Transcription
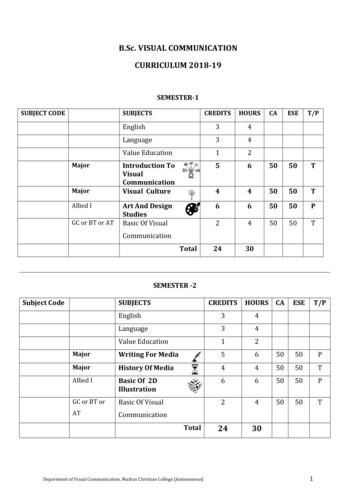
B.Sc. VISUAL COMMUNICATIONCURRICULUM 2018-19SEMESTER-1SUBJECT CODESUBJECTSMajorMajorAllied IGC or BT or ATCREDITSHOURSCAESET/PEnglish34Language34Value Education12Introduction ToVisualCommunicationVisual Culture565050T445050TArt And DesignStudiesBasic Of Visual665050P245050T2430CommunicationTotalSEMESTER -2Subject CodeSUBJECTSCREDITSHOURS CAESET/PEnglish34Language34Value Education12MajorWriting For Media565050PMajorHistory Of Media445050TAllied IBasic Of 2DIllustration665050PGC or BT orBasic Of Visual245050TATCommunication2430TotalDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]1
SEMESTER- 3Subject CodeSUBJECTSCREDITHOURS CAESET/PSEnglish34Language34Personality Development-2MajorBasic Photography445050PMajorManagement &445050TMarketing for MediaMajorComputer Graphics445050PAllied IIElective: Media Theories/ Media Psychology445050TIDEPresentation Skills342530HOURS CAESET/PTotalSEMESTER - 4Subject CodeSUBJECTSCREDITSEnglish34Language34Personality Development32MajorFilm Studies455050TMajorAdvertising & Public445050TRelationsMajorResponsive Web Design335050PAllied IIElective: RadioJockeying /Video JockeyingEnvironmental Studies445050P242630TotalDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]2
SEMESTER – 5Subject CodeSUBJECTSCREDITSHOURS CAESET/PMajorMedia Research445050TMajorMedia Laws & Ethics345050TMajor3D Modelling And685050PAnimationMajorTelevision 325050PCreative Painting345050P2530HOURS CAESET/PTotalSEMESTER – 6Subject CodeSUBJECTSCREDITSMajorInstructional --5050PExtensionActivitiesPhysical Education1Service Learning ProgramNSS/NCC/SPORTS/SCRUBDept Association ActivitiesTotal1630Grand Total140180(Sem1 to 6)CreditsHoursApart from the above requirements student is expected to have completed a mandatoryinternship program during his/her second year for a period of one month.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]3
SEMESTER IDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]4
INTRODUCTION TO VISUAL COMMUNCIATIONCODE:I YEAR – I SEMESTER – MAJOR - TCREDITS: 5HOURS: 6OBJECTIVEØ To provide the fundamentals of Human CommunicationØ To understand the models of Communication and mass mediaØ To give an idea about visual analysis and technologies.UNIT ICommunication - Definition, Need for Human Communication and VisualCommunication. Types & Levels Of Communication, Barriers Of Communication, Typesof Mass Media, Functions & Characteristics of Mass Media and Mass Audience.UNIT IIElements Of Communication, Western Models Of Communication – Aristotle,Lasswell, Shannon And Weaver, Osgood And Schramm, SMCR - Berlo, Knapp’s ModelsOf Relationship Escalation And Deterioration, Indian Theories Of Communication,Sadharanikaran Model.UNIT IIIUnderstanding Communication – Meaning Of Content, Connotation, Denotation,Culture, Signs, Symbols And Codes, Measuring The Levels Of Communication –Technical, Semantic And Pragmatic.UNIT IVVisual Process, Visual and Sensory Perception, Colour Psychology, Optical/VisualIllusion, Visual Saturation. Visual Technologies- Virtual & Media Reality, ArrestingReality, Space and Perspective, New Trends in Visual Technologies.UNIT VReading the Visual- seeing as Reading, The Habitus and Cultural Literacies, popculture, Seeing in Context, Time And Motion, Text And Inter-Text. Selling the VisualMedia as a Commodity.METHODOLOGY:Topics will be taught through Lectures, Assignment, and Discussions which will be aidedby Seminars, Role Play, Debates, Brain Storming Sessions, A/V Content and published materialsto provide and enhance the subject knowledge.REFERENCE:KEY TEXT1. Nancy Bonvillain Language, Culture, and Communication 7th Edition2. Keval J. Kumar (2012) Mass Communication in India. 4th Edition3. Tony Schirato and John Webb (2004) Understanding the Visual. SAGE Publications.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]5
