Transcription
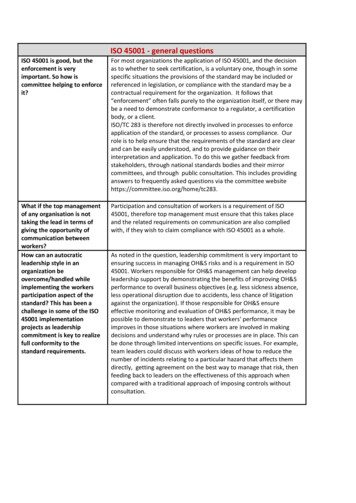
ISO 45001 - general questionsISO 45001 is good, but theenforcement is veryimportant. So how iscommittee helping to enforceit?For most organizations the application of ISO 45001, and the decisionas to whether to seek certification, is a voluntary one, though in somespecific situations the provisions of the standard may be included orreferenced in legislation, or compliance with the standard may be acontractual requirement for the organization. It follows that“enforcement” often falls purely to the organization itself, or there maybe a need to demonstrate conformance to a regulator, a certificationbody, or a client.ISO/TC 283 is therefore not directly involved in processes to enforceapplication of the standard, or processes to assess compliance. Ourrole is to help ensure that the requirements of the standard are clearand can be easily understood, and to provide guidance on theirinterpretation and application. To do this we gather feedback fromstakeholders, through national standards bodies and their mirrorcommittees, and through public consultation. This includes providinganswers to frequently asked questions via the committee websitehttps://committee.iso.org/home/tc283.What if the top managementof any organisation is nottaking the lead in terms ofgiving the opportunity ofcommunication betweenworkers?How can an autocraticleadership style in anorganization beovercome/handled whileimplementing the workersparticipation aspect of thestandard? This has been achallenge in some of the ISO45001 implementationprojects as leadershipcommitment is key to realizefull conformity to thestandard requirements.Participation and consultation of workers is a requirement of ISO45001, therefore top management must ensure that this takes placeand the related requirements on communication are also compliedwith, if they wish to claim compliance with ISO 45001 as a whole.As noted in the question, leadership commitment is very important toensuring success in managing OH&S risks and is a requirement in ISO45001. Workers responsible for OH&S management can help developleadership support by demonstrating the benefits of improving OH&Sperformance to overall business objectives (e.g. less sickness absence,less operational disruption due to accidents, less chance of litigationagainst the organization). If those responsible for OH&S ensureeffective monitoring and evaluation of OH&S performance, it may bepossible to demonstrate to leaders that workers' performanceimproves in those situations where workers are involved in makingdecisions and understand why rules or processes are in place. This canbe done through limited interventions on specific issues. For example,team leaders could discuss with workers ideas of how to reduce thenumber of incidents relating to a particular hazard that affects themdirectly, getting agreement on the best way to manage that risk, thenfeeding back to leaders on the effectiveness of this approach whencompared with a traditional approach of imposing controls withoutconsultation.
