Transcription
CHARGEBACKREASON CODESTHE ENCYCLOPEDIA
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueTable of ContentsIssue1Introduction2What Causes Chargebacks?4The "Reason" is Not the Reason5Chargeback Causes by Industry6The "Big 6" Reason Codes91. Fraud – Card Not Present112. Goods or Services Not Provided123. Cancelled Recurring134. Credit Not Processed155. Transaction Not Recognized166. Not As Described or Defective Merchandise17The Encyclopedia Categories19List of Reason Codes20Transaction Modifiers25Conclusion: What's the Impact?28About the Gurus29page2reason codes
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueIntroductionTHE RATE AT WHICHMERCHANTS DISPUTECHARGEBACKS.THE RATE AT WHICHMERCHANTS WINDISPUTES. 1THE RATE AT WHICHTHE CHARGEBACKGURUS WIN DISPUTES.page3reason codes
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueWhat Causes Chargebacks?There are countless reasons why someone mightdispute a charge on their credit card statement –they may not recognize the transaction, they mayhave discovered a mistake such as a double-charge,or they may think it’s the only way to get a refund.Whatever their reason, it’s up to the issuing bank toassign the reason code that tells you why they’vereversed the transaction. The bank asks the customerwhy they are disputing the charge, then assignsthe “reason code” which best fits the customer’sexplanation; typically, the cardholder isn’t told whatcode the issuing bank assigns. With the exception of“Does Not Recognize”, a reason code cannot be changedonce the issuing bank assigns it to the chargeback.The problem is, there are about a hundred of thesecodes between the four biggest card networks – and it’snot like a chargeback notification comes with a writtenexplanation for the merchant. So merchants are left tofend for themselves, either using up valuable time andresources to identify each chargeback and investigatethe cause, or just accepting these chargebacks as“the cost of doing business”.Prevention is the best defense against chargebacks, buteven if you do everything right you will never reduce yourchargeback rate to zero, so don’t just sit back and eatthe cost of every chargeback you receive. You will stillget chargebacks that are no fault of your own – causedby “friendly” fraud, buyer’s remorse, or an innocentmistake, and these chargebacks can put a great deal ofstrain on any company, due to:True Cost ofChargebacks:page4 240reason codesTHE IMMEDIATE COST OF THECHARGEBACKIn addition to losing the revenue from the sale and thecost of the product, fees charged by the issuing bankcan be as high as 125 per chargeback.THE LAGIt can take anywhere from 15 days to 6 months for amerchant to be notified of a chargeback. This sudden,unexpected loss of revenue can make it challengingto assess your financial health and to address anyproblems that may be causing chargebacks until it ismuch too late.THE RISK OF LOSING PROCESSINGSERVICES DUE TO A HIGHCHARGEBACK RATEIf your chargeback rate rises too high – for mostindustries, the maximum is 1%, or 1 chargeback per100 transactions – then your payment processorwill flag you as a high-risk merchant, which will costyou more in service charges, or they may cancel yourmerchant account entirely.Reducing your losses and keeping your chargebackrate down begins with understanding the reasonsfor chargebacks. Knowing the reason codes used byall the major card networks can help you recognizewhich chargebacks are legitimate and which areworth disputing, and point the way toward gatheringevidence, presenting your case and winning backsome money.WHEN BANKING FINES, PENALTIES ANDADMINISTRATIVE COSTS ARE FACTORED IN,CHARGEBACKS COST MERCHANTS 240 FOREVERY 100 WORTH OF PRODUCT LOST2.
