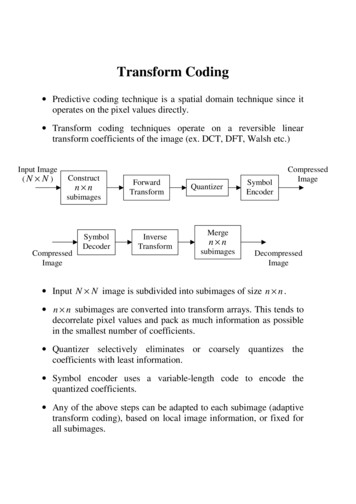
Transcription
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)ISSN: 2278-0181Vol. 3 Issue 2, February - 2014Transform Domain Technique in ImageSteganography for Hiding Secret InformationManibharathi. N1Krishnaprasad. S2Famila. S3(PG Scholar)Dr.Pauls Engg. CollegeVillupuram Dist, Tamilnadu, India605109(PG Scholar)Dr.Pauls Engg. CollegeVillupuram Dist, Tamilnadu, India605109(Asst. Professor)Dr.Pauls Engg. CollegeVillupuram Dist, Tamilnadu, India605109Abstract--Steganography is an important research field in manykeeping secret data protected from corruption andunauthorized access. The focus behind data security is toensure privacy while protecting personal or corporateinformation [4]. Privacy, on the other hand, is the ability of anindividual or group to seclude them or information aboutthemselves and thereby reveal them selectively.Data privacy or information privacy is the relationshipbetween collection and dissemination of data, technology, thepublic expectation of privacy, and the legal issues. Dataprivacy issues can arise from a wide range of sources such ashealthcare records, criminal justice investigations andproceedings, financial institutions and transactions, biologicaltraits, residence and geographic records. Data security or dataprivacy has become increasingly important as more and moresystems are connected to the Internet. There are informationprivacy laws that cover the protection of data or informationon private individuals from intentional or unintentionaldisclosure or misuse. Thus, hiding the data in a kind of formsuch as within an image is vital in order to make sure thatsecurity or privacy of the important data is protected.The main Objective of this project is Transferring theEmbedded information to the destination without beingdetected by the un-authorized user or any other system andusing the Transform domain technique (DWT) with Huffmancoding to improve the secrecy.An image is essentially a 2-D signal processed by humanvisual system. The signals are representing in analog form.The signals are representing in analog form. However, incomputer applications the analog signal converted into digitalform for processing, storage and transmission. A digital imageis a 2-D dimensional array of pixels [2]. Image processingplays an important role in society today because a picturegives a much clearer impression of a situation or an object.The objective of image processing includes: Improving theappearance of the visual data (Image enhancement, imagerestoration), extracting useful information (Image analysis,IJERTapplications. Image steganography is the technique used tohiding secret information into a cover image. This paper presentsa new approach for Image steganography based on DWT, whereDWT is used to transform original image (cover image) fromspatial domain to frequency domain. Firstly two dimensionalDiscrete Wavelet Transform (2-D DWT) is performed on a coverimage of size M N and Huffman encoding is performed on thesecret information before embedding. Also, the secret key is usedto protect the information from external user. To embed thesecret information into cover image various image steganographytechniques are given. The proposed algorithm, a system calledTransform domain based Stego Imaging System (SIS). Thisproposed system is tested to see the viability of the proposedalgorithm. Different sizes of secret information/data are storedinside the images. Hence this new Transform domain based StegoImaging System is very efficient to hide the secret informationinside the image.Keywords—Steganography, Discrete Wavelet Transform, Huffmancoding.I.INTRODUCTIONSteganography technique is a one of the method to hide thesecret information inside the cover images. An algorithm isdesigned to hide all the data inputted within the image toprotect the privacy of the data. Then, the system is developedbased on the new steganography algorithm. This proposedsystem provides an image platform for user to input image anda text box to insert texts. Once the proposed algorithm isadapted, user can send the stego image to other computer/userso that the receiver is able to retrieve and read the data whichis hidden in the stego image by using the proposed system.Thus, the data can be protected without revealing the contentsto other people.Transform domain based Stego Imaging System (SIS) is atechnique that is capable of hiding the Secret informationinside the image. The system is using a security password inorder to maintain data privacy. Data security is the function ofIJERTV3IS20757www.ijert.org1255
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)ISSN: 2278-0181Vol. 3 Issue 2, February - 2014reconstruction from projection), representing the image in analternate and possibly more efficient form (Transformationand image compression).The field of image processing refers to the processing ofdigital images by means of a digital computer. A digital imagecomprises of finite number of elements, these elementsreferred as picture elements or image elements pels or pixels.Pixels represent darkness or brightness of an image at thatpoint. An application of image processing includes: Medicalimaging, Earth resources observations, Astronomy, Computerversion and Feature detection. Image enhancement is amongthe simplest and most appealing areas of digital imageprocessing. It used to highlight the certain features of animage. The aim of image enhancement is to improve