6.1.2.3 Assessment of OH&Sopportunities and otheropportunities for the OH&Smanagement system Shall beconducted the part of HIRA orcan we do it separately?The identification, and assessment, of OH&S opportunities and otheropportunities for the OH&S management system, can be carried outalongside, or separate from, the hazard and risk assessment (HIRA).Certainly, HIRA can be used to identify some opportunities, howeveradditional assessment may be needed to ensure that opportunities arenot missed if identification is too narrowly focussed via HIRA.When an organizationimplements ISO 45001 theyshould analyse thepsychosocial risks, or onlywhen implementing ISO45003?ISO 45001 requires the organization to identify and assess all OH&Srisks to workers, so this already includes psychosocial risks. ISO 45003is being developed to provide additional guidance on this aspect, as it isone which many organizations have limited experience with, yet onewhich is becoming increasingly significant for many.Is responsiveness andtimeliness during emergenciesand times of crisis sufficientlyaddressed?ISO 45001 contains a section specific to emergency preparedness andresponse. Although there is no specific mention of timeliness, theorganization is required to test its plans periodically and to evaluatetheir effectiveness via these tests and any actual emergencies.Timeliness is clearly an important attribute when considering whetheran emergency plan is effective, so it should always form part of such anevaluation.Can ISO 45001 be used toaddress and manage thehuman factors?Yes, human factors are among the factors affecting OH&S risks toworkers. The organization should therefore consider human factorswithin the scope of its OH&S management system and use the ISO45001 framework in addressing and managing the related risks.Why does "workerparticipation" come togetherwith "leadership" in the in thePDCA cycle?It is important to note that each requirement in ISO 45001 isindependent and that the organization needs to comply with allrequirements, regardless of the order in which they appear or how theyare grouped together. There is no particular significance to the fact thatthese are grouped together within the document, other than becauseof the interaction between the two clauses: effectively meeting therequirements for leadership depends on meeting the requirements forworker participation and vice versa. Additionally, ISO 45001 uses thesame clause structure as other management system standards such asISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 14001 (EnvironmentalManagement); putting the requirements for worker participationalongside those for leadership helps preserve that common structure,and is a useful reminder that together these elements are enablers ofeffective OH&S management.
Could you please explainmore details about nonroutine operation in order toaddress the risks andopportunities? Do we have toadd the grading system forthe risks and theopportunities that we haveaddressed?Please see the questions and answers on this topic on the TC 283website –https://committee.iso.org/home/tc283 - in the FrequentlyAsked Questions section, in the area related to Clause 6 of thestandard. Establishing (grading) the magnitude of risks, taking intoaccount the controls in place, is key to establishing whether controlsare sufficient or whether action is needed; this applies equally toroutine and non-routine operations.In the case of non-routineactivities, workers have to betrained in changesincorporated in theinfrastructure, equipment,materials, physical conditionsof the workplace and hazardsarising from these changes. Ifthe situation persists for alonger period, should thisnon-routine activity beconsidered as having becomeroutine activity?Yes, some non-routine can become routine activities over time. Forexample, some of the changes that organizations have introduced toaddress the Covid-19 pandemic may become permanent, and thisshould be reflected in training, process documentation, etc. It’simportant that when we adjust work and workplaces (in this case toreduce the risks of transmission of the virus) that we assess howchanges affect the risks for regular (routine) activities, but also considermore occasional (non-routine) activities such as maintenance activitieson equipment or buildings, and that we consider emergencyarrangements such as evacuation to an assembly point.Can a company be certified ascomplying with the 45001standard?ISO 45001 can be used as the basis for a self-declaration of conformityby an organization, for a “second party” assessment of an organizationby a client, or for external, independent third-party certification.Independent third-party certification of a management system isvoluntary, in other words a choice on the part of the organization itself.That said, there are occasions where requirements for certification areapplied in supply chains where a client organization requires itssuppliers to be certified – this is currently less common with ISO 45001than, for example, with ISO 9001 (Quality Management).The credibility of any independent third-party certification, isinfluenced by the choice of certification body. National AccreditationCouncils provide oversight of management system certification bodies(“certifiers” or, in some countries “registrars”), reviewing aspects oftheir work including competence and impartiality, but thisaccreditation is voluntary on the part of certifiers. We wouldrecommend organizations employ a certifier accredited for ISO 45001.What is meant by aharassment from the point ofview of 45001?By harassment ISO 45001 is referring to aggressive pressure,intimidation or bullying including behaviour that demeans, humiliatesor embarrasses a person.
