Transcription
Freon 407C and 407ARefrigerants (R-407C and R-407A)Properties, Uses,Storage, andHandling
Freon RefrigerantsTable of ContentsIntroduction.4Air Monitors and Leak Detection . 16Freon 407C and Freon 407A RefrigerantDescriptions. 4Types of Detectors.16Uses .4Halogen-Selective Detectors.16Physical Properties .4Compound-Specific Detectors.16Nonselective Detectors.16Fluorescent Additives.16Chemical/Thermal Stability . 10Storage and Handling . 17Stability with Metals .10Shipping Containers in the United States.17Thermal Decomposition.11Bulk Storage Systems.17Compatibility Concerns If HCFC-22 and Freon Refrigerants Are Mixed.11Converting Bulk Storage Tanks from HCFC-22 toFreon 407C or Freon 407A.18Materials Compatibility . 11Material Compatibility Concerns.18Elastomers.11Handling Precautions for Freon 407Cand Freon 407A Shipping Containers.19Plastics.11Desiccants.12Recovery, Recycle, Reclamation, and Disposal . 19Refrigeration Lubricants . 12Recovery.19Safety . 14Recycle.19Inhalation Toxicity.14Reclamation.20Cardiac Sensitization.14Disposal.20Skin and Eye Contact.14Spills or Leaks.15Nonflammability.15Combustibility of Freon 407C and Freon 407A.153
Freon RefrigerantsIntroductionFreon 407C and Freon 407A Refrigerant DescriptionsBackgroundFreon 407C and Freon 407A are non-ozone depletingblends of three hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerants.Chlorodifluoromethane (R-22 or HCFC-22) has been usedFreon 407C exhibits performance characteristics similaras a refrigerant in various refrigeration, industrial cooling,to R-22.air conditioning, and heating applications for over fivedecades. The low ozone depletion potential of R-22The compositions of Freon 407C and Freon 407A arecompared to CFC-11 (chlorofluorocarbon 11) and CFC-12as follows:and its excellent refrigerant properties have helpedfacilitate the transition away from CFCs. However, R-22HFC-32HFC-125HFC-134awill be phased out in the first quarter of the 21st century.Freon 407C (R-407C), wt%232552In preparation for this phaseout, Chemours offers Freon Freon 407A (R-407A), wt%204040407C and Freon 407A, environmentally acceptablealternatives to R-22. Additionally, R-407A offers similarBecause Freon 407C and Freon 407A are mixtures ofperformance to R-404A in new medium and lowHFCs, they have zero ozone depletion potential.temperature refrigeration systems.Table 1 lists the chemical names and formulae of thecomponents that make up Freon 407C and Freon 407A.Table 1. Components of Freon 407C and Freon 407A: HFC-32/HFC-125/HFC-134aComponentChemical NameFormulaCAS NumberMolecular al PropertiesFreon 407C refrigerant performs similarly to HCFC-22General physical properties for Freon 407C andunder evaporator temperatures ranging from –7 to 10 CFreon 407A are shown in Table 3. The pressure-enthalpy(20 to 50 F). It is designed for use in new equipment anddiagrams for Freon 407C are shown in Figures 1 and 2.as a service refrigerant for existing HCFC-22 airAdditional physical property data may be found in otherconditioning, heat pump, and medium temperaturerefrigeration equipment.Chemours publications. Thermodynamic propertiesFreon 407A is intended for use in new medium and lowin both English and metric units. Transport propertiestemperature refrigeration systems that have traditionallybooklets are available for Freon 407A in both English andused R-404A. R407A has a global warming potential aboutmetric unitsbooklets are also available for Freon 407C and Freon 407A50% lower than R-404ATables 2a and 2b show theoretical performance of Freon 407C, Freon 407A, and HCFC-22. Freon 407C exhibitssimilar performance to HCFC-22 at air conditioningconditions, while Freon 407A exhibits similar performanceto R-404A with lower capacity at low and mediumtemperature refrigeration conditions.4