theinterpretability or perception of information in images forhuman viewers, or to provide better' input for other imageprocessing techniques. There are two types of Imageenhancement techniques. They are, Spatial domain methods,which operate directly on pixels of an image, and Frequencyor Transform domain methods are another technique, whichoperate on the Fourier transform of an image. Imageenhancement techniques used as pre-processing tools for otherimage processing techniques, and then quantitative measurescan determine which techniques are most appropriate.TRANSFORM DOMAIN SYSTEMThe transform of a signal is a method for representing thesignal in another form. However, the information contentpresent in the signal does not changed. The WaveletTransform is a method for representation of time-frequency ofthe signal. The shortcoming of the Short Time FourierTransform (STFT), is overcome by this wavelet transform.Wavelet transform used to analyze stationary and nonstationary signals. In all frequencies STFT provides theconstant resolution, the Wavelet Transform uses multiresolution technique by which different frequencies areanalyzed with different resolutions.A. Continuous wavelet transformThe Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT) is provided byequation1, where x(t) is the continuous time signal to beanalyzed. Ψ (t) is the basis function; it also called as motherwavelet. All through translation (shifting) and scaling (dilationor compression).𝑡 𝜏𝑋𝑤𝑡 𝜏, 𝑠 1/ 𝑠 𝑥 𝑡 . Ψ 𝑑𝑡(1)𝑠The mother wavelet used to generate all the basic functionsdesigned based on some desired characteristics associatedwith that function. Where τ is the translation parameter, itrelates to the wavelet function shifted through the signal, andthe location of the wavelet function as it is. Thus, itcorresponds to the time information in the WaveletTransform. The scale parameter s is defined as 1/frequency and corresponds to frequency information. Scaling eitherdilates (expands) or compresses a signal. Large scales (lowfrequencies) dilate the signal and provide detailed informationIJERTV3IS20757B. Discrete wavelet transformThe Wavelet Series is just a sampled version of CWT anddepending on the resolution required, its computation mayconsume significant amount of time and resources. TheDiscrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), which based on subband coding. It found to yield a fast computation method ofWavelet Transform. The implementation of DWT is veryeasier. It also reduces the amount of resources required andcomputation time.Wavelets are functions defined over a finite interval andhaving an average value of zero. Wavelets provide an efficientmeans for approximating source signal with a small number ofbasic elements. The basic idea behind the wavelet transform isto represent any arbitrary function (t) as a superposition of aset of such wavelets or basis functions. In general, thewavelets are a set of functions that are generated from a singlefunction, called the mother wavelet, by dilations orcontractions (scaling) and translations (shifts) [2]. The basicfunctions thus obtained are called baby wavelets. The wavelettransform is computed separately for different segments of thetime domain signal at different frequencies.In CWT, a set of basic functions are used to analyze thesignals, which relate to each other by simple scaling andtranslation function. In DWT, digital filtering techniques areused to obtain the time-scale representation of the digitalsignal. The analyzed signal is passed through filters withdifferent cutoff frequencies at different scales. The 2-D DWTcan be implemented using a set of up-samplers, downsamplers, and recursive two channels digital filter banks.There are many available filters, but the most commonly usedare Haar Wavelet filters. Each of these filters decomposes theimage into several frequencies. Important properties ofwavelet filters in digital image compression are symmetry(used for avoiding artifacts at the borders), orthogonality (fatalgorithm), regularity, and degree of smoothness. In HaarDWT the low frequency wavelet coefficients are generated byaveraging the two pixel values and high frequency coefficientsare generated by taking half of the difference of the same twopixels.IJERTII.hidden in the signal, while small scales (high frequencies)compress the signal and provide global information about thesignal. The Wavelet Transform performs the convolutionoperation and the basis function of the signal. The CWTbecomes very useful as in most practical applications, in highfrequencies (low scales) do not last for a long duration of thesignal and appear as short bursts, while low frequencies (highscales) usually last for entire duration of the signal.C. Huffman codingA number of variations can be used for hiding secret imagein transform domain technique. In the first case secret imagecan be Huffman encoded to reduce the size of the image [1].Huffman codes are optimal codes that map one symbol to onecode word.www.ijert.org1256