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueThe “Reason” is Not the ReasonEvery chargeback will cite a reason code, and decoding it is the first step to fighting back. But to win, youwill need to understand exactly what is going on –and the "reason" doesn't necessarily match the rootcause.There is any number of situations in which thereason code may not reflect the real cause behindthe chargeback. For instance, the customer mighthave had second thoughts about buying somethingand wanted to cancel the transaction without goingthrough your customer service department – butwhen the bank asks, the customer says instead thatit was a fraudulent transaction. 99% of the time, thebank will take the customer's word for it.A false claim like this is called chargeback fraud or“friendly” fraud. In most instances of friendly fraud,the cardholder claims that the transaction was notauthorized, but they may also claim that goods orservices were not delivered, were not as described, orwere defective.But the real reason for thechargeback is more sinister,for example: They want to keep the productwithout paying for it. They have buyer’s remorse butdon't want to ask for a refund. The conditions for a refund haven'tbeen met (i.e. the time limit hadpassed). A family member made thepurchase but the primarycardholder doesn't want to honorthe charge.[1] n codes
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueAs you can see, most of the time there’s nothing “friendly” about friendly fraud.Chargebacks exist to protect cardholders from fraud and from businesses thatfail to deliver their services, but unfortunately it’s quite common for cardholdersto take advantage of the chargeback system in order to get something for free.But before you jump to any conclusions: even in cases of friendly fraud, it’s possiblethe cardholder made a mistake, didn’t recognize the charge or forgot aboutmaking the purchase.However, the likelihood that a fraud claim is legitimate is lower than you might think.Only 29% of chargebacks citing a reason code in the “fraud” category are true fraud.For those 29%, there’s nothing you can do to dispute the chargeback and get yourmoney back, but the 71% that are “friendly” fraud are worth fighting for.Compiling EvidenceTo win a chargeback dispute, you are required toproduce “compelling” evidence. For example, forVisa reason code 83, Fraud – Card Not Present, thisis defined as “Proof the cardholder participated inthe transaction, received the goods or services,or benefitted from the transaction”, and mostreason codes call for the same kinds of compellingevidence (defined in the card network’s productand service rules).Chargeback Causes by IndustryIn the chart below, we have identified the top three most frequently occurringchargeback reason codes for 14 different industries based on our data.These percentages are averaged across the four major card networks – Visa,Mastercard, American Express and Discover. Fraud – Card-Not-Present (CNP) is the leadingcause of chargebacks in 8 out of the 14 industries. Transaction Not Recognized is the leadingcause in Entertainment. Credit Not Processed is cited as the leading causein Insurance, Loyalty Rewards, and Marketing. Cancelled Recurring is the leading cause in CreditRepair Services.Service Not Provided or Merchandise NotReceived is the leading cause in Travel &Rental.page6reason codes
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueChargeback Causes by Industry Ctd.AdultIndustryConsultation& ift CardsHealth &Beautypage7reason codes67%9%5%20%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present35%27%10%27%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present43%23%13%21%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present60%21%12%8%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present70%16%6%8%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present32%17%13%38%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not PresentTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOther
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueChargeback Causes by Industry Ctd.InsuranceIT ilerspage8reason codes67%9%5%20%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present35%27%10%27%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present43%23%13%21%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present60%21%12%8%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present70%16%6%8%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present32%17%13%38%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not PresentTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOther
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueChargeback Causes by Industry Ctd.TelecomTravel &Rental67%9%5%20%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not Present35%27%10%27%Fraudulent Transaction - Card Not PresentTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherTransaction Not RecognizedCancelled RecurringOtherThe “Big 6” Reason CodesBetween the four major card networks – Visa, Mastercard, Amex and Discover – there are about a hundreddifferent chargeback reason codes. Some codes indicate fraud, while others indicate expired cards, defectivemerchandise or incorrect transaction amounts. Some deal exclusively with point-of-sale (POS) transactions,while others refer to card-not-present (CNP) transactions.Visa and Mastercard organize all of their reason codes into four different categories:12AUTHORIZATIONCONSUMER DISPUTES(AKA CARDHOLDERDISPUTERS)34PROCESSINGFRAUDERRORS(AKA POINT-OFINTERACTIONERRORS)American Express and Discover both have additional categories, but the industry is moving toward auniversal four-category system.Though this may seem like a lot of information to take in, you should keep in mind that most of these reasoncodes are extremely rare. For most businesses, there are really only six need-to-know codes that you canexpect to see with some regularity. We call these the “Big 6”.page9reason codes
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue1. Fraud - Card Not Present834837F29UA022. Goods or Services Not Provided304855C08RG3. Cancelled Recurring414841C28AP4. Credit Not Processed854860C02RN25. Transaction Not Recognized754863R04AA6. Not as Described or DefectiveMerchandise854860C02RN2The overwhelming majority of chargebacks fallunder one of 6 different “reasons”, but there is onethat towers over the others. “Fraud – Card NotPresent” is the most common chargeback code“ FRAUDCard NotPresent”page10reason codesby a wide margin. Our data shows that across allindustries, 39% of all chargebacks carry a “Fraud –Card Not Present” reason code – in some industriesthe proportion is as high as 84%.
