Transcription
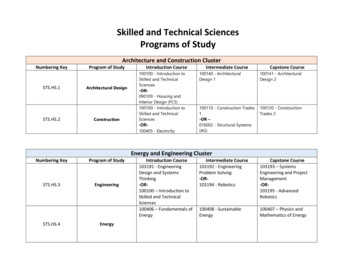
Skilled and Technical SciencesPrograms of StudyArchitecture and Construction ClusterNumbering KeySTS.HS.1STS.HS.2Program of StudyArchitectural DesignConstructionIntroduction Course100100 - Introduction toSkilled and TechnicalSciences-OR090109 - Housing andInterior Design (FCS)100100 - Introduction toSkilled and TechnicalSciences-OR100405 - ElectricityIntermediate CourseCapstone Course100140 - ArchitecturalDesign 1100141 - ArchitecturalDesign 2100110 - Construction Trades1-OR –016002 - Structural Systems(AG)100120 - ConstructionTrades 2Energy and Engineering ClusterNumbering KeyProgram of StudySTS.HS.3EngineeringSTS.HS.4EnergyIntroduction Course103191 - EngineeringDesign and SystemsThinking-OR100100 – Introduction toSkilled and TechnicalSciences100406 – Fundamentals ofEnergyIntermediate Course103192 - EngineeringProblem Solving-OR103194 - RoboticsCapstone Course103193 – SystemsEngineering and ProjectManagement-OR103195 - AdvancedRobotics100408 - SustainableEnergy100407 – Physics andMathematics of Energy
Manufacturing ClusterNumbering KeyProgram of StudyIntroduction Course100100 - Introduction toSkilled and TechnicalSciences-OR101920 – ManufacturingProcesses – Woods-OR101400 – ManufacturingProcesses – Metals-OR101950 – ManufacturingProcesses - PlasticsSTS.HS.5ManufacturingWelding-OR101930 – Welding 1-OR –100140 – ArchitecturalDesign 1Capstone Course101921 - ManufacturingProduction - Woods-OR101400 – ManufacturingProcesses – Metals-OR101950 – ManufacturingProcesses - Plastics-OR100401 – Introduction toElectronics-OR*101922 - AdvancedManufacturing andFabrication - Woods-OR101401 – ManufacturingProduction - Metals-OR*101402 - AdvancedManufacturing andFabrication - Metals-OR101951 – ManufacturingProduction - Plastics-OR*101952 AdvancedManufacturing andFabrication - Plastics-OR100402 – AdvancedElectronics-OR101900 - Introduction toMechatronics101940 – Welding 2– OR –*101941 – Welding 3-OR016005 - Metals andFabrication (AG)(Equivalent to Welding 2)-OR100140 – ArchitecturalDesign 1100100 - Introduction toSkilled and TechnicalSciencesSTS.HS.6Intermediate Course101920 – ManufacturingProcesses – Woods101930 – Welding 1– OR –101940 – Welding 2-OR016004 - Welding (AG)(Equivalent to Welding 1)
Transportation, Distribution, and Logistics ClusterNumbering KeyProgram of StudySTS.HS.7TDL - TechnicianSTS.HS.8TDL – Supply ChainIntroduction Course101600 – Transportation 1-OR100100 Introduction to theBuilt Environment-OR016003 Power andTechnology (AG)101601 – Introduction toTDLIntermediate Course101620 - Transportation 2Capstone Course101630 – Transportation 3-OR101640 – Collision Repair101610 - Distribution andLogistics101650 - Business Logistics
Architecture and Construction ClusterArchitectural Design Program of aSTS.HS.1.1.bSTANDARDSThe Student Will Be Able To.Identify safety guidelines.Identify architectural careeropportunities.STS.HS.1.2.aIdentify the primary duties and attributes of an architect orarchitectural technician.Desribe the various careers within the architectural profession (i.e.draftsman, designer, project manager, architect, landscapearchitect, and interior designer) and the training and certificationneeded for each.Identify the relationships between all stakeholders involved in aconstruction project.Identify how work varies with regard to site (i.e. confined spaces,outdoor areas, aerial space and a variety of climatic and physicalconditions).Identify positive work behaviors and personal qualities needed tobe .HS.1.2.eSTS.HS.1.3STS.HS.1.3.aThe Student Will Be Able To.Successfully complete written safety assessment.Identify the consents necessary to enter a confined space on aconstruction site.Identify the requirements of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).STS.HS.1.1.cSTS.HS.1.2INDICATORSAnalyze the historical beginnings ofarchitecture.Identify design principles, elements, and architectural styles.