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)ISSN: 2278-0181Vol. 3 Issue 2, February - 2014Figure 1: Basic block diagram of Steganography systemThe Fig.1 shows the block diagram of Steganograhysystem. Here the cover image encoded with the secretinformation and the secret key embedded into the secretinformation. From the resultant of stego image, the same keyused to extract the Secret information.There are many number of steganographic method used inour day-to-day life. Most of that methods are familiar with(especially for a large number of spy movies), ranging frommicrodots and invisible ink to secreting a hidden informationin spread spectrum radio communication [4]. There are somany ways to hiding information in computers and networks:They are, Covert channels (e.g., Loki and some distributed denial-ofservice (DOS) tools use the Internet Control MessageProtocol ( ICMP), as the communications channel betweenthe Unknown user or system and a compromised system). Hidden text files within the Web pages. Hiding the important information in "plain sight". Zero ciphers (e.g: to form a hidden message using the firstletter of each word otherwise innocuous text).IJERTFor an image Huffman coding assigns a binary code toeach intensity value of the image and convert it into a 1-D bitstream of lesser length than the original image. This helps inincreasing the embedding capacity as well as security. It alsoprovides a kind of authentication as any single bit change inthe Huffman coded bit stream is unable to decode. Then thereduced image is converted into 3-bit blocks and embedded inthe DWT-DCT converted cover image based on the size. The3-bit block is embedded in the DCT coefficients of the 8*8blocks. This will lead to better security and increase in thecapacity of embedding of the secret image.Huffman coding is an entropy-encoding algorithm used forlossless data compression. The variable-length code table forencoding a source symbol such as a character in a file. Basedon the estimated probability of occurrence in a particular wayfor each possible value of the source symbol, the variablelength code table has derived. The representation for eachsymbol has chosen by the specific method in the Huffmancoding. Resulting in a prefix code or prefix-free codes,representing some particular symbol in the bit string is not aprefix of that bit string. If representing any other mostcommon source symbols using shorter strings of bits.Huffman design the most efficient compression method of thistype: smaller average output size does not produce individualsource symbols to unique strings of bits when the actualsymbol frequencies agree with those used to create the code.The Huffman's method running time is efficient; ittakes operations to construct it. A later found method was todesign a Huffman code in linear time and input probabilitiessorted with the weights.Before embedding the secret image into cover image, itencoded using Huffman coding. Huffman codes are optimalcodes that map one symbol to one code word. For an image,Huffman coding assigns a binary code to each intensity valueof the image and a 2-D M2 N2. Image is converted to a 1-Dbits stream with length LH M2 N2.Huffman coding used to serve the following:Lossless Compression –It increases the embedding capacity.Security by means of encoding – Huffman encoded bitstream cannot reveals anything. To extract the exactmeaning –Huffman table is required to decode. In Huffmancoded stream, if any single bit changed; it provides one typeof authentication, and Huffman table is unable to decode.III.B. Transform domain based stego imaging(SIS)systemPROPOSED STEGO IMAGING SYSTEMA. Concept of steganographySteganography is the heart of science for hiding information.The concept of steganography based on cryptography. Themain goal of cryptography is to make data unreadable by anun-authorized user. The steganography is to hide theinformation in the sense data or image from an un-authorizeduser.Figure 2: Block diagram of proposed Stego Imaging systemIJERTV3IS20757www.ijert.org1257
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)ISSN: 2278-0181Vol. 3 Issue 2, February - 2014Step 7: Using the stego image by provides the security key assame as the previously used to extract the secret informationStep 8: Output: Get the secret information hided into the coverimage.The above algorithmic steps describes the process of theproposed Transform domain based Steganography ImagingSystem (SIS).IV.RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONIn this section, I present simulation results to demonstratethe highly secured Transform domain based Stego ImagingSystem (SIS). This proposed stego imaging system producesbetter result from this algorithm. The output results areobtained by using MATLAB software. The simulation resultsshown below:IJERTThe cover Image is an Image file in which we will hidethe Secret information, which may also been encrypted usingthe stego key. The resultant output file is the stego image(which will, of course be the same type of file as the coverImage). Generally, the cover medium is typically image oraudio files. Here, I focused on image files and will; therefore,the cover medium and stego medium are referring to the coverimage and stego image.The Fig.2 shows the block diagram of Transform domainbased Steganography Imaging System (SIS). Here DiscreteWavelet Transform used as the Transform domain. Embedthe secret information into the cover image by using Huffmancoding. To provide the higher security the password is createdafter that of the secret information hidden into the coverimage.The terminologies used in Image steganography are asfollows:Cover-Image: It is original image, which used as a carrier forhidden information.Secret Information: It is actual information, which used tohide into images. Message could be a plain text or some otherimage.Stego-Image: Stego-image is an image generated afterembedding the secret