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue1. Fraud — Card Not Presentnet workdescription fromthe card net workchargeback reasoncodeFraudulent TransactionCard Not Present83A complaint from a cardholder in regard to a cardabsent transaction, claiming that he or she did notauthorize or participate in the transactionFraudulent TransactionNo Cardholder Authorization4837The cardholder contacted the issuer claiming thatthe cardholder did not authorize the transactionFraudCard Not PresentF29Card member denies participating in charges relatedto mail, telephone, or internet transactionsFraudCard Not Present TransactionUA02Valid for a chargeback request relating to acardholder’s claim that the cardholder did not approveor participate in a card not present card saleThe bulk of chargebacks come with reason code83 or 4837. The former is Visa’s code indicating anunauthorized card-not-present (CNP) transaction;the latter is Mastercard’s code which includesunauthorized transactions for both card-presentand CNP transactions. For all card networks, thesetransactions fall under the “Fraud” category.The bank then reverses the transaction, removing thefunds from the merchant’s account and crediting thecardholder. If the cardholder is telling the truth (andthe issuing bank will usually take their word for it)then this is a case of identity theft. In such cases, themerchant is held accountable for the charge becausethey failed to adequately verify the cardholder’sidentity before processing the transaction.This reason code is cited when acardholder contacts their issuingbank to claim that they did notauthorize a transaction thattook place in a CNP environment(online, over the phone or by mail).But studies have shown that more than twothirds of these transactions are actually friendlyfraud – cardholders taking advantage of thechargeback system by knowingly reversing legitimatetransactions in order to get their money back withoutreturning the product. If you believe this to be thecase, and you can produce compelling evidence ofthe legitimacy of the transaction, you can win thisdispute and get your money back.page11reason codes
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue2. Goods or Services Not Providednet workchargeback reasonService Not Providedor Merchandise Not ReceivedGoods or ServicesNot ProvidedcodeThe card issuer received a claim from a cardholderthat merchandise, or services ordered were notreceived or that the cardholder cancelled the orderas the result of not receiving the merchandiseor services by the expected delivery date ormerchandise was unavailable for pickup.304855These reason codes occur when the cardholder tellstheir issuing bank that they knowingly performedthe transaction but claims that the goods orservices were never delivered. Visa reason code30, which applies in these circumstances, may alsoapply if the cardholder had cancelled the order priorto the payment being processed, but their card wascharged anyway.If you receive this type of chargeback and you arecertain the goods or services were delivered, oneof the following may have occurred:page12reason codesThe cardholder engaged in the transaction. Thepurchased goods or services were not received.Cardholder ordered goods and /or services and neverreceived the requested goods or services and theCard Sale was charged to the Account.Goods or ServicesNot ReceivedNon-Receipt of Goodor Servicesdescription from thecard net workUA02Cardholder offered goods and/or services and neverreceived the requested goods or services and theCard Sale was charged to the Account. The product failed to arrive within anexpected timeframe, so the customerissued the chargeback while thegoods were still in transit.They havebuyer’s remorse but don't want to askfor a refund. Your customer was dissatisfied withthe goods or services they purchased,even if the product was delivered aspromised. Your customer is attempting friendlyfraud.