STS.HS.1.3.bIdentify the building materials, locations, and design that havehistorically influenced civil engineering and architecture.STS.HS. 1.3.cRelate the influence that historical buildings have on today'sarchitecture.Identify general categories of structural systems used in historicalbuildings.STS.HS.1.3.dSTS.HS.1.4Apply geometric object measurments toarchitecture.STS.HS.1.4.aDefine the characteristics of an equilateral triangle, isoscelestriangle, square, parallelogram, hexagon, octogon, and circle andtheir application to architecture.Calculate the surface area and perimeter of two- dimensionalobjects.Calculate the volume and surface area of three- dimensionalobjects.Calculate the roof slopes, light angles, ground surfaces, structuralloads and heights of structures.Interpret a design brief, including knowing the design problem,design statement and be able to list design S.HS.1.4.eSTS.HS.1.5Identify site characteristics and how theyaffect building design and landdevelopment.STS.HS.1.5.aIdentify the impact of site development (I.e. storm water runoff,pedestrian and vehicular access).Explain the purpose for the use of Low Impact Developmenttechniques in site development.Identify specifications and codes for a site design process.Identify soil characteristics important to the design andconstruction of a building on the 6Identify typical building design andconstruction methods and practices.
STS.HS.1.6.aIdentify various digital drafting and modeling options (i.e.CADD/BIM).Identify the components that comprise architectural construction(working) drawings.Identify the types of materials, their properties and applicationsused in building construction.Identify different types of fasteners, adhesives and S.1.6.eSTS.HS.1.7Identify the environmental impact of material usage.Identify residential and commercialbuilding systems.STS.HS.1.7.aDescribe how construction is affected by the availability, quality,and quantity of resources.Identify typical utility services, transmission and usage measuringrequired for a residential and commercial building.STS.HS.1.7.bSTS.HS.1.7.cIdentify code requirements and constraints as they pertain to theinstallation of services and utilities.Identify the criteria and constraints to determine the size andlocation of new utility service connections.Identify system designs to incorporate energy .HS.1.8Create a cost and efficiency analysis.STS.HS.1.8.aSTS.HS.1.8.bCompare and contrast the terms R-value and U-factor.Create a cost estimate for a small construction project, including adetailed cost break-down.Calculate the heat loss for a building envelope.Calculate the overall R-value of a wall or roof section composed ofmultiple building components.Identify principles of sustainable 1.9Identify current local and nationalbuilding codes.
STS.HS.1.9.aSTS.HS.1.10Apply conventional General DraftingStandards used in architectural .HS.1.11.bSTS.HS.1.11.cSTS.HS.1.11.dDescribe how current building codes determine the type, sizing,and placement of site features (i.e. parking lots, and entrances andexit roads, pedestrian and handicapped access, and storm waterfacilities).Identify the protocol used in crisis management (i.e. an employeeinjury, equipment damage, and a collapse on a project of people ormaterials).Identify terms and definitions commonly used in the architecturalprofession including detail drawings, working drawings anddrafting.Define the function and graphical characteristics of each line in theAlphabet of Lines.Describe the orthographic elevation projection.Create different views such as floor plans, elevations, sections, site,and perspectives.Apply dimensional information and general notes in architecturalviews and plans.Apply schedules such as doors, windows and rooms in architecturalviews and plans.Describe the components that comprise architectural construction(working) drawings.Indicate plan review requirements needed to obtain a buildingpermit.Communicate design solutions.Prepare design ideas using architectural terminology for apresentation.Deliver an oral presentation with accompanying visuals featuringboth physical and digital work.Develop and maintain an architectural portfolio that includesphysical and digital works.Create shaded and rendered presentation drawings.