PRINT SOURCE1. Marcel Danesi Ph. D. Messages, Signs, and Meanings: A Basic Textbook in Semiotics andCommunication (Studies in Linguistic and Cultural Anthropology) 3rd Edition2. Lester (2000) Visual Communication: Images and Message. Thomson Learning Press3. Arthur Asa Berger (1982) Seeing is to believe. An introduction to Visual Communication.Prentice Hall4. Mc Graw Hill, Otto G. Ocvrik, Tolbert E. Stinson, Philit R. Wigg, Robert O. Bone, David L.Cayton (1998) Art Fundamentals – Theory and Practice.E-SOURCEhttp://www.iacact.com/?q am/10603/76571/7/07 beok Thomas Signs An Introduction to Semiocs 2nded 493c3eac9970a.pdfRECOMMENDED READING1. Michael Maher (July 25, 2016) The Seven Levels of Communication: Go from Relationshipsto Referrals2. Gregory Hartley, Maryann Karinch (January 1, 2010) The Body Language Handbook: Howto Read Everyone's Hidden Thoughts and IntentionsDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]6
VISUAL CULTURECODE:I YEAR – I SEM – MAJOR - TCREDITS: 4HOURS: 4OBJECTIVE:Ø To impart knowledge on visual arts and cultureØ To understand and appreciate the major art movement in India and in the westØ To improve the interpretation of communication through cultureUNIT IIntroduction to Visual Culture - Architecture, Painting- techniques of paintingand Sculpture – types of relief. Ancient Art, Egyptian Art - Mastaba, Pyramid, Egyptianlaw of frontality, Paintings, Egyptian Beliefs. Greek Art -Hellenes, Greek Philosophy,First Olympiad, Greek Column and its types, Theatre, Kouros figure, Greek Vases andpaintings. Roman Art –Emperor Augustus, Capitals, Vault, Pantheon, Basilica,Amphitheatre, Trajan’s Column, Head of an Unknown and Paintings.UNIT IIIntroduction to Christians Art –Mosaic, Calligraphy, stain glass. Examples fromMedieval Period, Early Christian Art, Byzantine Art, Romansque Art, Gothic Art.UNIT IIIRenaissance Period –Early And High Renaissance Period [Donatello, Giotto AndMasaccio, Leonardo Da Vinci, Michael Angelo, Titian, Raphael] Baroque Period,Rembrandt, Bernini, Caravaggio, What is Rococo?UNIT IVProtohistoric Period - Indus Valley Civilization , Architecture- Town planning,Privy, Great Bath, Granary, Lothal Key Plan, Sculpture – Bearded Man, Dancing Girl,Seals. Buddhist art – structures by Ashoka, Stupa, Stambha, Vedikas, Toranas. Ajantaand Ellora.UNIT VSouth Indian Temples –Rathas at Mamallapuram, Tanjore, Brahadeeswaratemple, Madurai Meenakshi Temple. Advent of Modern Art, Contemporary Indian Art,Introduction to Bengal School.METHODOLOGY:Theoretical inputs through classroom lectures and group exercises coupled with A/Vscreening, analysis of art through ages.REFERENCE:KEY TEXT1. Edith Tömöry (1989) A History of Fine Arts in India and the West2. Helen Gardner (1926) Gardner's Art Through the AgesDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]7
1. OUP India, B.N. Goswamy (5 Feb 2018)Oxford Readings in Indian Art2. Susie Hodge (September 6, 2016) Art in -server/eacharyadocuments/548158e2e41301125fd790cf INFIEP 72/94/ET/72-94-ET-V1-S1 06 /eacharyadocuments/548158e2e41301125fd790cf INFIEP 72/94/ET/72-94-ET-V1-S1 ic-25-lec.pdf’RECOMMENDED READING1. Elke Linda Buchholz, Susanne Kaeppele, Karoline Hille, Irina Stotland , Gerhard Buhler(1 Nov 2007) Art: A World History2. Anil Rao Sandhya Ketkar (2 Jan 2017) The History of Indian Art***Field Study to Santhome Cathedral - Early Christian Art and Architecture, St. Thomas MountChurch – Christian Art, Mamallapuram – Rathas, Shore Temple, Rock Cut Sculptures, Senji Fort –Indian Architecture.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]8