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue2. Goods or Services Not Provided (continued)Best Practices for ChargebackPrevention and ReductionFor any transaction where delivery occurs after thesale, the expected delivery date range should beclearly indicated on the transaction receipt or invoiceand in an email to avoid a pre-emptive chargeback. Ifthe delivery is going be delayed for any reason, notifythe customer in writing and let them know when toexpect the delivery. In this case, it may be a good ideato give the customer the option of proceeding withthe transaction or cancelling it.For digital goods which are downloaded via theinternet, the best practice is to collect data showingthat the software was successfully downloaded andreceived by the cardholder, verified by their IP address,GEO Location, Device ID and account history/usage.To help protect yourself against friendly fraud, you’llwant to be thorough in collecting proof of delivery.Use a tracking number during shipping and requirea signature from the cardholder upon receipt of thepackage. The existence of a signed delivery slip willgo a long way toward discouraging – and fighting, ifnecessary – a chargeback.3. Cancelled Recurringnet workchargeback reasonCancelled Recurringpage13code41Cancelled Recurring4841Cancelled RecurringC28Cancelled RecurringAPreason codesdescription from thecard net workThe merchant was notified to cancel the recurringtransaction or that the cardholder’s account wasclosed but has since billed the customerThe cardholder notified the merchant to cancel therecurring transaction and the merchant continued tobill the cardholderCard Member continues to be billed after he/sheclaims to have cancelled goods or servicesCardholder challenges the validity of RecurringPayments Card Sales after expiration or cancellationof the Recurring Payments Plan agreement
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue3. Cancelled Recurring (continued)This type of chargeback is closely associated withsubscription-based industries. While Fraud is theleading chargeback reason in almost every industry,Cancelled Recurring is one of the few thatoccasionally outranks it, such as in the LoyaltyRewards industry where this reason is cited on27% of Visa and Mastercard chargebacks.Typically, these reason codes occurwhen a cardholder cancels theirsubscription but the cancellation is notentered into your system before the next paymentdate arrives. As a result, the cardholder is billed bymistake. However, some cardholders viewchargebacks as a “hassle-free” wayto cancel a payment and may deliberatelyissue a Cancelled Recurring chargebackinstead of contacting you directly.page14reason codesBest Practices for ChargebackPrevention and ReductionFor a recurring billing, it’s very important to keep linesof communication open. Always respond in a timelymanner to any customer requests about renewal orcancellation and comply with cancellation requestsimmediately, ensuring that all current and futurebillings are cancelled. If an outstanding balanceis owed for the services, contact the customer toprocess that payment manually, and if any creditremains on their account, make arrangements forthem to collect it.To prevent them from going through their cardissuer to cancel their subscription, display return andcancellation policies visibly and accessibly, makingit as easy as possible for your customers to opt outof recurring billing. Require them to acknowledge thepolicy via checking an “Accept” or “Agree” button priorto order confirmation – this acknowledgement canlater be leverage in a chargeback dispute.
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue4. Credit Not Processednet workchargeback reasonCredit Not Processed41The merchant was notified to cancel the recurringtransaction or that the cardholder’s account wasclosed but has since billed the customerCredit Not Processed4841The cardholder notified the merchant to cancel therecurring transaction and the merchant continued tobill the cardholderCredit Not ProcessedC28Card Member continues to be billed after he/sheclaims to have cancelled goods or servicesCredit Not ProcessedAPCardholder challenges the validity of RecurringPayments Card Sales after expiration or cancellationof the Recurring Payments Plan agreementWhen a cardholder claims that they returned a productthey had purchased but the funds were never refundedto them, they can issue a chargeback on the initialtransaction which will cite Credit Not Processed asthe reason.This reason can also apply in any instancewhere the cardholder claims credit is owed to them,which leads it to be one of the most common chargeback reasons in the Insurance industry.Mastercard’s description for their Credit Not Processed reason code, 4860, goes into further detail,explaining that you can also be held at fault in thefollowing circumstances: pageYou failed to disclose your returnpolicy at the time of purchase andlater refused to issue a refund orcancellation.A customer has attempted to returna product or cancel a service but youhave been unresponsive.You partially refunded a product butdid not disclose the reason why therefund was not paid in full.15codedescription from thecard net workreason codesBest Practices for ChargebackPrevention and ReductionConsumers expect credits to be delivered instantly.This is simple enough in POS transactions as youcan issue the refund using their physical card, but forCNP transactions it’s import to issue the credit assoon as possible to prevent customers from disputingthe original payment. Make sure credits are properlyissued to the same card that was used for the originalpurchase and send the cardholder a notice that thecredit may appear on their next billing statement orthe one after that, informing them that it can take 5-10business days to post a credit.If merchandise is returned to you, send the customera notice informing them that you have received itand the credit has been issued. Similarly, if a productis returned or services have been cancelled usingan automated system, issue the credit and send thecustomer a notice informing them that the cancellationrequest has been received and the credit has beenissued. Always include the original transaction andrefund transaction date, amount and ID’s in the refundnotification so they can refer to them if needed.
