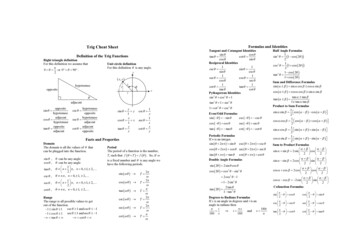
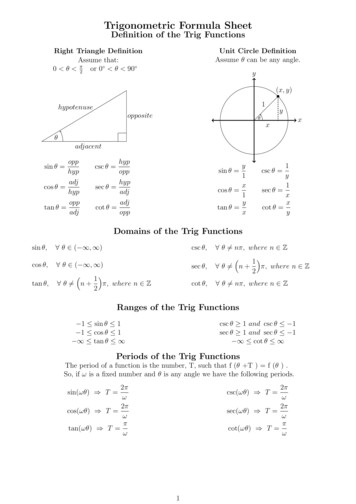
Transcription
CSC 170 – Introduction toComputers and Their ApplicationsLecture #2 – Digital Audio BasicsDigital Audio Basics Digital audio is music, speech, and othersounds represented in binary format for use indigital devices. Most digital devices have a built-inmicrophone and audio software, so recordingexternal sounds is easy.1
Digital Audio Basics To digitally record sound, samples of a soundwave are collected at periodic intervals andstored as numeric data in an audio file. Sound waves are sampled many times persecond by an analog-to-digital converter. A digital-to-analog converter transforms thedigital bits into analog sound waves.Digital Audio Basics2
Digital Audio Basics Sampling rate refers to the number of timesper second that a sound is measured during therecording process. Higher sampling rates increase the quality ofthe recording but require more storage space.Digital Audio File Formats A digital file can be identified by its type or itsfile extension, such as Thriller.mp3 (an audiofile). The most popular digital audio formats are:AAC, MP3, Ogg, Vorbis, WAV, FLAC, andWMA.3
Digital Audio File FormatsAUDIO FORMATEXTENSIONADVANTAGESDISADVANTAGESAAC (Advanced AudioCoding).aac, .m4p, or .mp4Very good sound qualitybased on MPEG-4; lossycompression; used foriTunes musicFiles can be copy protectedso that use is limited toapproved devicesMP3 (also called MPEG-1Layer 3).mp3Good sound quality; lossycompression; can bestreamed over the WebMight require a standaloneplayer or browser pluginOgg Vorbis.OggFree, open standard; lossycompression; supported bysome browsersSlow to catch on as apopular standard; part ofGoogle's WebM formatDigital Audio File FormatsAUDIO FORMATEXTENSIONADVANTAGESDISADVANTAGESWAV.WavGood sound quality;supported in browserswithout a pluginAudio data is stored in raw,noncompressed format, sofiles are very largeFLAC (Free LosslessAudio Compression).flacExcellent sound quality;lossless compressionOpen source format supportported by many devicesWMA (WindowsMedia Audio).wmaLossy or losslesscompression; very goodsound quality; used onseveral music downloadsitesFiles can be copy protected;requires an add-on playerfor some devices4
Digital Audio File Formats Ripping is a slang term that refers to theprocess of importing tracks from a CD or DVDto your computer’s hard disk. The technical term for ripping music tracks isdigital audio extraction. A download copies a file from a privatenetwork or Internet server to a local device. Audio files can be acquired as a live stream oron-demand stream in addition to downloads.Digital Audio File Formats5
Digital Audio File Formats To play a digital audio file, you must use sometype of audio software, such as:– Audio players: small standalone software application ormobile app.– Audio plugins: software that works in conjunction withyour computer’s browser to manage and play audio from aWeb page.– Audio software: general-purpose software and apps usedfor recording, playing, and modifying audio files, such asiTunes, Windows Media Player, and Audacity.Digital Audio File Formats6
MIDI MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) specifiesa standard way to store music data for synthesizers,electronic MIDI instruments, and computers. MIDI messages are instructions that specify the pitchof a note, the point at which the note begins, thevolume of the note, etc. An MIDI message may look like this:MIDI Music compositionsoftware with MIDIsupport makes it easy toplace notes on a screenbased music staff thenplay back thecomposition on a MIDIkeyboard or through thespeakers of a digitaldevice.7
Digitized Speech Speech synthesis is the process by whichmachines produce sound that resemblesspoken words. Speech recognition (or voice recognition)refers to the ability of a machine to understandspoken words.Digitized Speech Speech recognition software analyzes thesounds of your voice and converts each wordinto groups of phonemes (basic sound units). The software then compares the groups to thewords in a digital dictionary to find a match. When a match is found, the software candisplay the word on the screen or use it tocarry out a command.8
Digitized Speech9
Digital Audio Basics To digitally record sound, samples of a sound wave are collected at periodic intervals and stored as numeric data in an audio file. Sound waves are sampled many times per second by an analog-to-digital converter. A digital-to-analog converter transforms the digital bits into analog so