ART AND DESIGN STUDIESCODE:I YEAR – I SEM – ALLIED I - PCREDITS: 6HOURS: 6OBJECTIVE:Ø To provide knowledge on basics of drawingØ To understand and utilize the skills with different materialsØ To widen the perspectives on principles of design, typography and campaign designUNIT IBasics of Drawing: Line Study - Straight Line, Zigzag, Curves and Circles, Spiral,Knots, Waves. Shapes and Forms – 2D to 3D Drawing (Objects, Still Life, Leaves andTrees). Shading Techniques - Hatching, Cross Hatching, Stippling, Scumbling, Smudgingand Scribbling. Elements of Art – Dot, Line, Shape, Form, Value, Colour, Texture.UNIT IIMaterial Studies – Pencil, Pastel, Poster, Acrylic, Water Colour, Indian Ink andPen, Charcoal. Still Life, Principles of Still Life.UNIT IIIColour Study - Understanding Colours, Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Colours,Colour Wheel. Understanding Space, Colour, Light, and Shade through LandscapeStudies. Principles of Design - Balance, Proportion, Rhythm, Harmony, Perspective,Composition, Movement, Unity.UNIT IVTypography: Font Family – Serif and Sans Serif. Arial, Times New Roman, Impact,Comic Sans, Gothic, Calibri, Monotype Corsiva and Free Styling.UNIT VDesign and Types of Logo, Visiting Card, Letter Head, Poster, Brochure, Banner,Dangler, Bunting, Print Ad, Package Design, Mascot.METHODOLOGY: Extensive studio demonstrations and practical sessions [Indoor and Outdoor] Class projects will be assigned periodically with student having the option of workingindependently and submitting their work on the assigned dates Recurrent observations and criticisms will be done and guided accordinglyREFERENCE:KEY TEXT1. Guptill Arthur (1984) Free Hand Drawing Self-Taught. Watson Guptill Publication,Newyork.2. Paper Peony Press (October 27, 2017) Lettering and Modern Calligraphy: A Beginner'sGuide: Learn Hand Lettering and Brush Lettering. Paper Peony Press.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]9
1. Walter Foster Creative Team (September 1, 2005) Art of Basic Drawing: Discover simplestep-by-step techniques for drawing a wide variety of subjects in pencil -Collector'sSeries. Walter Foster Creative Team.2. PundalikVaze The Art of Shading Nature and Landscape. Jyotsna Prakasan MMENDED READING1. Basics of lighting and shading2. Basics of still life and landscapes drawing3. The Big Awesome Book of Hand & Chalk LetteringESE RECORD WORK SUBMISSION DETAILSRecord should contain at least TWO best exercises, submitted as assignments, whichshould be approved by the Subject In charge.Each of the topics should have written briefs, scribbles and final artwork. Cutting andpasting work for advertisements must be done with design elements (logos, illustrations,lettering, etc.) created by the students individually. (Cutting and pasting from magazine or anyother secondary sources will not be allowed).CONTENT1. Basics of line drawing - Straight Line, Zig-Zag, Curves, Circles, Spiral, Knots, Waves2. Types of shading techniques - Hatching, Cross hatching, Scumbling, Stippling,Smudging, Scribbling3. Shape to form4. Colour wheel5. Landscape with different medium6. Still life with different medium7. Typography - Font Family and Creative Fonts8. Logo Design9. Visiting Card10. Banner11. Letterhead12. Dangler13. Poster14. Brochure15. Print Ad16. Bunting17. Package Design18. Mascot.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]10
BASICS OF VISUAL COMMUNICATIONCODE:I YEAR – I SEM – GC - TCREDITS: 2HOURS: 4OBJECTIVE:Ø To give an overview to visual communication.Ø To expose the students to the opportunities available for careers in visualcommunication course.UNIT INeed for communication. What is communication? Communication as processCommunication models. Non-verbal communication. Communication and community.UNIT IIMeaning of messages. Connotation and Denotation. Culture. Codes, levels ofcommunication: technical, semantic & Pragmatic.UNIT IIIOrientation to drawing – different tools of drawing, pencil sketches,watercolours, paintings- mixed media.UNIT IVPrint medium illustration techniques, principles of design, design fundamentalsfor layout. Film & Television. Characteristics of different media. Approaches to design.Elements of design, shape, space, colour, texture, form etc. Principles of design: rhythm,content, Balance.UNIT VBasics of graphic design, elements of graphic design, the process of developingideas verbal visuals & combination. Visual thinking. Material and tools.METHODOLOGY:Classroom exercises coupled with practical exposure to different kinds ofmedium. Lectures, guest lectures, seminars, group discussion, use of print and eresourcesREFERENCE:Arthur Asa. Berger seeing is to believe an introduction to Visual Communication prentice hallpublications – 1976Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]11
