Transcription
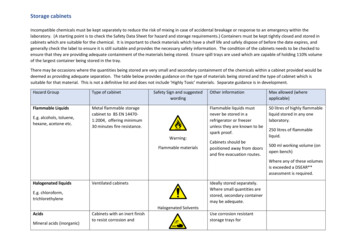
Storage cabinetsIncompatible chemicals must be kept separately to reduce the risk of mixing in case of accidental breakage or response to an emergency within thelaboratory. (A starting point is to check the Safety Data Sheet for hazard and storage requirements.) Containers must be kept tightly closed and stored incabinets which are suitable for the chemical. It is important to check materials which have a shelf life and safely dispose of before the date expires, andgenerally check the label to ensure it is still suitable and provides the necessary safety information. The condition of the cabinets needs to be checked toensure that they are providing adequate containment of the materials being stored. Ensure spill trays are used which are capable of holding 110% volumeof the largest container being stored in the tray.There may be occasions where the quantities being stored are very small and secondary containment of the chemicals within a cabinet provided would bedeemed as providing adequate separation. The table below provides guidance on the type of materials being stored and the type of cabinet which issuitable for that material. This is not a definitive list and does not include ‘Highly Toxic’ materials. Separate guidance is in development.Hazard GroupType of cabinetFlammable LiquidsMetal flammable storagecabinet to BS EN 144701:2004, offering minimum30 minutes fire resistance.E.g. alcohols, toluene,hexane, acetone etc.Safety Sign and suggestedwordingWarning:Flammable materialsOther informationMax allowed (whereapplicable)Flammable liquids mustnever be stored in arefrigerator or freezerunless they are known to bespark proof.50 litres of highly flammableliquid stored in any onelaboratory.Cabinets should bepositioned away from doorsand fire evacuation routes.250 litres of flammableliquid.500 ml working volume (onopen bench)Where any of these volumesis exceeded a DSEAR**assessment is required.Halogenated liquidsVentilated cabinetsIdeally stored separately.Where small quantities arestored, secondary containermay be adequate.E.g. chloroform,trichlorethyleneHalogenated SolventsAcidsMineral acids (inorganic)Cabinets with an inert finishto resist corrosion andUse corrosion resistantstorage trays for
Hazard GroupType of cabinetEg Hydrochloric acid,Phosphoric acid, Sulphuricacidvented where possible toremove fumesSafety Sign and suggestedwordingCorrosive SubstanceAcidEg acetic acid, formic acidSame type cabinets as acidstorageAlkali / BaseEg Permanganates,perchlorates, fuming nitricacidcontainment of leaks, dripsetc.Do not store acids aboveeye level.Corrosive SubstanceOxidisersMax allowed (whereapplicable)Separate storage fororganic and inorganic acids.Organic acidsAlkalis (bases)Other informationMetal cabinet.Where space is limited andquantities are small, can bestored in the acid cabinet,must be on separate shelf orsecondary containers used.Must not be stored withflammable solvents orreducing agents.Oxidising Agentse. Metal hydrides, boranes,silanes, hydrazine etc.** DSEAR – Dangerous Substances and Explosive Atmospheres regulationsAdditional guidance on chemical reactivity - Brethericks; NIOSH pocket guidesNBMaterials which are subject to licence requirements for purchase, storage or use will be stored in accordance with the requirements of that licence,eg explosive materials.
Some common lab/workshop chemicals.ChemicalIncompatible with:ChemicalIncompatible with:Acetic acidChromic acid, nitric acid, hydroxyl compounds,ethylene glycol, perchloric acid, peroxides,permanganatesBromineSee ChlorineAcetyleneChlorine, bromine, copper, fluorine, silver,mercuryCalcium oxideWaterAcetoneConcentrated nitric acid and sulphuric acidmixturesCarbon (activated)Calcium hypochlorite, all oxidizing agentsAlkali and alkaline earthmetalsWater, carbon tetrachloride or otherchlorinated hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide,halogensChloratesAmmonium salts, acids, powered metals, sulphur, finelydivided organic or combustible materialsAmmonia (anhydrous)Mercury(e.g., in manometers), chlorine,calcium hypochlorite, iodine, bromine,hydrofluoric acid (anhydrous)Chromic acid andchromium trioxideAcetic acid, naphthalene, camphor, glycerol. Alcohol,flammable liquids in generalAmmonium nitrateAcids, powered metals, flammable liquids,chlorates, nitrites, sulphur, finely dividedorganic combustible materialsChlorineAmmonia, acetylene, butadiene, butane, methane, propane(or other petroleum gases), hydrogen, sodium carbide,benzene, finely divided metals, turpentineAnilineNitric acid, hydrogen peroxideChlorine dioxideAmmonia, methane, phosphine, hydrogen sulphideArsenical materialsAny reducing agent (e.g. boranes, metalhydrides, hydrazine, silanes etc.)CopperAcetylene, hydrogen peroxideAzidesAcidsCumene hydroperoxideAcids (organic and inorganic)
Some common lab/workshop chemicals.ChemicalIncompatible with:ChemicalIncompatible with:CyanidesacidsNitratesAcidsFlammable liquidsAmmonium nitrate, chromic acid, hydrogenperoxide, nitric acid, sodium peroxide,halogensNitric acid(concentrated)Acetic acid, aniline, chromic acid, hydrocyanic acid,hydrogen sulphide, flammable liquids and gases, copper,brass, any heavy metalsFluorineAll other chemicalsNitritesAcidsHydrocarbons (such asbutane, propane,benzene)Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, chromic acid,sodium peroxideNitroparaffinsInorganic bases, aminesHydrocyanic acidNitric acid, alkaliOxalic acidSilver, mercuryHydrofluoric acid(anhydrous)Ammonia (aqueous or anhydrous)OxygenOils, grease, hydrogen, flammable liquids, solids, and gasesHydrogen sulphideFuming nitric acid, oxidizing gasesPerchloric acidAcetic acid, anhydride, bismuth and its alloys, alcohols,paper, wood, grease, oilsHypochloritesAcids, activated carbonPeroxides, organicAcids (organic or mineral), avoid friction, store coldIodineAcetylene, ammonia (aqueous or anhydrous),hydrogenPhosphorus (white)Air, oxygen, alkalies, reducing agentsMercuryAcetylene, fulminic acid, ammoniaPotassium chlorateSulphuric and other acids
Some common lab/workshop chemicals.ChemicalIncompatible with:ChemicalIncompatible with:Potassium perchlorate(see also chlorates)Sulphuric and other acidsSodium nitriteAmmonium nitrate and other ammonium saltsPotassium permanganateGlycerol, ethylene glycol, benzaldehyde,sulphuric acidSodium peroxideEthyl and methyl alcohol, glacial acetic acid, aceticanhydride, benzaldehyde, carbon disulfide, glycerin,ethylene glycol, ethyl acetate, methyl acetate, furfuralSelenidesReducing agentsSulphidesAcidsSilverAcetylene, oxalic acid, tartaric acid, ammoniumcompounds, fulminic acidSulphuric acidPotassium chlorate, potassium perchlorate, potassiumpermanganate (similar compounds of light metal, such assodium, lithium)SodiumCarbon tetrachloride, carbon dioxide, waterTelluridesReducing agents
Flammable Liquids E.g. alcohols, toluene, hexane, acetone etc. Metal flammable storage cabinet to BS EN 14470 - 1:2004, offering minimum 30 minutes fire resistance. Warning: Flammable materials Flammable liquids must never be stored in a refrigerator or freezer unless they are known to be spark proof. Cabinets should be positioned away from doors