Freon RefrigerantsTable 2a. Theoretical Cycle PerformanceHCFC-22Freon 407C (R-407C)1.001.00Refrigeration Capacity (HCFC-22 1.0)Coefficient of Performance6.436.27Compression Ratio2.662.83Compressor Discharge Temperature, C ( F)77.3 (171.2)75.1 (167.1)Compressor Discharge Pressure, kPa abs (psia)1662 (241.0)1763 (255.6)0 (0)4.9 (8.9)Temperature Glide, C ( F)Conditions: 43.3 C (110 F) condenser/7.2 C (45 F) evaporator/2.8 C (5 F) of subcooling/8.3 C (15 F) of superheatTable 2b. Theoretical Cycle PerformanceMedium TemperatureLow TemperatureR-404AR-407AR-404AR-407ARelative Capacity (R-404A 1.00)1.000.891.000.86Coefficient of Performance2.62.41.41.5Compression Ratio4.45.810.514.5Compressor Discharge Temperature, C ( F)Compressor Discharge Pressure, kPA abs (psia)68 (154)91 (196)78 (172)104 (219)2034 (295)2096 (304)2034 (295)2096 (304) 2.2 (4) 4.4 (8) 2.2 (4) 4.4 (8)Temperature Glide , C ( F)LT conditions: -28.9 C (-20 F) evap, 43.3 C (110 F) cond, 5.5 C (10 F) SH and SCMT conditions: -6.7 C (20 F) evap, 43.3 C (110 F) cond, 5.5 C (10 F) SH and SCTable 3. General Property Information of Freon 407C, Freon 407A, and HCFC-22Physical PropertyUnitFreon 407C (R-407C)Freon 407A (R-407A)HCFC-22Molecular Weight, avg.g/mol86.2090.1186.47kPa abs (psia)1174.1 (170.29)1253.1 (181.74)1043.1 (151.40)Boiling Point (1 atm) C ( F)–43.56 (–46.40)-45.01 (-49.01)–40.80 (–41.40)Critical Temperature C ( F)86.74 (188.13)82.26 (180.06)96.24 (205.24)Vapor Pressure at 25 C (77 F)Critical PressurekPa abs (psia)4619.10 (669.95)4515.2 (654.9)4980.71 (722.39)Critical Densitykg/m3 (lb/ft3)527.30 (32.92)498.86 (31.14)524.21 (32.73)Liquid Density at 25 C (77 F)kg/m (lb/ft )1134.0 (70.80)1145.1 (71.49)1194.68 (74.53)Density, Saturated Vapor at 25 C (77 F)33kg/m (lb/ft )41.98 (2.62)49.75 (3.11)44.21 (2.76)Specific Heat, Liquid at 25 C (77 F)kJ/kg·K (Btu/lb· F)1.54 (0.367)1.52 (0.363)1.24 (0.296)Specific Heat, Vapor at 25 C (77 F) (1 atm)33kJ/kg·K (Btu/lb· F)0.830 (0.198)0.829 (0.198)0.685 (0.157)Vapor Pressure of Saturated Liquid at 25 C (77 F)kPa abs (psia)1173.4 (170.3)1253.1 (181.74)1043.1 (151.4)Heat of Vaporization at Normal Boiling PointkJ/kg (Btu/lb)245.1 (105.4)235.6 (101.34)233.5 (100.4)W/m·K (Btu/hr·ft· F)W/m·K (Btu/hr·ft· F)0.0819 (0.0455)0.01314 (0.00758)0.0795 (0.0460)0.01368 (0.00791)0.0849 (0.0458)0.01074 (0.00621)Pa·sPa·s1.60 x 10–41.23 x 10–51.51 x 10–41.25 x 10–51.59 x 10–41.30 x 10–5Thermal Conductivity at 25 C (77 F)LiquidVapor (1 atm)Viscosity at 25 C (77 F)LiquidVapor (1 atm)Flammability Limit in Air (1 atm)Ozone Depletion PotentialGlobal Warming Potential (AR4)TSCA Inventory StatusInhalation Exposure Limit*vol%NoneNoneNoneCFC-11 1.0000.05CO2 1.0 (100-yr ITH)177421071810IncludedYesYesYesppm (8- and 12-hr TWA)100010001000*The exposure limit is calculated based on the Chemours Acceptable Exposure Limit (AEL) for each component of the refrigerant blend. AEL is an airborne exposure limit established byChemours that specifies time-weighted average (TWA) concentrations to which nearly all workers may be repeatedly exposed without adverse effects during an 8- or 12-hr workday anda 40-hr work week.5
Freon RefrigerantsFigure 1. Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram for Freon 407C (SI Units)6
Freon RefrigerantsFigure 2. Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram for Freon 407C (ENG Units)7
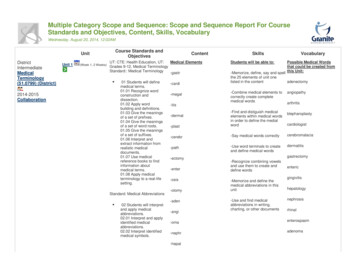
8Pressure 2864310-1000.00065100100-90-80-70Temperature -60oC150sa turatevolume 0.00070 m3/kg-40-30-20-10-60200-70u id0.000 80010-20400 oC10300-10Temperature 0-30250-4030060C20o7001140506001200. 0400014400te d v apo r3 0. 0c.p.0100.70350300. 00. 0350Enthalpy (kJ/kg)50200 .0 0 0 9500 .0 0 1 030015)0 1 6 0 .0 0 14500 .0450805503.02.01.00.40.30.20.10.050.060.070.080 .040 .030 .020 .0150 .0060 .0080 .003.00 40 .005500.53m /kgv o lu m e 0.60.70.8205000 .00901001101201301405005250g .K2002J /(k150-500. 10. 2dliq0. 30. 4qua l i ty 0 . 50. 61.400. 70. 80. 9s a tu ray .0 0k00502. 951.001.051.101.151.201.251.301.351.451.501.551 .6 01 .6 51 .7 01 .7 51 .801 .851 .901 5.9entro p2. 052. 12-20-1001020304050Temperature 60 o C7080. 152. 22. 252. 32. 42. e (Bar)Figure 3. Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram for Freon 407A (SI Units)Freon Refrigerants