SEMESTER IIDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]12
HISTORY OF MEDIACODE:I YEAR- II SEM – MAJOR - TCREDITS: 4HOURS: 4OBJECTIVE:Ø To introduce the various Folk Media and Tradition in IndiaØ To understand the rise and growth of media through generationsØ To comprehend the recent technologies and its usageUNIT IEmergence and Development of Folk Media, Traditional Folk Media – Meaning,Characteristics, Its difference from Mass Media, Different Forms of Folk Media:Tamasha, Pawada, Keertana, Yakshagana, Therukoothu, Nautanki, Jatra, Bhavai, Ramlilaand Raslila, Puppetry: Forms In Different States. Oral to Electronic Media.UNIT IIEmergence and Development Print Media. Advent of Printing Press in India andNewspaper, Forms and Genres, New Trends, Advantages and DisadvantagesUNIT IIIEmergence and Development of Radio as a Medium of Mass Communication,Forms and Genres, New Trends. FM Radio, Satellite Radio, Internet Radio, CommunityRadio, Visual Radio.UNIT IVEmergence and Development Of TV As Medium Of Mass Communication In India,Story Of Indian TV Advent And Growth Of Satellite And Cable TV In India. Forms andGenres, DTH, INTERNET, CHROME CAST, ANDROID TV. New Trends. Film as Medium ofCommunication, Historical Development of Film in India, Regional Cinema.UNIT VEmergence and Development of Social Media, New Media Technologies, SocialNetworking Sites, Media Convergence, Interactive Features.METHODOLOGY:Topics will be taught through Lectures, Assignment, and Discussions which will be aidedby Seminars, Debates, Brain Storming Sessions and published materials.REFERENCEKEY TEXT1. Asa Briggs and Peter Burke (14 December 2001) A Social History of the Media: FromGutenberg to the Internet. 3rd Edition2. Nadiq Krishna Moothy (1966) Indian Journalism. Prasaranga, University of Mysore.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]13
PRINT SOURCE1. Chatterjee P.C. (1990 Broadcasting in India. Sage, New Delhi.2. Luthra I.I.R (1986) Indian Broadcasting. Publications Division, New Delhi.3. Wendy Hui Kyong Chun, Anna Watkins Fisher, Thomas Keenan (21 Sep 2015) NewMedia, Old Media: A History and Theory Reader4. Wouter de Been, P. Arora , M. Hildebrandt (1 Jan 2015) Crossroads in New Media,Identity and Law: The Shape of Diversity to JnKLwHCnL72vedxjQkDDP1mXWo6uco/wiki/List of Indian folk luhan-innis/RECOMMENDED READING:1. Keval J. Kumar (2012) Mass Communication in India. 4th Edition2. Henry Jenkins (1 Sep 2008 ) Convergence Culture: Where Old and New Media Collide3. Helmut Kipphan (2001) Handbook of Print Media : Technologies and Production MethodsDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]14
WRITING FOR MEDIACODE:I YEAR – II SEM MAJOR - PCREDITS: 5HOURS: 6OBJECTIVE:Ø To develop the writing skills and different formats for mediaØ To publicize the thoughts in diverse media platformsØ To establish the command over language using mediaUNIT IIntroduction to writing, History and Process of Word making and change ofmeaning, perspective writing, Effective Writing, Types of Writing – Expository,Descriptive, Persuasive, narrative, Usage of Punctuation marks, Writing for MassAudience. Microsoft Office - WordUNIT IINEWS WRITING: What is news? News values, Different kinds of the news, sourceof news, layout of a Newspaper, organizational structure of the newspaper industry,kinds of reporting. Difference between feature, article and editorial. News Writing: 5Wsand 1H, the inverted pyramid, the chronological story, the composite story, featurenews, Column writing, editorial. Headlines – types, New trends. Adobe InDesignUNIT IIISCRIPT WRITING : Introduction to script and its formats, Process of scriptwriting - research, premise, synopsis, outline, treatment. Script writing format – MasterScript, Single Column Format, Two Column Format, Screenplay Format. Scripting forfiction: Story & Plot, Characterization, Three Act Structure. Script for TV, Radio,Documentary, PSA, TVC. CeltexUNIT IVCORPORATE WRITING: Publication Design, Newsletter Preparation, PublicityWriting, Business Letter [Positive News Letter, Negative News Letter, FundraisingLetter, Cover Letter], Email, Memo, Proposal, Press Release, Report [Progress Report,Informative Report, Recommendation Report, Business Plan]. Blogger, WordPressUNIT VWRITING FOR DIGITAL SPACE: Writing Techniques, Sentences, Links, andTables, Meaningful Linking, Effective Illustrations and Design, Content Strategy,Message, Media, Style, and Tone, Conversations and Key Messages, Parts and Purposesof a site, Current Platforms - Blogs/ Vlogs, WordPress, Twitter, Facebook, Tumblr,providing credit/courtesy and copyrights, memes, captioning and commenting.Multimedia campaign. SNS.METHODOLOGY: Classroom interaction and presentations with illustrations Lectures from Resource personalities to give the big picture Recurrent Class projects will be assigned which will be critiqued and assessed.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]15
REFERENCE:KEY TEXT1. Walter Fox (1 Jun 2001) Writing the News: A Guide for Print Journalists2. Usha Raman (15 Dec 2009) Writing for the Media3. Lajos Egri (1946) The Art of Dramatic Writing: Its Basis in the Creative Interpretation ofHuman4. George Arnold (25 Aug 2010) Media Writer's HandbookPRINT SOURCE1. William Zinsser (5 Apr 2016 ) On Writing Well: The Classic Guide to Writing Nonfiction2. Christopher Riley (2005) The Hollywood Standard: The Complete and Authoritative Guideto Script Format3. John Truby (30 October 2007) The Anatomy of Story: 22 Steps to Becoming a MasterStoryteller4. Robert W. Bly (4 APRIL 2006) The Copywriter's Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide ToWriting Copy That Sells. 3rd mlRECOMMENDED READING1. Ramakrishna Reddy Write Effective Emails at Work: 6 Keys That Take 5 Minutes or LessESE RECORD WORK SUBMISSION DETAILS Each student will have to complete Set A & BSet A- (All)1. Writing an argument [Word limit/Genre]2. Article – Hard/Soft News, Editorial, Column, Feature.3. Script Writing - PSA/Short Film/ TVC - 3 each4. Corporate Writing – Press Release/ Recommendation LetterSet B (Any 2)1. Digital story writing2. Photo voice – Photos will be provided to the students3. Meme creation - Photos will be provided to the students4. Same message in different platformsDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]16
BASICS OF 2D ILLUSTRATIONCODE:I YEAR – II SEM – ALLIED I - PCREDITS: 6HOURS: 6OBJECTIVE:Ø To provide the students with an understanding of human anatomyØ To develop the rendering skills of human figures in various art materialsØ To enable them to visualize and create story boardsUNIT IBasic Anatomy Structure – The Basic Figure, Pelvis, Legs and Knees, Ribcage,Belly Button, Shoulders, Arm, Wrists and Hands. The Basic Profile- Spine in Profile,Ribcage and Legs in Profile, Arms in Profile, Proportion Reminders.UNIT IIStudy of Head and face - Proportions of the Face, The Features- Eyes andEyebrows, Details of – Eyes, Nose, Lips, Ears. Looking Up, Looking Down, And TurningSideways. Views: front profile, one third, side view and back view. Study of hand and leg- Basics, Proportions, Range of Motion, Shapes.UNIT IIIBasic Animation Structures, Draped Figure In Space – Poses: Standing, Sitting,and Reclining, Figures in Action, Figures in Composition, Stick Figures, Retro Characters.UNIT IVPerspective Drawing – Types, 2d Figures- Match Stick Figures Concept Based.UNIT VStoryboard – Figures through simple lines, Simple Illustrations and ConceptBased, comic strip, Graphic Novel, Flip Book.METHODOLOGY Extensive studio work and outdoor studies with demonstrations. Class projects will be assigned periodically with student having the option of workingindependently and submitting their work on the assigned dates Recurrent observations and criticisms will be done and guided accordingly Audio Visual materials will be screened for better understandingREFERENCE:KET TEXT1. Bridgman B. George (1962) The Book Of A Hundred Hands, Dover Publications, NewYork.2. Buchan Jack and Baker Jonathan (1995), Step By Step Art School Portraits, Hamlyn,Britain.PRINT SOURCEDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]17