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue5. Transaction Not Recognizednet workchargeback reasoncodedescription from thecard net workCancelled Recurring41The merchant was notified to cancel the recurringtransaction or that the cardholder’s account wasclosed but has since billed the customerCancelled Recurring4841The cardholder notified the merchant to cancel therecurring transaction and the merchant continued tobill the cardholderCancelled RecurringC28Card Member continues to be billed after he/sheclaims to have cancelled goods or servicesCancelled RecurringAPCardholder challenges the validity of RecurringPayments Card Sales after expiration or cancellationof the Recurring Payments Plan agreementAs with Fraud – Card Not Present, this chargebackreason is categorized by the card networks as afraudulent transaction. These reason codes arefrequently a result of businesses having a bank accountunder a different name than their Doing Business As(DBA) name. This causes the charge appearing on acustomer’s credit card statement to be unfamiliarto them. If your brand does not match the nameassociated with your business account, make a pointof informing your customers when they place theorder, telling them what to look for on their credit cardstatement.Best Practices for ChargebackPrevention and ReductionUnusually, Mastercard’s description of theirTransaction Not Recognized reason code, 4863,specifically mentions that the card issuer should makea “good faith effort to identify the transaction for thecardholder”.For businesses selling digital goods, protect yourselffrom fraud – and friendly fraud – by gathering thedata to prove that all software sold was successfullyreceived and downloaded by the cardholder, along withtheir IP address, GEO Location, Device ID and accounthistory/usage information.page16reason codesTransaction Not Recognized, one of the mostcommon chargeback reasons, is also one of the mostavoidable. It’s crucial that your DBA name is properlyidentified in the clearing record to ensure that thename appearing on the cardholder’s billing statementis correct and recognizable. Work with your acquirerto ensure that your location and phone number alsoappear on your customers’ credit card statements incase they have any questions about the charge.
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue6. Not as Described or DefectiveMerchandisenet workchargeback reasoncodedescription from thecard net work Merchandise or services did not match what wasdescribed on the transaction receipt or otherdocumentation presented at the time of purchase Not the same as the merchant’s verbal description(for a telephone transaction)Not as Described orDefective Merchandise The merchandise was received damaged ordefective53 The cardholder disputes the quality of themerchandise or services The merchandise was identified as counterfeit bythe owner of the intellectual property or authorizedrepresentative, a custom’s agency, law enforcementagency, other governmental agency or neutral bonafide expert- The cardholder claims that the terms of the salewere misrepresented by the merchantDefective / Not as Described4853 When delivered from the merchant, the goodsarrived broken or could not be used for theintended purpose- Goods and services did not conform to theirdescriptionGood / Services Not asDescribedC31 Card Member claims to have received goods and/or services that are different than the writtendescription provided at the time of the Charge- Cardholder claims that the quality of goods orservices received from the Merchant were not asexpected or advertisedCardholder Disputes Qualityof Goods or ServicesRM- Cardholder claims that goods received weredamaged or defective, and the Cardholder returnedthe goods to the Merchant- Cardholder claims that goods or services were notas represented by the Merchant- Cardholder refused delivery of goods or servicesbecause the quality of the goods or services wasinsufficient, however the Merchant submitted aCard Sale to the Account- Cardholder claims that the Merchant deliveredCounterfeit Merchandisepage17reason codes
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenue6. Not as Described or Defective Merchandise(continued)A common chargeback reason in the online retailmarket, the ability to dispute the quality of goods orservices protects customers from retailers who sellmislabelled, damaged or counterfeit merchandiseor who fail to fulfill a service as promised. Thisincludes cases in which the product was damagedduring shipping, the incorrect item was delivered,or the merchandise was identified by the creator,a government agency, or an expert in the field ascounterfeit.Though not categorized as fraud by the cardnetworks, this reason is frequently used by friendlyfraudsters. The reason for this is that merchants willtypically require a customer to prove that the productis defective or not as described and/or return theproduct in order to be awarded the refund; the issuingbank, on the other hand, will take the cardholder attheir word and issue the chargeback, rarely requiringproof of any kind.page18reason codesBest Practices for ChargebackPrevention and ReductionEcommerce comes with unique challenges causedby the fact that your customers can’t physically touchyour products before they pay for them. It’s criticalthat descriptions of your products as shown online, incatalogues, on transaction receipt and over the phoneare accurate, complete, and in no way misleading.If providing a service that you are for any reasonunable to fulfill as promised, contact the customerto renegotiate the terms or to offer a full or partialrefund.Solicit feedback from your customers to gaugehow well your products met their expectations toensure that your descriptions match the perceptionof real customers. High quality content – written,photography and video – will go a long way, as willincluding customer reviews on your website. It’salso important to regularly review your shipping andhandling processes to ensure that orders are beingfulfilled accurately and securely.