information into cover image.Stego-Key: It is a secret key that are used for embedding orextracting the information from cover-images and stegoimages.The uses of steganography system are many and one of themost widely used applications is digital watermarking. Awatermark is a method that uses a replication of an image,logo or text on paper stock. So the source of the documentauthenticated partially [3]. The same function accomplishedby the digital watermark scheme. The communicationsbetween the underground communities are done by usingstego image. There are several reports explains thesteganography is used to embed messages for the group withinimages.Steganalysis is the science of detecting hidden informationfrom the stego image [4]. The main objective of Steganalysisis detection of stego image and break steganography. Almostall steganalysis algorithms rely on the Steganographicalgorithms introducing statistical differences between coverand stego image.C. Algorithm for proposed stego imaging systemStep 1: Input: select the cover image.Step 2: Then apply the discrete wavelet transform to the coverimage.Step 3: The DWT separates the cover image into different subband images (LL, LH, HL, and HH).Step 4: In order to apply the secret information with use ofHuffman coding.Step 5: Hide the secret information into the cover image andgenerate the security key to provide high security.Step 6: From this result the stego image is generated.IJERTV3IS20757Figure 3: Input Cover image (without secret information)The Fig.3 shows the Input Cover Image. It does not containany secret information within the image.Figure 4: Cover image split by the 2Level DWTThe Fig.4 shows the input of the cover image split by the2Level DWT using Haar wavelets.www.ijert.org1258
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)ISSN: 2278-0181Vol. 3 Issue 2, February - 2014The above Fig.7 shows the resultant output of stego imagehaving secret information inside the image.Figure 5: Secret InformationThe above Fig.5 shows secret information. This secretinformation is embedding into the cover image.Figure 8: Steganalysis of secret informationIJERTThe Fig.8 describes the steganalysis of secret informationfrom the stego image using same the password as we are usingat the time embedding the secret information.Figure 6: Creating Password keyThe Fig.6 shows the creation of password key on embeddingprocess. This security password helps to provide the highersecurity.Figure 9: Extracted Secret informationThe Fig.9 shows extracted secret information from the stegoimage.V.Figure 7: Stego image (with secret information)IJERTV3IS20757CONCLUSIONImage Steganography methods in spatial domain LSBsubstitution system does not provide the basic demand ofsecrecy. The attacker can easily destroy the secret informationby applying signal-processing techniques. The proposedTransform domain based Stego Imaging System (SIS) providethe higher security for protecting the secret information fromthe external user. The secret password given at the time ofsecret information embedded in to the cover image. In theprocess of steganalyst the same password is used to extract thesecret information from the stego image. In addition, the timeconsumed for the extraction of secret information is less thanthat of time taken for embedding the secret information.www.ijert.org1259
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)ISSN: 2278-0181Vol. 3 Issue 2, February - 2014As a scope of future work, Embedding the secret imageinto the cover image using the watermarking technique toembedding the secret image.REFERENCESIJERT[1] Mukta Goel and Rohit Geol, “Current Image steganograhy techniquesfor higher compression and robustness”, VSRD International Journal ofComputer Science & Information Technology, Vol. 3 No. 2 Feb 2013.[2] Weiqi Luo, Fangjun Huang, and Jiwu Huang, “Edge adaptive imagesteganography based on LSB matching revisited,” in IEEE Transactionson Information Forensics and Security, vol.5, no.2, June 2010.[3] L. Luo, Z. Chen, M. Chen, X. Zeng, Z. Xiong, “Reversible imagewatermarking using interpolation technique,” IEEE Transactions onInformation Forensics and Security , 5 ,1, PP 187–193, 2010.[4] Matthew L.Miller, Ingemar J.Cox, “Digital Watermarking andSteganography”:Second Edition, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.[5] K. M. Singh, L. S. Singh, A. B. Singh, and K. S. Devi, “Hiding secretmessage in edges of the image” International Conference onInformation and Communication Technology, PP 238–241, 2007.[6] J. Fridrich, M. Goljan, and R. Du, “Detecting LSB steganography incolor, and gray-scale images,” IEEE Multimedia, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 22–28, Oct. 2001.[7] D. Wu and W. Tsai, “A steganographic method for images by pixelvalue differencing,” Pattern Recognit. Lett., vol. 24, pp. 1613–1626,2003[8] D. Artz, “Digital Steganography: Hiding Data within Data”, IEEEInternet Computing Journal, 4, 2, PP 127- 135, 2001.[9] Z. Ni, Y.Q. Shi, N. Ansari, W. Su, “Reversible data hiding” , IEEETransactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, PP 354–362,2006.IJERTV3IS20757www.ijert.org1260
operate on the Fourier transform of an image. Image enhancement techniques used as pre-processing tools for other image processing techniques, and then quantitative measures can determine which techniques are most appropriate. II. TRANSFORM DOMAIN SYSTEM The transform of a signal is a method for representing the signal in another form.