Architecture and Construction ClusterConstruction Program of aSTANDARDSThe Student Will Be Able To.Apply safety principles, practices andguidelines to the work environment.Apply the safe use of tools, machines, and equipment in alignmentwith industry standards to maintain a safe workplace.Describe the role of government agencies in providing a safeworkplace.STS.HS.2.1.cInvestigate career opportunities in theconstruction industry.STS.HS.2.2.aIdentify the responsibilities and characteristics of professionals inthe construction industry.Identify employment trends in various construction sectors(residential, commercial, industrial, energy, green technologies,etc.).Describe work behaviors needed to be employable.Identify the training, education, certification and licensingrequirements for various careers in the construction S.2.3STS.HS.2.3.aSTS.HS.2.3.bSTS.HS.2.3.cThe Student Will Be Able To.Successfully complete written safety assessment.Apply the requirements of safety glasses and other PersonalProtective Equipment Demonstrate use of constructioncommunications.Accurately interpret construction terminology, plans, drawings andschedules.Develop a flowchart of project schedule.Develop a schedule materials in proper sequence.
STS.HS.2.4Identify building codes and permittingprocesses.STS.HS.2.4.aIdentify local, state and national building regulations and codes.STS.HS.2.4.bDescribe the requirements needed to obtain a building permit.STS.HS.2.4.cSTS.HS.2.5Identify appropriate building inspections.Summarize building systems and components.STS.HS.2.5.aDescribe the building systems needed to complete a constructionproject.Describe the building components needed to complete aconstruction project (i.e. trusses, joists, beams, etc.).Identify the types and sizes of construction materials needed tocomplete a construction project.Identify different types of fasteners, adhesives and finishes neededto complete a construction project.Identify green building 2.6.cDemonstrate the installation of constructionsub-systems.Accurately use math functions and formulas to completejob/workplace tasks.Correctly and accurately use tools and equipment to performmaterial takeoff (MTO) to drawings and specifications.Construct structural, mechanical and finish sub-systems correctly tomeet current local, state, and national codes.
Energy and Engineering ClusterEnergy Program of e Student Will Be Able To.Apply safety principles, practices andguidelines to the work environment.INDICATORSThe Student Will Be Able To.STS.HS.3.1.aApply the requirements of safety glasses and otherPersonal Protective Equipment (PPE) in the workplace.STS.HS.3.1.bDemonstrate the safe use of tools, machines, andequipment in alignment with industry standards.STS.HS.3.1.cAnalyze the role of government agencies in providing asafe workplace.STS.HS.3.2Investigate career opportunities in theenergy field to gain knowledge forinformed career decisions.STS.HS.3.2.aIdentify the responsibilities of professionals in theenergy industry.Identify opportunities and employment trends invarious energy sectors.Identify the training, education, certification andlicensing requirements for occupational .3.aSTS.HS.3.3.bExplain the history of energy and energygeneration.Summarize the general hisory and key events inelectric power generation and distribution.Explain the history of fluid and liquid fuel productionand distribution.
STS.HS.3.4Classify the various types of energy andtheir uses.STS.HS.3.4.aSTS.HS.3.4.bEvaluate the seven forms of energy.Assess energy transformations in various settings. (ex.home, farm, car, county fair, ecosystem).STS.HS.3.4.cCompare and contrast renewable and non-renewableenergy.Identify the law of conservation of energy.Explain the purpose of regulatory bodies within theenergy ntiate between types of energystorage and distribution methods.STS.HS.3.5.aExplain the components of an energy delivery system.STS.HS.3.5.bIdentify key pieces of equipment that are used in thedistribution and storage of fluid fuels and electricalpower (i.e. pipelines, tank farms, unit trains, supertankers, transmission lines, towers, generatingstations, sub-station, etc.).Compare and contrast centralized power generationand distributed S.3.6.bEmploy various measures of energy.Calculate equations using Ohm's Law.Calculate equations using thermal energy formulas.STS.HS.3.6.cSTS.HS.3.7STS.HS.3.7.aUtilize energy related measurement tools inappropriate scenarios.Plan, build and maintain an energy relatedproduct or structure.Create sketches and plans for an energy relatedproduct or structure.
STS.HS.3.7.bSTS.HS.3.7.cDetermine structural requirements, specifications andestimate costs of structures.Interpret plans to construct, maintain, or repair energyrelated product or structure.
