Transcription
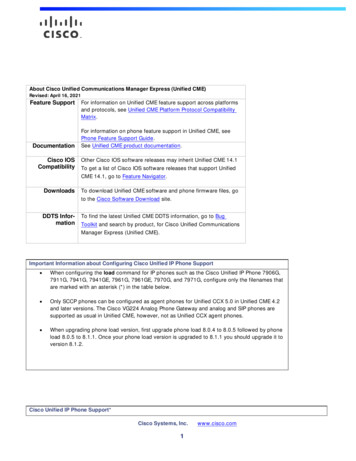
Ganado Unified School District #206th Grade MathPACING Guide SY 2021-2022Resources AZ College and Career ReadinessStandardMcGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.RP.A.1Understand the concept of a ratioand use ratio language betweentwo quantities. For example, “Theratio of wings to beaks in the birdhouse at the zoo was 2:1, becausefor every 2 wings there was 1beak.” “For every vote candidateA received, candidate C receivednearly three votes.”McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.RP.A.2Understand the concept of a unitrate a/b associated with a ratio a :b with b 0, and use ratelanguage (e.g., for every, for each,for each 1, per) in the context of aratio relationship. (Complexfractions notations is notexpectation for unit rates in thisgrade level.)Essential Question (HESS Matrix)1st QuarterBloom’s Taxonomy: Application ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Learning GoalVocabulary(Content/Academic)I will be able to: Understand the concept of aratio. Use ratio language todescribe a ratio relationshipbetween two quantities. ratiotermscoordinate planeequivalent ratioI will be able to: understand the concept of aunit rate a/b associated witha ratio a:b with b not equalto 0 use rate language in thecontext of a ratiorelationship rateunit rategraphgreatest commonfactorleast commonmultipleEssential Question(s): What are ratios and ratesand how are they used insolving problems?Bloom’s Taxonomy: Application ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): What are ratios and ratesand how are they used insolving problems? Page 1Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.RP.A.3Use ratio and rate reasoning tosolve mathematical problems andproblems in real-world context(e.g., by reasoning about datacollected from measurements,tables of equivalent ratios, tapediagrams, double number linediagrams, or equations).a. Make tables of equivalentratios relating quantities withwhole-numbermeasurements, find missingvalues in the tables, and plotthe pairs of values on thecoordinate planes. Use tablesto compare ratios.b. Solve unit rate problemsincluding those involving unitpricing and constant speed.c. Find a percent of a quantity asa rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of aquantity means 30/100 timesthe quantity). Solve percentproblems with the unknownin all positions of theequation.d. Use ratio reasoning to convertmeasurement units;manipulate and transformunits appropriately whenmultiplying or dividingquantities.What procedures can beused to solve proportions?Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2 DOK Level 3Essential Question(s): What are ratios and ratesand how are they used insolving problems? What procedures can beused to solve proportions? What is the meaning ofpercent? How can percent beestimated and found?I will be able to: use ratio and rate reasoningto solve real-world andmathematical problems,e.g., by reasoning abouttables of equivalent ratios,tape diagrams, doublenumber line diagrams, orequations make tables of equivalentratios relating quantitieswith whole-numbermeasurements find missing values in thetables plot the pairs of values onthe coordinate plane use tables to compare ratios solve unit rate problemsincluding those involvingunit pricing and constantspeed find a percent of a quantityas a rate per 100 (e.g., 30%of a quantity means 30/100times the quantity) solve problems involvingfinding the whole, given apart and the percent use ratio reasoning toconvert measurement units manipulate unitsappropriately when proportionfractiondecimalpercentordered pairrateunit timilli-Page 2Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART Board6.NS.A.1Interpret and compute quotientsof fractions to solve mathematicalproblems and problems in realworld context involving division offractions by fractions using visualfraction models and equations torepresent the problem. Forexample, create a story contextfor 2/3 3/4 and use a visualfraction model to show thequotient; use the relationshipbetween multiplication anddivision to explain that 2/3 3/4 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. Ingeneral, a/b c/d ad/bc.6.NS.B.2Fluently divide multi-digitnumbers using a standardalgorithm.Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How can numbers be brokenapart into factors? How can fractions berepresented and simplified? How are decimals andfractions related? What are standardprocedures for estimatingand finding products offractions and mixednumbers? What are standardprocedures for estimatingand finding quotients offractions and mixednumbers?Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2multiplying or dividingquantities transform unitsappropriately whenmultiplying or dividingquantitiesI will be able to: interpret quotients offractions compute quotients offractions solve word problemsinvolving division offractions by fractions I will be able to: subtract with regrouping multiply multi-digit numbers divide multi-digit numbers use standard algorithm plest form;lowest terms;simplifying;reducingproper fractionimproper fractionmixed natorsunlikedenominatorsleast otienttraditionalmethodpartial quotientsPage 3Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
ALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online) McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online) McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.NS.B.3Fluently add, subtract, multiply,and divide multi-digit decimalsusing a standard algorithm foreach operation.Essential Question(s): What are whole numbersplace values? How can whole numbers bewritten, compared, andordered? use algebra notation toshow different ways to writemultiplication and division double downdivisionBloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationI will be able to: add multi-digit decimals subtract multi-digit decimals multiply multi-digit decimals divide multi-digit decimals use standard algorithm ngdecimalsnon-terminatingdecimalHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): What are wholenumbers/decimal placevalues? How can wholenumbers/decimals bewritten, compared, andordered? How are sums anddifferences involvingdecimals estimated andfound?6.NS.B.4Use previous understanding offactors to find the greatestcommon factor and the leastcommon multiple.a. Find the greatest commonfactor of two whole numbersless than or equal to 100.b. Find the least commonmultiple of two wholeGanado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How can numbers be brokenapart into factors? How can fractions berepresented and simplified? I will be able to: find the GCF of two wholenumbers less than or equalto 100. find the LCM of two wholenumbers less than or equalto 12. use the distributive propertyto express the sum of 2whole numbers factormultipledivisibleprime numbercompositenumberprimefactorizationfactor treegreatest commonfactor (GCF)Page 4
numbers less than or equal to12.c. Use the distributive propertyto express a sum of two wholenumbers 1 to 100 with acommon factor as a multipleof a sum of two wholenumbers with no commonfactor. For example, express36 8 as 4(9 2). McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.NS.C.5Understand that positive andnegative numbers are usedtogether to describe quantitieshaving opposite directions orvalues. Use positive and negativenumbers to represent quantitiesin real-world context, explainingthe meaning of 0 in eachsituation.McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.NS.C.6Understand a rational number canbe represented as a point on thenumber line. Extend number linediagrams and coordinate axesfamiliar from previous grades torepresent points on the line and inthe plane with negative numbercoordinates.a. Recognize opposite signs ofnumbers as indicatinglocations on opposite sides of0 on the number line; common multipleleast commonmultiple (LCM)I will be able to: understand that /numbers are used todescribe quantities havingopposite directions or values use /- numbers torepresent quantities in realworld context explain the meaning of 0 ineach situation oppositesinteger(s)absolute valueI will be able to: understand a rationalnumber as a point on thenumber line extend number linediagrams and coordinateaxes familiar from previousgrades recognize opposite signs ofnumbers indicating locationson opposite sides of 0 oppositesinteger(s)absolute valuerationalnumber(s)coordinate planeaxesx-axisy-axisquadrant(s)order pair(s)originWhat are standardprocedures for estimatingand finding sums anddifferences of fractions andmixed numbers?2nd QuarterBloom’s Taxonomy: Application ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How are integers related towhole numbers?Bloom’s Taxonomy: Application ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How are integers related towhole numbers? Page 5Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
recognize that the opposite ofthe opposite of a number isthe number itself and that 0 isits own opposite.b. Understand signs of numbersin ordered pairs as indicatinglocations in quadrants of thecoordinate plane; recognizethat when two ordered pairsdiffer only by signs, thelocations of the points arerelated by reflections acrossone or both axes.c. Find and position integers andother rational numbers on ahorizontal or vertical numberline diagram; find and positionpairs of integers and otherrational numbers on acoordinate plane. McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.NS.C.7Understand ordering and absolutevalue of rational numbers.a. Interpret statements ofinequality as statementsabout the relative position oftwo numbers on a numberline.b. Write, interpret, and explainstatements of order forrational numbers in real-worldcontext.Bloom’s Taxonomy: Application ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How are integers related towhole numbers?recognize that the oppositeof the opposite of a numberis the number itself understand signs ofnumbers in ordered pairs asindicating locations inquadrants of the coordinateplane recognize that when twoordered pairs differ only besigns, the locations of thepoints are related byreflections across one orboth axes find integers on a horizontalor vertical number line position integers on ahorizontal or verticalnumber line find pairs of integers andother rational numbers on acoordinate plane position pairs of integersand other rational numberson a coordinate planeI will be able to: understand ordering ofrational numbers understand absolute valueof rational numbers interpret statements ofinequality as statementsabout the relative positionof two numbers on anumber line oppositesinteger(s)absolute valuerationalnumber(s)inequalityPage 6Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
