal surfaces could be termed as the "Facial"surfaces.3. Lingual surface: is the surface which is facing the tongue(all teeth).4Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
4. Occlusal surface: is the surface of the posterior teeth comingin contact with the teeth in the opposite jaw during closing themouth.In anterior teeth, this surface is called "Incisal ridge".5. Proximal surface: is the surface of the tooth facing towardsadjacent teeth in the same dental arch.a. Mesial surface: is the surface which is facing towards themedian line.b. Distal surface: is the surface which is facing away from themedian line.All teeth have their mesial surfaces touching the distal surfacesof the adjacent tooth except the maxillary and mandibular centralincisors (both permanent and deciduous).5Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
Contact area: the area of the mesial or distal surface of thetooth which touches its neighbor in the arch.Line angle: it is formed by the junction of two surfaces and getsits name from these surfaces. Example: mesio-labial line angle.Point angle: it is formed by the junction of 3 surfaces and getsits name from these surfaces. Example: mesio-linguo-incisal pointangle.6Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
Division of the crown into thirds:For description, the crown and the root are divided into thirdsaccording to the position of the icalCervicalMiddleIncisalApical7Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
Dental Anatomy Numbering Systems Lecture 2 1. Universal notation system: A. Permanent Teeth: Examples: #11: Permanent Maxillary Left Canine. #29: Permanent Mandibular Right Second Premolar. #8: Permanent Maxillary Right Central Incisor. B. Deciduous