Energy and Engineering ClusterEngineering Program of e Student Will Be Able To.Apply safety principles, practices andguidelines to the work environment.STS.HS.4.1.aSTS.HS.4.1.bInvestigate careers in the engineering fieldto gain knowledge for informed careerdecisions.STS.HS.4.2.aIdentify opportunities and employment trends in variousengineering sectors.Identify training, education, certification and licensingrequirements for occupational choice.STS.HS.4.2.bSTS.HS.4.3The Student Will Be Able To.Successfully complete written safety assessment.Apply the requirements of safety glasses and other PersonalProtective Equipment (PPE).Apply the safe use of tools, machines, and equipment inalignment with industry standards to maintain a safe workplace.STS.HS.4.1.cSTS.HS.4.2INDICATORSEmploy engineering design processprinciples to solve an engineering problem.STS.HS.4.3.aDefine an engineering problem and research possible solutions.STS.HS.4.3.bUse basic technical sketching and drawing skills, engineeringnotebook standards and engineering protocols to documentresearch and solutions.STS.HS.4.4STS.HS.4.4.aBuild an engineering related product orstructure.Determine structural requirements, specifications and estimatecosts for the products or structures.
STS.HS.4.4.bSTS.HS.4.5Accurately follow plans to construct an engineering relatedproduct or structure.Describe the functions of a basic robot.STS.HS.4.5.aSTS.HS.4.5.bSTS.HS.4.6Identify basic programming concepts: structures, variables,constants and logical operators.Identify various aspects of robotics in industry.Design and assemble robots that arefunctionally and structurally sound.STS.HS.4.6.aGenerate a solution for a robot to overcome a physics challenge.STS.HS.4.6.bConstruct a fully functioning robot that has proof of conceptthrough engineering notebook protocols.Assemble drive trains that utilize different gear ratios tounderstand mechanical setups.STS.HS.4.6.c
Manufacturing ClusterManufacturing Program of E STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO Apply safety principles, practices andguidelines to the work environment.INDICATORSTHE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO STS.HS.5.1.aSuccessfully complete written safety assessment.STS.HS.5.1.bApply the requirements of safety glasses and otherPersonal Protective Equipment (PPE).Apply the safe use of tools, machines, and equipmentin alignment with industry standards to maintain a safeworkplace.Describe the role of government agencies in providinga safe igate career opportunities in themanufacturing industry.STS.HS.5.2.aIdentify the responsibilities and characteristics ofprofessionals in the manufacturing industry.Identify employment trends in manufacturing.Describe work behaviors needed to be .HS.5.3STS.HS.5.3.aSTS.HS.5.3.bIdentify the training, education, certification andlicensing requirements for various careers in themanufacturing industry.Demonstrate use of manufacturingcommunications.Interpret manufacturing terminology, plans, sketches,drawings and schedules.Develop a flowchart of a project schedule.
STS.HS.5.3.cSTS.HS.5.4Develop a schedule of materials in proper sequence.Identify the materials, tools and equipmentneeded to manufacture a product.STS.HS.5.4.aDetermine types of materials, fasteners, adhesives andfinishes needed to produce a specific product.STS.HS.5.4.bDetermine the correct tools and equipment needed toproduce a specific ure a product usinf manufacturingtechnology.Correctly use math functions and formulas to completejob/workplace tasks.Correct and accurately use tools and equipment toperform manufacturing operations according todrawings and specifications.
Manufacturing ClusterWelding Program of HE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO THE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO STS.HS.6.1Apply safety principles, practices andguidelines to the work environment.Successfully complete written safety assessment.Apply the requirements of safety glasses and other PersonalProtective Equipment (PPE).STS.HS.6.1.aSTS.HS.6.1.bSTS.HS.6.1.cApply the safe use of tools, machines, and equipment in alignmentwith industry standards to maintain a safe workplace.Describe the role of government agencies in providing a safeworkplace.STS.HS.6.1.dSTS.HS.6.2Investigate career opportunities inthe welding industry.STS.HS.6.2.aIdentify the responsibilities and characteristics of professionals in thewelding industry.Identify employment trends in welding.Describe work behaviors needed to be employable.Identify the training, education, certification and licensingrequirements for various careers in the welding te use of weldingcommunications.Accurately interpret welding terminology, plans, sketches, drawingsand schedules.Develop a flowchart of a project schedule.Develop a schedule of materials in proper sequence.
