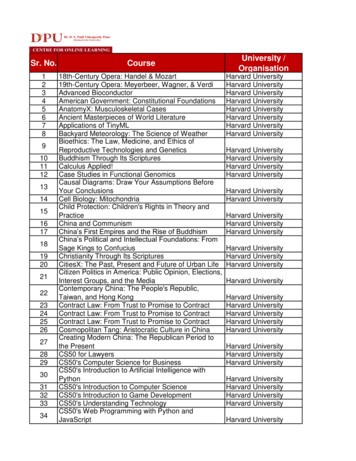
Transcription
Global Warming 20 Years Later:Tipping Points NearJim Hansen23 June 2008National Press Club, andHouse Select Committee onEnergy Independence & Global WarmingWashington, DC
1988 Testimony: Conclusions1. Earth is warmer in 1988 than at any time inthe history of instrumental measurements2. Global warming is now large enough thatwe can ascribe with a high degree ofconfidence a cause and effect relationshipto the greenhouse effect3. Greenhouse effect is already large enoughto effect the probability of extreme eventssuch as summer heat waves
Basis of Testimony19881. Basic Physics, Planetary & Paleo Studies2. Observed On-Going Climate Change3. Climate Models20081. Paleoclimate: History of Earth’s Climate2. Global Observations of Climate Processes3. Climate Models
Major Flaws in 1988 TestimonyDid Not Emphasize Warming vs Chaos- Weather Variations Climate Trend- Small Change of Mean Has Big EffectsDid Not Emphasize That Global WarmingEnhances Both Extremes of Water Cycle- More Intense Droughts, Heat Waves, Fires- Heavier Rainfall, Greater Floods, StrongerStorms Driven by Latent Heat (ThunderStorms, Tornados, Tropical Storms)
Global Warming Status1. Knowledge Gap Between- What is Understood (science)- What is Known (public)2. Planetary Emergency- Climate Inertia Æ Warming in Pipeline- Tipping Points Æ Could Lose Control3. Good News & Bad News- Safe Level of CO2 350 ppm- Multiple Benefits of Solution
United NationsFramework Convention on Climate ChangeAim is to stabilize greenhouse gas emissions “ at a level that would preventdangerous anthropogenic interferencewith the climate system.”
Metrics for “Dangerous” ChangeExtermination of Animal & Plant Species1. Extinction of Polar and Alpine Species2. Unsustainable Migration RatesIce Sheet Disintegration: Global Sea Level1. Long-Term Change from Paleoclimate Data2. Ice Sheet Response TimeRegional Climate Disruptions1. Increase of Extreme Events2. Shifting Zones/Freshwater Shortages
Target CO2: 350 ppmTo preserve creation, the planeton which civilization developed
Tipping Point Definitions1. Tipping Level- Climate forcing (greenhouse gas amount)reaches a point such that no additionalforcing is required for large climatechange and impacts2. Point of No Return- Climate system reaches a point withunstoppable irreversible climate impacts(irreversible on a practical time scale)Example: disintegration of large ice sheet
98765Extent (million sq km)4197819821986199019941998200220072006
Observations: Domingues, C.M. et al., Nature 453, 1090-1093, 2008.Model: Hansen, J. et al., Science 308, 1431-1435, 2005.
Arctic Sea Ice Criterion*1. Restore Planetary Energy BalanceÆ CO2: 385 ppm Æ 325-355 ppm2. Restore Sea Ice: Aim for -0.5 W/m2CO2: 385 ppm Æ 300-325 ppmRange based on uncertainty in present planetaryenergy imbalance (between 0.5 and 1 W/m2)*Assuming near-balance among non-CO2forcings
Greenland Total Melt Area –2007 value exceeds last maximum by 10%1998Total Melt AreaApril - OctoberArea Melted (km2)3.00E 072007200519982.50E 07198720072002199119952.00E 071.50E 07198319961.00E 07199619925.00E 061978198319881993199820032008YearKonrad Steffen and Russell Huff, CIRES, University of Colorado at Boulder
Surface Melt on GreenlandMelt descendinginto a moulin,a vertical shaftcarrying waterto ice sheet base.Source: Roger Braithwaite,University of Manchester (UK)
Jakobshavn Ice Stream in GreenlandDischarge from majorGreenland ice streamsis accelerating markedly.Source: Prof. Konrad Steffen,Univ. of Colorado
Greenland Mass Loss – From Gravity Satellite
Sea Level Criterion*1. Prior Interglacial PeriodsÆ CO2 300 ppm2. Cenozoic EraÆ CO2 300 ppm3. Ice Sheet ObservationsÆ CO2 385 ppm*Assuming near-balance among non-CO2forcings
Pier on Lake Mead.
