Transcription
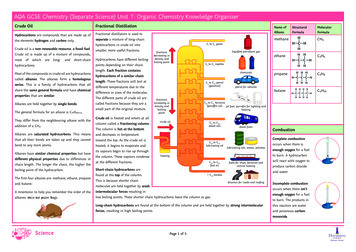
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 7: Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserCrude OilFractional DistillationHydrocarbons are compounds that are made up ofFractional distillation is used tothe elements hydrogen and carbon only.separate a mixture of long-chainCrude oil is a non-renewable resource, a fossil fuel.smaller, more useful fractions.Crude oil is made up of a mixture of rbons.Most of the compounds in crude oil are hydrocarbonscalled alkanes. The alkanes form a homologousseries. This is a family of hydrocarbons that allshare the same general formula and have chemicalproperties that are similar.Alkanes are held together by single bonds.The general formula for an alkane is CnH₂n ₂.They differ from the neighbouring alkane with theaddition of a CH₂.Hydrocarbons have different boilinglength. Each fraction containshydrocarbons of a similar chaindifferent temperatures due to thedifference in sizes of the small part of the original mixture.Crude oil is heated and enters at allcolumn called a fractioning column.CombustionThe column is hot at the bottomheated, it begins to evaporate andand butane.ethanecalled fractions because they are abond to any more atoms.The first four alkanes are: methane, ethane, propaneCH₄The different parts of crude oil aretoward the top. As the crude oil isboiling point of the hydrocarbon.methanelength. These fractions will boil atthat all their bonds are taken up and they cannotchain length. The longer the chain, the higher theMolecularFormulapoints depending on their chainand decreases in temperaturedifferent physical properties due to differences inStructuralFormulahydrocarbons in crude oil intoAlkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. This meansAlkanes have similar chemical properties but haveName ofAlkaneComplete combustionoccurs when there isenough oxygen for a fuelits vapours begin to rise up throughto burn. A hydrocarbonthe column. These vapours condensewill react with oxygen toat the different fractions.produce carbon dioxideShort-chain hydrocarbons areand water.found at the top of the column.This is because shorter chainIncomplete combustionmolecules are held together by weakoccurs when there isn’tA mnemonic to help you remember the order of theintermolecular forces resulting inalkanes: mice eat paper bags.low boiling points. These shorter chain hydrocarbons leave the column as gas.enough oxygen for a fuelto burn. The products inLong-chain hydrocarbons are found at the bottom of the column and are held together by strong intermolecularthis reaction are waterforces, resulting in high boiling points.and poisonous carbonmonoxide.Page 1 of 5visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 7: Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserCrackingTest for AlkanesCracking is an example of a thermal decomposition reaction. Long-chainBromine, when added to an alkane, will remain brown/hydrocarbons can be broken down into shorter, more useful hydrocarbonorange. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, they havechains.no double bonds which could be broken to accept theCracking can be carried out with a catalyst in catalytic cracking or withShort-Chain Moleculesbromine molecule and so remain orange.steam in steam cracking.Catalytic cracking involves heating a hydrocarbon to a high temperatureunsaturated hydrocarbons. The double bond breaks and(550 C) and passing over a hot catalyst.the bromine molecule is accepted.the boiling point of thebrown/orange to colourless. This is because alkenes arealkaneLong-Chain MoleculesAs chain length increases,Bromine, when added to an alkene, will change fromCracking of a long-chain hydrocarbon produces a short-chain alkane andIncreasing Chain Lengthhydrocarbon chains alsoincreases.alkenean alkene.thinViscosity describes howthickeasily a substance canflow e.g. treacle is veryno changeto bility is aMaking Polymersmeasure of how easily aThe fractional distillation of crude oil and crackingsubstance burns.produces an array of hydrocarbons that are key to oureveryday lives.Alkenes are used to produce plastics such as poly(ethene)which is used to make plastic bags, drinks bottles anddustbins. Poly(propene), another polymer, forms verystrong, tough plastic.Page 2 of 5visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 7: Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserAlkenes (Chemistry Only)Name ofStructural ns of Alkenes (Chemistry Only)Alcohols (Chemistry Only)Alkenes, just like alkanes, also undergo combustion reactions. AlkenesAlcohols all belong to the same homologous group. This is a group of organicrarely combust completely and tend to undergo incomplete combustion.When burning in the air, they produce a smoky flame.Alkenes have the functional group C C. This double bond between thecarbon atoms is able to undergo an addition reaction. This means thatthe double bond can break andwill accept another molecule.propeneC₃H₆Alkanes are unable to take partcompounds that have the same functional group (-OH, hydroxyl group) andthat have similar chemical properties but different physical properties to eachother. Note that alcohols all have the suffix ‘ol’.Name ofStructural FormulaMolecularAlcoholFormulamethanolCH₃OHin addition reactions as theirUseschemicalfeedstockfunctional group is C-C. Thismeans the bond cannot break inorder to accept a new tC₂H₅OHdrinks,with hydrogen in an additionreactioncalledfuels andhydrogenation.This particular reaction requirespenteneC₅H₁₀alcoholicsolventsa catalyst.propanolAlkenes can also react withC₃H₇OHfuels andsolventswater to produce an alcohol. Thisis called a hydration reaction.Alkenes are another type of hydrocarbon that is double bonded.The general formula for an alkene is CnH₂n.Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. In a chemical reaction,the double bond of the alkenes can break. This allows othermolecules to bond to it. Note that alkenes all have the suffix‘ene’.The type of compound producedcontains a hydroxyl group (-OH),butanolthis compound is an alcohol.(300 C)andfuels andsolventsThe reaction requires a nsalsooccurwith the group 7 elements, thehalogens. The reaction is called ahalogenation reaction. When analkene reacts with a halogen, analkyl halide is produced.Page 3 of 5visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 7: Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserFermentationCombustionOxidation of AlcoholThe alcohol that is found in beers, wines andComplete combustion occurs when there isAlcohols can be oxidised to produce a carboxylicspirits is called ethanol. Ethanol isn’t just used inenough oxygen for a fuel to burn. An alcoholacid. Carboxylic acids are a family of compoundsalcoholic drinks, it can also be used as a fuel inwill react with oxygen to produce carbon dioxidethat contain the functional group –COOH (carboxylvehicles. Ethanol is made through the process ofand water.group). Note that carboxylic acids have the suffixfermentation.ethanol oxygenFermentation is an anaerobic process and thismeans that it occurs without oxygen.glucosecarbon dioxide waterC₂H₅OH 3O₂2CO₂ 3H₂Oethanol carbon dioxideFor example:‘oic acid’. The carboxylic acids have varying physicalproperties but similar chemical properties.Oxidation can mean a number of different things:ethanoic acid ethanolethyl ethanoate waterName he loss of electrons, the addition of oxygen or themethanoicremoval of hydrogen. In a chemical equation, theacidHCOOHoxidising agent is represented as [O], this symbolmeans oxygen from the oxidising agent.ethanol oxidising agentCH₃CH₂OH 2[O]water, a warm temperature between 25-35 C andStage 1: CH₃CH₂OH [O]a reaction vessel that will allow carbon dioxide toStage 2: CH₃CHO [O]escape but not allow oxygen to get in.by a single-celled fungus called yeast. If theReactions with Sodium MetalWhen dropped into ethanol, sodium producesfermentation process will happen very slowly orsodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas. Methanol,not at all.propanol and butanol all undergo a similarreaction with sodium.The word equation for this reaction is:the process of fermentation will stop.sodium ethanol If oxygen is allowed to enter the reaction vessel, theThe symbol equation for this reaction is:the drink taste of �COOHCarboxylic acids are able to react with bases toproduce a salt and water. They are also able to reactsodium ethoxide hydrogen2Na 2C₂H₅OH butanoicC₃H₇COOHacidwith carbonates to produce a salt, water and carbondioxide.When a carboxylic acid is heated with an alcohol intoo hot, the enzymes may become denatured andethanol will oxidise