STS.HS.6.4Identify the materials, tools andequipment needed to manufacture aproduct.STS.HS.6.4.aDetermine types of materials, fasteners, adhesives and finishesneeded to produce a specific product.Determine the correct tools and equipment needed to produce aspecific .5.bSTS.HS.6.5.cSTS.HS.6.5.dProduce a product using weldingtechonolgy.Accurately use math functions and formulas to completejob/workplace tasks.Correctly and accurately use tools and equipment to perform weldingoperations according to drawings and specifications.Perform metal cutting operations using various methods (i.e. oxyacetylene, mechanized oxyfuel gas, plasma arc and manual air carbonarc).Weld using various methods of welding (i.e. gas metal arc welding,GMAW-S, GMAW spray transfer, flux core arc welding, gas tungstenarc welding, shielded metal arc welding, oxy-acetylene) and usingvarious positions (i.e. flat, horizontal, vertical up, verticle down, andoverhead).
Transportation, Distribution and Logistics Career ClusterTDL Technician Program of IDICATORSTHE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO.THE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO.Apply safety principles, practices and guidelinesto the work environment.Successfully complete written safety assessment.Apply the requirements of safety glasses and other PersonalProtective Equipment (PPE).STS.HS.7.1.aSTS.HS.7.1.bSTS.HS.7.1.cApply the safe use of tools, machines, and equipment inalignment with industry standards to maintain a safe workplace.Describe the role of government agencies in providing a safeworkplace.STS.HS.7.1.dSTS.HS.7.2Investigate career opportunities in thetransportation industry.STS.HS.7.2.aIdentify the responsibilities and characteristics of professionals inthe transportation industry.Identify employment trends in the transportation S.7.3STS.HS.7.3.aDescribe work behaviors needed to be employable.Identify the training, education, certification and licensingrequirements for various careers in the transportation industry.Describe the systems and components used inthe transportation technician industry.Describe the function and operation of the systems of a vehicle orequipment (i.e. mechanical, electrical, fuel, suspension, etc.) andthe components needed to operate those systems.
STS.HS.7.3.bSTS.HS.7.4Demonstrate the use of communication tools (i.e. manuals, on-linespecification and service procedures, etc.) used in thetransportation service industry.Diagnose and repair the systems and componentsof a vehicle or equipment.STS.HS.7.4.aDetermine the correct tools and equipment used for the diagnosis,service and repair of the systems and components.STS.HS.7.4.bDetermine the different types of fasteners, adhesives and finishesneeded to complete service and repair of the vehicle or equipment.STS.HS.7.4.cDemonstrate the use of measurement and math functions/formulasneeded to complete job/workplace tasks.
Transportation, Distribution and Logistics Career ClusterTDL Supply Chain Program of IDICATORSTHE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO.THE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO.Apply safety principles, practices andguidelines to the work environment.STS.HS.8.1.aSuccessfully complete written safety assessment.Apply the requirements of safety glasses and otherPersonal Protective Equipment (PPE).Apply the safe use of tools, machines, and equipmentin alignment with industry standards to maintain a safeworkplace.Describe the role of government agencies in providinga safe HS.8.2Investigate career opportunities in thetransportation industry.STS.HS.8.2.aIdentify the responsibilities and characteristics ofprofessionals in the transportation industry.Identify employment trends in the transportationindustry.Describe work behaviors needed to be .HS.8.3STS.HS.8.3.aIdentify the training, education, certification andlicensing requirements for various careers in thetransportation industry.Identify the segments and functions of thetransportation distribution industry.Describe the five modes of transportation used todistrubute people and products.
STS.HS.8.3.bCompare the different types of cargo with thedifferent modes of transportation.Explain product order processing, product receiving,product storage and retrieval, and product packagingand shipping in the global supply chain logistics .8.4.bSTS.HS.8.4.cSTS.HS.8.4.dExplain the purpose and components oftransportation logistics.Explain dispatch and the purpose of tracking ofproducts as they are transported throughout thesupply chain.Describe the components that impact transportationlogistics (i.e. routing, scheduling, equipment, operator,etc.).Explain the different types of shipping documentationand terms.Describe strategic, tactical and systems planning.
Design 1 101920 - Manufacturing Processes - Woods -OR- 101400 -Manufacturing Processes Metals-OR- 101950 - Manufacturing Processes - Plastics . STS.HS.2.2.a Identify the responsibilities and characteristics of professionals in the construction industry. STS.HS.2.2.b Identify employment trends in various construction sectors .