c. Understand the absolutevalue of a rational number asits distance from 0 on thenumber line; interpretabsolute value as magnitudefor a positive or negativequantity in real-world context.d. Distinguish comparisons ofabsolute value fromstatements about order inmathematical problems andproblems in real-worldcontext. McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.NS.C.8Solve mathematical problems andproblems in real-world context bygraphing points in all fourquadrants of the coordinateplane. Include use of coordinatesand absolute value to finddistances between points with thesame first coordinate or the samesecond coordinate.Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationMcGraw-Hill MathTextbook6.EE.A.1Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationGanado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)HESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How are integers related towhole numbers?write statements of orderfor rational numbers in realworld context explain statements of orderfor rational numbers in realworld context understand the absolutevalue of a rational numberas its distance from 0 on anumber line interpret absolute value asmagnitude for a /- quantityin a real-world situation distinguish comparisons ofabsolute value fromstatements about orderI will be able to: solve real-world problemsby graphing points in all fourquadrants of the coordinateplane solve mathematicalproblems by graphing pointsin all four quadrants of thecoordinate plane include use of coordinates tofind distances betweenpoints with the same firstcoordinate or the samesecond coordinate include use of absolutevalue to find distancesbetween points with thesame first coordinate or thesame second coordinateI will be able to: coordinate planex-axisy-axisquadrant(s)ordered pairsorigin standard formexpanded formPage 7
PowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)Write and evaluate numericalexpressions involving wholenumber exponents. EvaluationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2 DOK Level 3Essential Question(s): What are whole numbersplace values? How can whole numbers bewritten, compared, andordered?6.EE.A.2Write, read, and evaluatealgebraic expressions.a. Write expressions that recordoperations with numbers andvariables.b. Identify parts of an expressionusing mathematical terms(sum, term, product, factor,quotient, and coefficient);view one or more parts of anexpression as a single entity.c. Evaluate expressions givenspecific values of theirvariables. Include expressionsthat arise from formulas usedto solve mathematicalproblems and problems inreal-world context. Performarithmetic operations,including those involvingwhole-number exponents, inthe conventional order whenthere are no parentheses toBloom’s Taxonomy: Application Comprehension EvaluationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 1 DOK Level 2 DOK Level 3Essential Question(s): What are algebraicexpressions and how canthey be written andevaluated? What arithmetic numberrelationships, calledproperties, are always true? read and write numbers totrillions in standard,expanded, and word formand give the values ofspecific digitswrite numerical expressionsinvolving whole-numberexponentsevaluate numericalexpressions involving wholenumber exponents word formtrillionperiodbaseexponentpowerexponential formsquaredcubedrootI will be able to: write expressions in whichletters stand for numbers read expressions in whichletters stand for numbers evaluate expressions inwhich letters stand fornumbers write expressions thatrecord operations withnumbers and with lettersstanding for numbers identify parts of anexpression usingmathematical terms view one or more parts of anexpression as a single entity evaluate expressions at theirspecific values of theirvariables include expressions thatarise from formulas used inreal-world problems variabletermvariable termconstant tioninput/outputtablefactor Page 8Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
specify a particular order(Order of Operations). McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.EE.A.3Apply the properties of operationsto generate equivalentexpressions. For example, applythe distributive property to theexpression 3 (2 x) to produce theequivalent expression 6 3x.Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2perform arithmeticoperations, including thoseinvolving whole-numberexponents, in theconventional order whenthere are no parenthesesorder (Order of Operations)I will be able to: apply the properties ofoperations to generateequivalent expressions Essential Question(s): What are algebraicexpressions and how canthey be written andevaluated? What arithmetic numberrelationships, calledproperties, are always true? McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART Board6.EE.A.4Identify when two expressions areequivalent. For example, theexpressions y y y and 3y areequivalent because they name thesame number regardless of whichnumber y stands for.Bloom’s Taxonomy: ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2I will be able to: identify when twoexpression are equivalent commutativeproperty ofadditioncommutativeproperty ofmultiplicationassociativeproperty ofadditionassociativeproperty ofmultiplicationidentity propertyof additionidentity propertyof multiplicationorder onequationequationaddition propertyof equalitysubtractionproperty ofequalityEssential Question(s):Page 9Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
ALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online) What procedures can beused to solve equations? 3rd Quarter6.EE.B.5Bloom’s Taxonomy:Understand solving an equation or Applicationinequality as a process of Comprehensionreasoning to find value(s) of thevariables that make that equation HESS Matrix:or inequality true. Use DOK Level 2substitution to determinewhether a given number in aEssential Question(s):specified set makes an equation How are sums, differences,or inequality true.products, and quotientsinvolving decimals estimatedand found? What procedures can beused to solve equations? How can equations begraphed? What patterns can be foundin the graph of equations?6.EE.B.6Use variables to representnumbers and write expressionswhen solving mathematicalproblems and problems in realworld context; understand that avariable can represent anunknown number or any numberin a specified set.Bloom’s Taxonomy: Application ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): What are algebraicexpressions and how canmultiplicationproperty ofequalitydivision propertyof equalityI will be able to: understand solving anequation or inequality as aprocess of answering aquestion use substitution todetermine whether a givennumber in a specified setmakes an equation orinequality true inequalityinverserelationshipI will be able to: use variables to representnumbers write expressions whensolving real-world problem write expressions whensolving mathematicalproblems understand that a variablecan represent an unknown verserelationship Page 10Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART Board6.EE.B.7Solve mathematical problems andproblems in real-world context bywriting and solving equations ofthe form x p q, x – p q, px q, and x/p q for cases in which p,q, and x are all non-negativerational numbers.6.EE.B.8Write an inequality of the form x c, x c, x c, or x c to representa constraint or condition to solvemathematical problems andproblems in real-world context.they be written andevaluated?What arithmetic numberrelationships, calledproperties, are always true?How are sums, differences,products, and quotientsinvolving decimals estimatedand found?What procedures can beused to solve equations?Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): What procedures can beused to solve equations? What are standardprocedures for estimatingand finding quotients offractions and mixednumbers? How can equations begraphed? What patterns can be foundin the graphs of equations?Bloom’s Taxonomy: Application ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2number, or depending onthe purpose at hand, anynumber in a specific setI will be able to: solve real-world problemsby writing equations of theform x p q and px q forcases in which p, q and x areall nonnegative rationalnumbers solve mathematicalproblems by solvingequations of the forms x p q and px q for caseswhich p, q, and x arenonnegative rationalnumbers I will be able to: write an inequality of theform x c or x c torepresent a constraint orcondition in a real-world ormathematical problem equationaddition propertyof equalitysubtractionproperty ofequalitymultiplicationproperty ofequalitydivision propertyof equalityinverserelationshipinequalityPage 11Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
ALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)Recognize that inequalities haveinfinitely many solutions;represent solutions of suchinequalities on number lines. McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.EE.C.9Use variables to represent twoquantities that change inrelationship to one another tosolve mathematical problems andproblems in real-world context.Write an equation to express onequantity (the dependent variable)in terms of the other quantity (theindependent variable). Analyzethe relationship between thedependent and independentvariables using graphs and tables,and relate these to the equation.Bloom’s Taxonomy: Application AnalysisMcGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.G.A.1Find the area of right triangles,other triangles, specialquadrilaterals, and polygons bycomposing into rectangles ordecomposing into triangles andother shapes; apply thesetechniques to solve mathematicalproblems and problems in realworld context.Bloom’s Taxonomy: Application Essential Question(s): How can equations begraphed? What patterns can be foundin the graphs of equations?HESS Matrix: DOK Level 3Essential Question(s): How can equations begraphed? What patterns can be foundin the graph of equations?HESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): What are standardprocedures for estimatingand finding products offractions and mixednumbers?recognize that inequalitiesof the x c or x c haveinfinitely many solutions;represent solutions of suchinequalities on number linediagramsI will be able to: use variables to representtwo quantities in a realworld problem that changein relationship to oneanother write an equation to expressone quantity, thought of asthe dependent variable, interms of the other quantity,thought of as theindependent variable analyze the relationshipbetween the dependent andindependent variables usinggraphs and tables, andrelate these to the questionI will be able to: find the area of righttriangles find the area of othertriangles find the area of specialquadrilaterals find the area of polygons bycomposing into rectangles find the area of polygons bydecomposing into trianglesand other shapes formulaT-tablelinear acute angleright angleobtuse anglestraight angleacute triangleright triangleobtuse triangleequilateraltriangleisosceles trianglescalene trianglePage 12Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentations6.G.A.2Find the volume of a rightrectangular prism with fractionaledge lengths by packing it withunit cubes of the appropriate unitfraction edge lengths, and showthat the volume is the same aswould be found by multiplying theedge lengths of the prism.Understand and use the formula V B · h, where in this case, B is thearea of the base (B l x w) to findvolumes of right rectangularprisms with fractional edgelengths in mathematical problemsand problems in real-worldcontext.6.G.A.3Draw polygons in the coordinateplane given coordinates for thevertices; use coordinates to findHow can angles bemeasured, drawn, andclassified?What are special shapes andhow can they be describedand compared?What are the meanings ofperimeter and area?How can the perimeter andarea of certain shapes befound?Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): What is the meaning ofvolume and how can volumebe found? What is the meaning ofsurface area and how cansurface area be found? How can the volume ofcertain figures be found?4th QuarterBloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: ngthwidth2-dimensionalfiguresI will be able to: find the volume of a rightrectangular prism withfractional edge lengths bypacking it with unit cubes ofthe appropriate unit fractionedge lengths show that the volume is thesame as would be found bymultiplying the edge lengthsof the prism apply the formulas V l w hand V b h to find thevolumes of right rectangularprisms with fractional edgelengths in the context ofsolving real-world andmathematical problems formulavolumecubeI will be able to: draw polygons in thecoordinate plane givencoordinates for the vertices pointlinerayline segment apply these techniques inthe context of solving realworld problemsapply these techniques inthe context of solvingmathematical problemsPage 13Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
WorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)the length of a side joining pointswith the same first coordinate orthe same second coordinate.Apply these techniques to solvemathematical problems andproblems in a real-world context. McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.G.A.4Represent three-dimensionalfigures using nets made up ofrectangles and triangles, and usethe nets to find the surface areaof these figures. Apply thesetechniques to solve mathematicalproblems and problems in realworld context.Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationMcGraw-Hill A.1Recognize a statistical question asone that anticipates variability inthe data related to the questionand accounts for variability in theBloom’s Taxonomy: ComprehensionDOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How are integers related towhole numbers? How can angles bemeasured, drawn, andclassified? What are special shapes andhow can they be describedand compared?HESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): What is the meaning ofarea? How can the area of certainshapes be found? What is the meaning ofvolume and how can volumebe found? What is the meaning ofsurface area and how cansurface area be found? How can the volume ofcertain figures be found?HESS Matrix: DOK Level 1 use coordinates to find thelength of a side joiningpoints with the same firstcoordinate or the samesecond coordinateapply these techniques inthe context of solving realworld and mathematicalproblems congruent linesegmentsmidpointintersecting linesplaneparallel linesperpendicularlinesI will be able to: represent three-dimensionalfigures using nets made upof rectangles and triangles using the nets to find thesurface area of these figures apply these techniques inthe context of solving realworld and mathematicalproblems revertexsurface arealengthwidthheight3-dimensionalfiguresI will be able to: recognize a statisticalquestion as one thatanticipates variability in thedata related to the question statisticalquestionPage 14Ganado USD – PACING GUIDE (MATH/6TH GRADE)
SMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online) McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online) answers. For example, "How oldam I?" is not a statisticalquestion, but "How old are thestudents in my school?" is astatistical question because oneanticipates variability in students'ages6.SP.A.2Understand that a set of datacollected to answer a statisticalquestion has a distribution whosegeneral characteristics can bedescribed by its center, spread,and overall shape.Essential Question(s): How can graphs be used torepresent data and answerquestions?Bloom’s Taxonomy: ComprehensionHESS Matrix: DOK Level 1Essential Question(s): How can graphs be used torepresent data and answerquestions?McGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKSconnected.mcgrawhill (Online)6.SP.A.3Recognize that a measure ofcenter for a numerical data setsummarizes all of its values with asingle number, while a measure ofvariation uses a single number todescribe the spread of the dataset.Bloom’s Taxonomy: ComprehensionMcGraw-Hill MathTextbookPowerPointPresentationsWorksheetsSMART BoardALEKS6.SP.B.4Display and interpret numericaldata by creating plots on anumber line including histograms,dot plots, and box plots.Bloom’s Taxonomy: ApplicationHESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s): How can graphs be used torepresent data and answerquestions?HESS Matrix: DOK Level 2Essential Question(s):and accounts for it in theanswersI will be able to: understand that a set ofdata collected to answer astatistical question has adistribution, which can bedescribed by its center,s
6th Grade Math PACING Guide SY 2021-2022 Resources AZ College and Career Readiness Standard Essential Question (HESS Matrix) Learning Goal Vocabulary (Content/Academic) 1st Quarter 6.RP.A.1McGraw-Hill Math Textb