Rongbuk GlacierRongbuk glacier in 1968 (top) and 2007. The largest glacieron Mount Everest’s northern slopes feeds Rongbuk River.
Ice Loss1973-1998Black bar: ice loss in 1973-1998. Curve:years until ice gone, at that loss rate.Paul, F. et al., Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L21402, 2004.
Stresses on Coral ReefsCoral Reef off Fiji (Photo: Kevin Roland)
Assessment of Target CO2PhenomenonTarget CO2 (ppm)1. Arctic Sea Ice300-3252. Ice Sheets/Sea Level300-3503. Shifting Climatic Zones300-3504. Alpine Water Supplies300-3505. Avoid Ocean Acidification300-350Æ Initial Target CO2 350* ppm*assumes CH4, O3, Black Soot decrease
The fraction of CO2 remaining in the air, after emission by fossil fuelburning, declines rapidly at first, but 1/3 remains in the air after a centuryand 1/5 after a millennium (Atmos. Chem. Phys. 7, 2287-2312, 2007).
Initial Target CO2: 350 ppmTechnically Feasible(but not if business-as-usual continues)Quick Coal Phase-Out Critical(long lifetime of atmospheric CO2)(must halt construction of any new coalplants that do not capture & store CO2)
“Free Will” Alternative1. Phase Out Coal CO2 Emissions- by 2025/2030 developed/developing countries2. Rising Carbon Price- discourages unconventional fossil fuels &extraction of every last drop of oil (Arctic, etc.)3. Soil & Biosphere CO2 Sequestration- improved farming & forestry practices4. Reduce non-CO2 Forcings- reduce CH4, O3, trace gases, black soot
Carbon Tax & 100% Dividend1. Tax Large & Growing (but get it in place!)- tap efficiency potential & life style choices2. Entire Tax Returned- equal monthly deposits in bank accounts3. Limited Government Role- keep hands off money!- eliminate fossil subsidies- let marketplace choose winners- change profit motivation of utilities- watch U.S. modernize & emissions fall!
Key Elements in TransformationLow-Loss Electric GridClean Energy by 2020 (West) & 2030Allows Renewable Energy AscendancyCarbon Tax and 100% DividendTax at First Sale of Coal/Oil/GasTax Can Rise & Spur Transformations“100% or Fight! No Alligator-Shoes!”
Basic ConflictFossil Fuel Special InterestsvsYoung People & Nature (Animals)Fossil Interests: God-given fact that allfossil fuels will be burned (no free will)Young People: Hey! Not so fast!Nice planet you are leaving us!
What are the Odds?Fossil Interests: have influence incapitals world-wideYoung People: need to organize, enlistothers (parents, e.g.), impact electionsAnimals: not much help (don’t vote, don’ttalk)
The ChallengeWe can avoid destroying creation!( cleaner planet, good jobs!)We have to figure out how to livewithout fossil fuels someday Why not now?
Web Sitewww.columbia.edu/ jeh1includesGlobal Warming Twenty Years Later:Tipping Points Near (today’s statement)Target Atmospheric CO2: Where ShouldHumanity Aim?
Earth’s history provides most important information on global warming.Recorded human history occurs within the Holocene warm period.
Cenozoic Era65 Million Years AgoGlobal Climate ForcingsExternal (solar irradiance): 1 W/m2Surface (continent locations): 1 W/m2Atmosphere (CO2 changes): 10 W/m2Present Day
Summary: Cenozoic Era1. Dominant Forcing: Natural ΔCO2- Rate 100 ppm/My (0.0001 ppm/year)- Human-made rate today: 2 ppm/yearHumans Overwhelm Slow Geologic Changes2. Climate Sensitivity High- Antarctic ice forms if CO2 450 ppm- Ice sheet formation reversibleHumans Could Produce “A Different Planet”
Tipping Point Definitions 1. Tipping Level - Climate forcing (greenhouse gas amount) reaches a point such that no additional forcing is required for large climate change and impacts 2. Point of No Return - Climate system reaches a point with unstoppable irreversible climate impacts (irreversible on a practical time scale)