001000000.01-200.020.01200.0320Temperature 20o200.04F0.05400.06v o lum e 0 .01 3 ft3/lb600.0740sa tura te0. 2dliq800. 01 4u id1001200 .0 1 5602040Temperature 601400. 018016060.017F12080o1000. 0180180.0140a li ty 0 . 7190. 02001600 .820100c.p.1000 .980Enthalpy (BTU/lb)0.30. 40 .6qu602200.03vap o r0.12004120240100120040. 2260.051400. 0o0.014080. 090. 000. 12807mv o lu300e 0 .41 .01600 .9 00 .8 03202601600 .7 024030 .6 00 .5 0b0 ft /l0 .3 00.202201401802006160/(l b - oF)90400.10.080.090.100. 110 .1 20.130. 140. 50. 150 .1 60 .1 70 .1 80 .1 90 .2 00 .2 10 .2 2sa tu ra ted0. 2350. 2e n trpy 0.26BTU0. 270. 280. 20. e 4. Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram for Freon 407A (ENG Units)Freon Refrigerants
Freon RefrigerantsChemical/Thermal Stabilityand visual ratings were obtained on both the liquid solutionsand the metal coupons after the designated exposure time.Stability with MetalsThe stability ratings range from 0 to 5, with 0 being theStability tests for refrigerants with metals are typicallybest and 5 being the worst. Visual ratings indicate how theperformed in the presence of refrigeration lubricants. This testmetal or refrigerant or lubricant/refrigerant solutionis run in sealed glass tubes at temperatures much higher thanappeared to a visual inspection. A rating of “0” indicates nothose encountered in refrigeration and air conditioningperceptible change in appearance. Any perceptible changesystems and is therefore referred to as an accelerated agingof color, clarity, or surface finish changes the rating to “1.”test. Results of sealed tube stability tests for HCFC-22/Mixtures of CFC refrigerants and conventional mineral oilsmineral oil and alkylbenzene lubricants have shown long-termgenerally get a rating of “3,” which is the limit ofstability in contact with copper, steel, and aluminum. And theacceptability. The new refrigerants and lubricants mustfact that HCFC-22/mineral oil and alkylbenzene systems haveoutperform those being replaced in order to be consideredbeen performing in the field in air conditioner and refrigerationacceptable.systems for the last 50 years verifies the results from thesestability tests. Polyol ester lubricants (POEs) are among theAfter the visual ratings were obtained, sample tubes wereproposed lubricants for use with Freon 407C and Freon opened, and the lubricant and refrigerant were analyzed.407A. Therefore, stability tests of Freon 407C with POEsThe lubricant was typically checked for halide content andand metals were performed. Freon 407A contains slightlybreakdown products, while the refrigerant was examined fordifferent concentrations of the same components as Freon the presence of decomposition products. Table 4407C, so the stability test results for Freon 407C can alsosummarizes the data from these sealed tube stability testsbe used for Freon 407A.for Freon 407C and various commercial POE lubricants.Stability and visual ratings are listed for the neatThe test method followed was generally the same asrefrigerant, the lubr
temperature refrigeration systems that have traditionally used R-404A. R407A has a global warming potential about 50% lower than R-404A Tables 2a and 2b show theoretical performance of Freon 407C, Freon 407A, and HCFC-22. Freon 407C exhibits similar performance to HCFC-22 at air conditioning conditions, while Freon 407A exhibits similar performance to R-404A with lower capacity at .