Transcription
SWEN 256 – Software Process & Project Management
What is quality?
A definition of quality should emphasize three importantpoints:1. Software requirements are the foundation from whichquality is measured. Lack of conformance to requirement islack of quality.2. Specified standards define a set of development criteriathat guide the manner in which software is engineered. Ifthe criteria are not followed, lack of quality will almostsurely result.3. There is a set of implicit requirements that often goesunmentioned (e.g. good maintainability). If softwareconforms to its explicit requirements but fails to meetimplicit requirements, software quality is suspect.[DACS]
The purpose of software testing is to assess and evaluatethe quality of work performed at each step of the softwaredevelopment process.Although it sometimes seems that way, the purpose oftesting is NOT to use up all the remaining budget orschedule resources at the end of a development effort.The goal of testing is to ensure that the software performsas intended, and to improve software quality, reliability andmaintainability.Software testing is a full-life-cycle assessment of quality[DACS]
A good development process, tools, methods, and peoplego far in providing quality products Testing is one aspect of assuring software qualityo It is a measure of quality, it does not deliver quality “Quality cannot be tested into a product” Software Quality Assurance includeso Software engineering process improvement Prevent the insertion of defectso Fault tolerant software design Tolerate the existence of defectso All aspects of software verification and validation Including testing
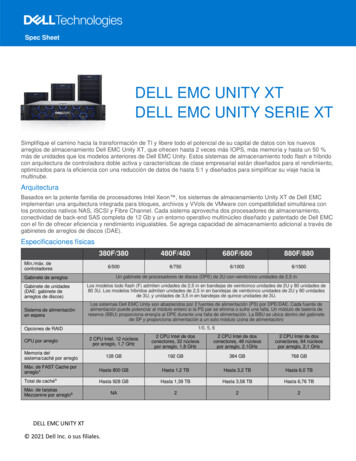
Failures are usually a result of system errors (which turninto defects) that are derived from faults in the systemHowever, faults do not necessarily result in system failureso The faulty system state may be transient and ‘corrected’ beforean error arisesErrors do not necessarily lead to system failuresooThe error can be corrected by built-in error detection and recoveryThe failure can be protected against by built-in protectionfacilities For example, protect system resources from system errors[Sommerville]
Defect preventionand reductionHuman(developer)ErrorFault detectionand containmentSoftwareDefect(bug)Build timeSystemFaultLatent(dormant)defectRun timeSystemFailure
Assuring that a software system meets a user's needs
Verification:o “Are we building the product right?”o The software should conform to its design Validation:o “Are we building the right product?” Validate requirementso “Did we build the right product?” Validate implementationo The software should do what the user really requires V&V:Build the right product and build it right![Sommerville]
V&Vis a whole life-cycle processo V & V must be applied at each stage in the softwareprocess V&Vhas two principal objectiveso The discovery of defects in a systemo The assessment of whether or not the system is usablein an operational situation[Sommerville]
Softwaretesting:o Concerned with exercising and observing productbehavioro Dynamic V&V Softwareinspections:o Concerned with studying software product artifacts todiscover defectso Static V&Vo May be supplemented by tool-based (semi-automated)document and code analysis
Dependson:o System’s purpose Criticality of software function Mission critical (organization depends on it) Safety critical Societal impacto User expectationso Marketing environment Cost-benefittrade-offso High confidence is expensive. Is it necessary?
Ateach stage of the software developmentprocess, there are activities that should be donewhich will help develop the testing plans and testcases Remember: V&V is expensive.o Plan to do it right the first time!
Plan and develop tests throughout the life cycleImplement tests when there is an implementation ready to testIterative and incremental: Repeat “V” at each models-testing-315
Quality as a System and a Process
Quality assurance (QA) activities strive to ensure: Few, if any, defects remain in the software system when it isdelivered Remaining defects will cause minimal disruptions ordamages
The following need to be considered: Scope, Stakeholders,Risks, Internal and External Environmental Factors, ProcessProject-specific standards and procedures are createdooooooBased on quality standards for each deliverableIncludes how PM activities themselves should be donePlans/Project must comply with external standards (CISG,ISO 9000, OSHA, etc)Plans/Project must comply with organizational standardsPlans/Project must meet the customer’s quality standardsTracking / Proof may be needed (metrics, measurements,etc.)
Defect Preventiono Remove (human) error sourceso Block defects from being injected into software artifacts Defect Reductiono Detect defects Inspection Testingo Remove defects Debugging—iterate on the software engineering activity Rework requirements, design, code, etc. Defect Containmento Fault toleranceo Fault containment
Remove the root causes of errors Education and training address human misconceptions thatcause errorso Domain and product knowledgeo Software engineering processo Technology knowledge Formal methods can help identify and correct imprecisespecifications, designs and implementationsStandards conformance, use of best practices and patternscan help prevent fault injection
Discover and remove defectsInspection: direct fault detectiono requirements, design, code, manuals, test cases Testing: failure observation and fault isolationo Execute the software and observe failureso Use execution history/records to analyze and locate fault(s) anddefect(s) causing the failure
Need implemented software to execute Need software instrumentation, execution history to:o isolate faultso trace to defects Impossible to test everythingo - Expensive to test most things Risk of too much and not enough testingo- Use project risks to guide investment
QuantityNumber ofmissed defectsCost oftestingAmount ofTestingUnder-testingOptimalAmount ofTestingOver-testing
Denotes a potential negative impact that may arise fromsome present process or from some future event. What is your risk exposure to a defect that is hidden?o Likelihood of defect existenceo Likelihood of failure occurrenceo Impact if failure occurs Risk exposure determines .o Testing priorityo Testing deptho What to test and not to test
Software fault toleranceo Safety-critical or mission-critical software often must be faulttolerant The system can continue in operation in spite of a fault occurrenceo Techniques: exception handling, recovery blocks Software failure containmento Fault detection and isolationo Techniques: safety interlocks, physical containment (barriers), disaster planning, etc.
Input to ge Scenariosand 3e4e5x2f4e6ErrorRemovalLegendapresence of “a”FaultRemovalaremoval of “a”FailurePreventionab“a” causes “b”defect barrier/remover
QA ensures software:o delivered with few defects,o remaining defects will cause minimal disruptions or damages QA techniques:o classified according to how when they handle defectso defect prevention,o reduction,o containment
Defect prevention: Remove the root cause of human errorsDefect reduction: Discover defectsuses inspectiono testingoDefect containment: Limit the impact of a faultuses fault toleranceo fault & failure containmento
[DACS] Data and Analysis Center for Software, SoftwareReliability Source Book, http://iac.dtic.mil/dacs[Patton] Ron Patton, Software Testing, Sams Publishing,2001.[Sommerville] Ian Sommerville, Software Engineering, 6thEdition, Addison-Wesley, 2001.[RUP] Rational Unified Process, IBM Rational Software(installed on lab machines)[Whittaker] “What Is Software Testing? And Why Is It SoHard?,” IEEE Software, January-February 2000, pp. 70-79.
A good development process, tools, methods, and people go far in providing quality products Testing is one aspect of assuring software quality o It is a measure of quality, it does not deliver quality "Quality cannot be tested into a product" Software Quality Assurance includes o Software engineering process improvement Prevent the insertion of defects