Specific significant changesfrom OHSAS 18001 please?Principal differences between the requirements of ISO 45001 and thoseof OSHAS 18001 are summarised in a PowerPoint presentationavailable on the ISO/TC 283 website(https://committee.iso.org/home/tc283). These differences include:alignment to the structure and core requirements of other ISOmanagement system standards (e.g. ISO 9001); more emphasis on thecontext of the organization, leadership and worker participation andconsultation.ISO 45001 implementation handbook for small organizationsWhat is the Handbook? Doesthe Handbook provideguidance to smallorganizations in applying therequirements of ISO 45001:2018?Yes, the handbook is a guidance document explaining how smallerorganizations can implement the requirements of ISO 45001. It hasdeliberately been written in a less formal style and provides practicalexamples, to help organizations that do not have in-house OH&Sspecialists. It has been developed to support ISO 45001, not to replaceit, although organizations beginning their journey in OH&Smanagement could choose to use the Handbook as a starting point fordeveloping an OH&S management system, rather than trying to complyto ISO 45001 from the outset.When will the Handbook bepublished?Publication is planned for early August 2020Where will I be able to get it?ISO will make the Handbook available to all national standards bodies.It is up to each individual standards body if this is made availablethrough the national standards body. The handbook will always beavailable from ISO directly if a national standards body decides not toadopt it. The Handbook is currently being translated into a number ofdifferent languages and national standards bodies will be able totranslate it into their own language should they choose to.Is there a draft of the guidefor smaller organizationsissued?Drafts were not made available to users due to the speed theHandbook was developed and to ensure that anything made publicyavailable was sufficiently developed to provide accurate advice,properly aligned to ISO 45001.ISO 45003 - general questionsWill we need special skills toperform risk assessment forthese psychological needs?ISO 45003 provides practical guidance, with many examples, to helpnon-specialist workers assess psychosocial risks effectively. Specialisedtraining/skills can be useful to assess risks and manage psychologicalhealth, but it is recognised that this is not always an option, so theseguidelines aim to assist all organizations even where there is nospecialist knowledge.Will you be linking emotionalstress in ISO 45003? Does ISO45003 address PTSD?ISO 45003 addresses all types of psychosocial risks, including differenttypes of stress. It does not include specific guidance on PTSD.
How can we deal with personwith underlying conditionswhile respect their privacywithout compromising thelaw, say HIPAA in the US?Legislation and regulation always take precedence over requirementsin standards, therefore these must always be considered first. Whensupporting a worker with underlying conditions, the organizationshould consult with the worker on any personal information to beaccessed and retained by the organization and why this is needed.Additionally the organization should make clear how that data will beprocessed, how access will be controlled, and how confidentiality willbe maintained. Where possible such information should beanonymized.What is the modality ofperforming audits of ISO45003?ISO 45003 contains guidance, rather than requirements, therefore it isnot a standard designed for separate audit. However this guidance canbe used as a basis for assessing how psychosocial risks are beingmanaged within an overall OH&S management system, for example aspart of an ISO 45001 audit.When an organizationimplements ISO 45001 theyshould analyse thepsychosocial risks, or onlywhen implementing ISO45003?ISO 45001 requires the organization to identify and assess OH&S risksto its workers, so this already includes psychosocial risks. ISO 45003provides additional guidance on this aspect of OH&S as it is a subjectmany organizations have limited knowledge of and lack thecompetence to manage the risks effectively, yet it is also becomingincreasingly significant for many.Is it possible to add a chapterin ISO 450003, including tipson how to raise awarenessabout psychological risks inthe work place in developingcountries, where mentalhealth is still highly neglected.ISO 45003 provides tips on raising awareness of psychosocial risks forany organization in any setting - mental health is neglected in manycountries, not just in the developing world, so the guidelines addressthis as widely as possible. ISO/TC 283 is also exploring the particularneeds of developing countries, however, through the establishment ofa new developing countries coordination group, so if further specificguidance is deemed useful we can consider developing something at alater date.Most of the psychosocial risksin an organization aremanaged by the HumanResource department throughtheir Health and Wellnessprogrammes. However, theorganizations do not want toclassify these risks asoccupational risks. How doesone educate the organizationthat
ISO 45001 - general questions ISO 45001 is good, but the enforcement is very important. So how is committee helping to enforce it? For most organizations the application of ISO 45001, and the decision as to whether to seek certification, is a voluntary one, though in some specific situations the provisions of the standard may be included or