1. Raynes John (1979), Human anatomy for the Artist, Hamlyn, London.2. John Hart (November 1, 2007) The Art of the Storyboard: A Filmmaker's Introduction.Second EditionRECOMMENDED READING:1. George B. Bridgman Constructive Anatomy (June 1, 1973) Anatomy for Artists2. William Maughan (1 Jan 2004) The Artist's Complete Guide to Drawing the Head3. Craig Attebery (29 Mar 2018) The Complete Guide to Perspective Drawing: From OnePoint to fs/Perspective Drawing files.wordpress.com/2012/01/reference-book 1.pdfESE RECORD WORK SUBMISSION DETAILSRecord should contain at least TWO best exercises, submitted as assignments, whichshould be approved by the Subject In charge.Each of the topics should have written briefs, scribbles and final artwork.CONTENT1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.Basic Anatomy StructureHead in different viewsThree types of –eyes, nose, ears, lips.Hand and leg – range of motion.Basic animation structures.Recreation with poses.Draped figure in space.Retro charactersPerspective drawing- one point, two point, three point.Stick figuresFlip bookStoryboard – with cartoon characters and without characters.Department of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]18
SEMESTER IIIDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]19
BASIC PHOTOGRAPHYCODE:II YEAR – III SEM – MAJOR- PCREDITS: 4HOURS: 4OBJECTIVEØ To equip the students with basics of photographyØ To understand the process of producing the right photoØ To give them exposure to various types and forms of PhotographyUNIT IPhotography- Fundamentals, History – early experiments and developments,Human Eye and camera, Camera – history and types, Films and its types, Working of aD/SLR – Operations, Modes and Advantages.UNIT IIFeatures of Camera, Lens and its types, Functions of a Camera - Exposure,Aperture, Shutter, ISO. Depth of Field, Action Control, Sensitivity. Camera Accessories:Types and Usage of Filters, Light Measuring Devices, Tripods. File Formats –Converters.Digital Storage Devices – Cable and Cards.UNIT IIIStudy on Lighting, Indoor Lighting Techniques - Key Light, Fill Light, Back Light,Rim Light, Kicker Light, Background Light. Low Key and High Key. Lighting Equipment’s,Elements to support Lighting, Outdoor Lighting. Colour Temperature.UNIT IVComposition and Framing Techniques, Rule of Thirds, Angle of View, LeadingLines, Negative Space, Golden Triangle, Golden Spiral, Balance, Symmetry, patterns,Texture, Rule of Odds, Colours. Genres of Photography– Panorama, Silhouette, Cameo,Black and White, Montage, HDR, Macro, Miniature, Stop Motion, Bulb Mode, LightPainting, Candid, Photo- Journalism, Photo-features, Photo-essays, Product, Industrial,Abstract, Portrait, Sports, Food, Travel, Street, Bokeh, Event, Time Lapse, Hi Speed,Conceptual.UNIT VPlanning a shoot- Indoor and Outdoor, Budgeting, Set props. Image editing manipulation of image, framing & trimming, Writing captions, Panorama Stitch, Specialeffects techniques, Colour profiles, colour management, layout design. Printingmaterials and types.METHODOLOGY: Classroom lectures for theoretical inputs combines with demonstrations. Field visit for students to apply and experience Guest lectures accompanied with audio visual materialsDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]20