and form ethanoic acid makingCH₃CHO H₂OethanoicCarboxylic Acidstemperature of the reaction mixture is too cold, theIf the reaction mixture containing the yeast becomesCH₃COOH H₂OThe equation can also be written in two stages.The first stage shows the formation of ethanal andthe second stage shows its oxidation.The fermentation process requires yeast, sugar andThe enzymes needed for fermentation are providedethanoic acid waterthe presence of an acid catalyst (usually concentratedsulfuric acid), an ester is formed. Esters typicallyCarboxylic acids are acidic due to the hydrogen in thefunctional group (COOH). When a carboxylic acid forms asalt, the hydrogen is lost and replaced with a metal.smell fruity and are used in perfumes. They have thefunctional group –COO-.2C₂H₅ONa H₂Page 4 of 5visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 7: Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserCarboxylic Acids - Higher Tier OnlyWhen dissolved in water, carboxylic acids are ableto form acidic solutions. The pH of the solution isless than 7. They are weak acids. Carboxylic acidsolutions contain fewer hydrogen ions comparedwith a solution that is the same concentration andcontains a strong acid. Strong acids are fully ionisedin solution whereas weak acids are only partiallyionised in solution.Addition PolymerisationAddition polymerisation occurs when two or moreBiological PolymersAmino Acids – Higher Tier OnlyDNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is an example of aThere are 20 different types of amino acids and when arranged in a particular order, they produce thenaturally occurring polymer. DNA is a doubleproteins that are found within our cells.helix (twisted ladder) and it is made up of twopolymer chains that are twisted to form a doublehelix. The monomers of the two polymer chainsare called nucleotides. The four nucleotides inAn amino acid is a molecule that has two functional groups. The amine group (NH₂) and the carboxyl group(COOH). In between these two functional groups is a single carbon atom with a hydrogen atom bonded to it,along with another group.DNA are called adenine, guanine, cytosine andAmino acids bond together through the process of a condensation polymerisation reaction.thyroxine. The nucleotide sequence codes for genes.For every monomer (amino acid) that is added to the growing chain of the polymer, a molecule of water isGenes are sections of DNA that determine anproduced.organisms characteristics.Amino Acid StructureAmino Acid Structurehyrdogenhyrdogenaminocarboxyl aminocarboxylmonomers join together to form a polymer.For example, during the polymerisation of ethene,etcmany monomers (single units of ethene) are joinedtogether to make poly(ethene). Poly meaning ‘many’R-group(variant)(many ethene molecules joined together).The number of ethene molecules that are joinedetcR-group(variant)together could be in the thousands, therefore,when writing the equation the letter ‘n’ is used torepresent the large number of molecules.Amino Acids – Higher Tier OnlyNotice that the monomer of ethene has a doublebond. When it bonds to form poly(ethene) thedouble bond breaks and a single bond is formed.Proteins are another example of a naturally occurringpolymer. Proteins are made from individual monomerunits called amino acids. Proteins have many roleswithin our bodies; all enzymes are made fromAddition polymerisation requires themonomers to have a C C double bond.Condensation polymerisation does notrequire a C C double bond but doesproteins.need two functional groups. When twoPlants make the biological polymers starch andusually produced.monomers react, a water molecule iscellulose. They are made up of individual monomerunits of sugar molecules. Plants use starch as a wayto store energy. Cellulose is used by plants to give thecell wall strength.An example of a condensation polymeris polyester. Polyester is made from onemonomer that has two hydroxyl groupsand another monomer which has twocarboxylic acid groups.Page 5 of 5visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Separate Science) Unit 7: Organic Chemistry Knowledge Organiser Crude Oil Hydrocarbons are compounds that are made up of the elements hydrogen and carbon only. Crude oil is a non-renewable resource, a fossil fuel. Crude oil is made up of a mixture of compoun