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueThe EncyclopediaCategories [D1]– Chargeback reason codes can, for the most part, be divided into fourunofficial categories: Fraud, Authorization, Processing Errors, and Consumer Disputes.The industry is gradually moving toward this universal four-category standard, with Visaleading the way – as of April 2018, Visa will transition to a new, simplified set of reasoncodes which will officially organize disputes into the four categories below:Fraud refers to any reason codes likelyFraudto be related to fraudulent transactions,including POS and CNP transactions. This category is used when thecardholder claims they did not authorize a transaction or do not recognize a transactionbut the transaction was authorized by somebody – presumably a fraudster who hasacquired the cardholder’s personal information. In reality, most of the chargebacks that fallunder this category are cases of friendly fraud, meaning the cardholder did authorize thetransaction but is lying about it or has forgotten.AuthorizationAuthorization chargebacks reflect instances where authorizationwas not obtained for the transaction. For example, if a merchant has your card informationon file and charges your card by mistake when another customer places an order, or if theycharge you for an amount exceeding the amount you had agreed to pay.Processing ErrorsProcessing Errors refers to chargebacks caused by a mistake in the transaction. This caninclude duplicate transactions, incorrect charge amount, a credit processed as a charge orvice versa, and other similar situations.Consumer DisputesConsumer Disputesinclude any chargebacks related to the fulfillment of the product andservice by the merchant. This includes the product not being delivered in full (or at all),disputes about the quality of the product, cancelled recurring billing and credit notprocessed disputes.[D1] Updated to clarify that the categories we’re using are unofficial and to referenceVisa’s upcoming update to their reason codes.page19reason codes
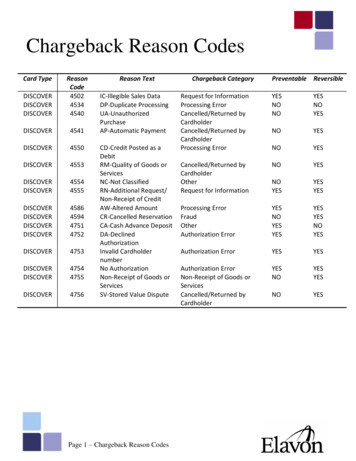
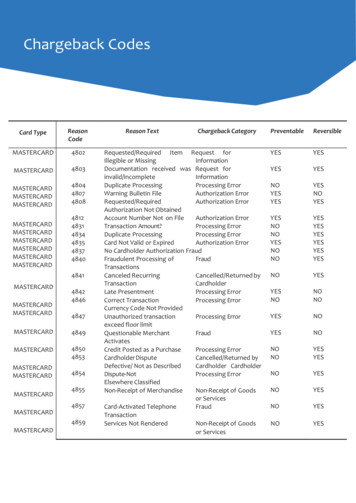
recoverlostr e c o v eyourr yo ur l orevenuest revenueList of Reason Codes Ctd.VISA (before April 2018)codepagedescriptioncategory81Fraud – Card-Absent Present EnvironmentFraud83Fraud – Card-Absent EnvironmentFraud57Fraudulent Multiple TransactionsFraud62Counterfeit TransactionFraud93Visa Fraud Monitoring ProgramFraud72No AuthorizationAuthorization70Card Recovery Bulletin or Exception FileAuthorization71Declined AuthorizationAuthorization73Expired CardAuthorization78Service Code ViolationAuthorization82Duplicate ProcessingProcessing Errors76Incorrect Currency or Transaction CodeProcessing Errors74L
page 6 reason codes Chargeback Causes by Industry In the chart below, we have identified the top three most frequently occurring chargeback reason codes for 14 different industries based on our data. These percentages are averaged across the four major card networks - Visa, Mastercard, American Express and Discover.