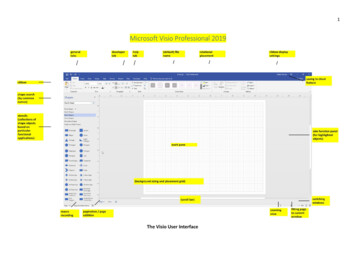
Transcription
Creating Visio Service MapsFrom an ITIL ServiceManagement CMDBAnthony Brimacombe, Senior ManagerConfiguration ManagementLloyds Banking Group
Presentation Structure1. The Team2. The Database (CMDB)3. The Challenge of Visualisation4. The Need for Visualisation
1. The TeamAnthony BrimacombeSenior ManagerCMDBArchitectureService Variation& Data CleaningCI Data Owner &Customer LiaisonIntegration
1. The TeamAnthony BrimacombeSenior ManagerCMDBArchitectureService Variation& Data CleaningCI Data Owner &Customer LiaisonIntegration3 PeopleThe CMDB Architects are responsible for: Assessing new requirements for CMDB Data. Designing the CMDB data model, from the overall structure down to the specific attributes. Designing the Configuration Management Process, including the automated data feeds from systemssuch as Tivoli. Providing consultancy on how CMDB data could be used to enable or enhance other service relatedprocesses.
1. The TeamAnthony BrimacombeSenior ManagerCMDBArchitectureService Variation& Data CleaningCI Data Owner &Customer LiaisonIntegration4 PeopleService Variation (SV) Deals with the change control and Audit Trail of Service documentation. Act on behalf of Service Managers (SMs) to manage changes to their data within the CMDB.Data Cleaning Ensuring that hardware and logical level CIs (Configuration Items) are correct, contact details for SMs are upto date and relationships for CIs are in place.
1. The TeamAnthony BrimacombeSenior ManagerCMDBArchitectureService Variation& Data CleaningCI Data Owner &Customer LiaisonIntegration2 PeopleProvide Support and Guidance for: CI Data Owners to enable them to manage their Configuration Items. Our Customers (the Incident, Problem and Change Management and Business Services Teams). Our CMDB Data Consumers to ensure they understand the benefit it provides in order for them to makeinformed decisions.This is achieved by: Building relationships with CI Data Owners, Customers and Consumers, creating Job Aids and Training Packs,delivering training, requesting reports and providing ad-hoc support when requested.
1. The TeamAnthony BrimacombeSenior ManagerCMDBArchitectureService Variation& Data CleaningCI Data Owner &Customer LiaisonIntegration1 PersonThe Configuration Integration function exists to deliver the Configuration (CMDB and Data) elements of theIntegration plan.
2. The Database (CMDB)LTSB legacyitemsCompletevolumeBasic 48System195731160330 000 Logical Host055Cluster9213982920 000 HardwarePlatform teams ownHBOS legacyitemsBSM / SAM ownAn Overview of Basic CMDB Structure & ContentService: A set of related functions provided by IT in support of one or morebusiness processes that are collectively seen by the customer as a selfcontained entity. In LBG terms, this is the whole IT capability delivered to aspecific Business Unit regardless of size, costs or ownership and is defined ina Service Agreement. (E.g. Internet Banking).Sub Service: A logical sub-division of a Service. One or more “EnablingBusiness Function(s)” that grouped together make up a single Service.These Sub Services are underpinned by one or more IT systems. (E.g.Internet Banking LBG Sub Service).System: A set of one or more applications, software and hardwaretechnology platforms, satisfying a single business requirement. (E.g. CBS,OCIS, IB Registration)Logical Layer: These represent Logical Partitions, Logical Hosts and thelogical representation of the physical Hardware (partitioned or nonpartitioned)Logical Cluster Layer: These represent VMWARE clusters in theDistributed Windows environments. This layer is optional as only Distributedplatforms include them (new to the CMDB in 2010). The vast majority oflogical layer items are not clustered and will relate directly to ComputerHardware.Computer Hardware: These represent the Computer hardware of varyingtypes for z-Series, I-Series, Unix , Tandem and etc. The names for ALLHardware items relate to the unique Asset Tag numbers from „Archibus‟ (E.g.12345, 84746)
2. The Database (CMDB)
2. The Database (CMDB)
3. The Challenge of Visualisation For this example we will look at the IT ServiceDelivery Tools Service (SM7 is part of this) Choose RelationshipGraph from tool bar Service Level CI Viewing windowScope. More CI‟sreduces what youcan see clearly This is a very simplestructure that makes iteasy for us to see thedifferent layers Sub-Service Level CI System Level CI Here we can see SM7 Logical Layer „click on ‟
3. The Challenge of VisualisationIt gets complex:There are 161CIs shown the CMDB has 30,000.Dependenciesare checkedand updateddaily.Automation isused wherepractical.
3. The Challenge of VisualisationSERVICE INFORMATION REQUIREMENTS (1)Service“Top Down”Servicefocused whichcomponentssupport thisservice?HostHardware/Virtual (133)
3. The Challenge of VisualisationSERVICE INFORMATION REQUIREMENTS (2)“Bottom Up”Componentfocused whichServices usethiscomponent?Services (33)
3. The Challenge of VisualisationREAL EXAMPLE – The HR Service:
4. The Need for VisualisationThe primary uses of the data in our CMDB are:1) To ensure that Change Raisers and Approvers understand thetrue potential impact of a change (and therefore reduce the risk ofa change related outage). We currently have 4,500 ChangeRecords raised per month.2) To ensure that all data necessary for swift Incident resolution isavailable when required.3) To assist with Problem Record trending.4) For data review, verification and correction to support the above.However,1) The CMDB GUI is forms based – it is not easy to comprehend complex data.2) Alternate formats (such as Excel Spreadsheets and Visio diagrams) arepreferred by our customers.Explaining service relationships is best done visually.
4. The Need for VisualisationACCESS TO SERVICE KNOWLEDGE1. I, P and C forms and user interface2. Internal Reporting3. Some Visualisation – limited by complexityDirect CMDBaccess required4. Standard Visio service maps – “the maintained view”5. Ad hoc Visio service maps to suit project / process needs6. Multi-level / multi-CI query for change impact assessment7. Integration with other systems8. KMDB – SharePoint basedNo need forCMDB access
5. In SummaryA complex CMDB can be delivered, used andmaintained. It underpins Service Managementprocesses but requires good reporting and visualisationto be fully effective.In practice, service understanding requires CMDB datato be visible and accessible in different formats atdifference times. E.g.: Automation of Visio diagrams for CI Data Ownerreview and verification. Production of ad hoc views to suit Management orProject team needs.
4. Standard Visio service maps – “the maintained view” 5. Ad hoc Visio service maps to suit project / process needs 6. Multi-level / multi-CI query for change impact assessment 7. Integration with other systems 8. KMDB – SharePoint based