ESE Record Work Submission DetailsEach topic should have 10 images each in colour & black & white. Best two images in each topichas to be added in the album (1 colour & 1 B&W). The album should contain minimum numberof 40 images (8X12 inches) covering all topics. Album Type: Synthetic.1. Lights – Key, Fill, Background, Backlight, low key, high key2. Still life - Portraits- Indoor & Outdoor Landscape Silhouette Product – Indoor&Outdoor3. Architecture- Interior & Exterior Industrial Photography Sculpture4. Wildlife Photography Event Coverage5. Multiple Exposure Photo feature Photo language Environmental exposure ActionFreeze6. Panorama Montage Special effectsREFERENCE:KEY TEXT1. Michael Longford, Basic Photography; London focal press2. John Hedgeco (1979) Complete Photography Course, fireside book, New York.3. Digital photography, A Step- by- Step Guide and Manipulating Great Images by Tom AngMitchell Beazley.4. O.P. Sharma Practical Photography– Hind pocket books.PRINT SOURCE1. Richard Zakia, LeatieStroebel (1993) The Focal Encyclopedia of Photography Focal pressbaston, London. Third edition.2. Peter K Burian (2001) Mastering Digital Photography and Imaging Publisher Sybex. USA.First edition.3. John Hedgecoe (1999) The Photographer’s Handbook. Alfred A.Knopf Publisher4. Roger Hicks and Frames Schultz (2002) Interior Shots Rotovision, Switzerland.5. Joseph A. Iippolito (2003) Understanding Digital Photography. Thomson DelmarLearning, USA6. Catherine Jamieson/ Sean McCormick (2005) Digital Portrait Photography and Lighting:Take Memorable Shots Every Time. Wiley Jamieson and McCormick, London.7. Mitchell Bearley & John Hedgeese (2005)New Introductory Photography istory-timeline/RECOMMENDED READING (magazines)Smart PhotographyBetter PhotographyNational GeographicDepartment of Visual Communication, Madras Christian College [Autonomous]21
MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING FOR MEDIACODE:II YEAR- III SEM - MAJOR-TCREDIT: 4HOURS: 4OBJECTIVEØ To help the students comprehend the basic concepts of managementØ To acquire management and marketing skills for effective execution in the industry.Ø To study different kinds of media ownership patterns and policies.Unit IAn overview of electronic media, India’s Creative industry. Management- rolesand functions, Principles of management, levels of management. Managing mediaorganization –planning, coordination, motivation, control, decision- making,departmentalization, Policy Making, Leadership qualities.Unit IIPersonnel management- Hiring process, Interviewing orientation, Performancereviews, Legal issues in personnel management. Labour issues: Working with unions,other labour law. Media regulations, foreign equity and FDI in Indian media,Convergence of media.Unit IIIOwnership- Definition & Concept; Licensing & Franchising; Rules & RegulationsMonopolies, Oligopolies, Conglomerates, Mergers, & Acquisitions. Mass-Mediaownership pattern in India- Sole Proprietorship, Private Limited Company, Partnership,cross media ownership, Vertical Ownership Pattern, Employee Ownership Pattern,Trusts, Cooperatives, Religious Institutions & Franchises.Unit IVMarketing- definition; Characteristics, Principles & Types of Marketing;Marketing Mix- concept & elements; Promotion Mix, Marketing - Globalization &Glocalization, Consumer Behaviour; Retail and Service Marketing, New trends inMarketing- Social media marketing; Corporate social responsibilities – Greenmarketing- social marketing and other concepts.Unit VMedia Planning- Media selection, scheduling, Space and Time Buying; CostConsiderations; the Role of a Media Planner and a Media Buyer; Media Trends. Salespromotion- meaning, purpose, tools and techniques; Strengths and Limitations of SalesPromotion, Organising consumer Sales Promotion; Trade Promotions. Recent Trends insales promotion.METHODOLOGY:Theoretical inputs will be given through lectures. The students will be asked to do casestudies on different media organisation.
1. Michael Maher (July 25, 2016) The Seven Levels of Communication: Go from Relationships to Referrals 2. Gregory Hartley, Maryann Karinch (January 1, 2010) The Body Language Handbo











