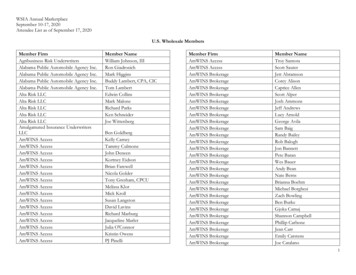
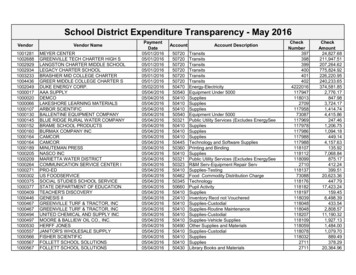
Transcription
2016 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.comClear-Aligner Treatment ofOvererupted Upper MolarsVERED BARZILAY, DMD, MHAWILLY DAYAN, DDSLoss of teeth is often followed by overeruptionof the opposing teeth and consequent esthetic,functional, and occlusal issues. Such overeruptedteeth must be corrected prior to any prostheticrehabilitation. Since coronal-reduction techniques1,2 may require additional endodontic andperiodontal treatment before final crown restorations, overerupted teeth are typically treated withorthodontic intrusion.Surgically assisted methods such as corticotomy3,4 or surgical impaction5 increase the risksand cost of treatment. Extraoral devices requirepatient cooperation. Orthodontic correction usingfixed appliances and bite planes6 may cause extrusion of the anchorage unit. Miniscrews canprovide absolute skeletal anchorage without theneed for patient cooperation, but are more invasive.4,7-10 This article suggests a way to intrudeovererupted upper molars using anchorage fromclear aligners.Case ReportA 69-year-old female was referred by hergeneral dentist with a missing lower right secondmolar, left first molar, and left second molar. Shehad a Class I molar and canine relationship withgood overjet, slightly excessive overbite, and minoranterior crowding (Figs. 1,2A). Her upper rightsecond molar, left first molar, and left second mo-48lar were overerupted due to the lack of antagonists.The alveolar bone loss seen initially on the panoramic x-ray was relatively horizontal, with novertical bone defects that could be worsened byintrusion. The patient’s periodontal disease hadbeen successfully treated, but she continued herrecommended periodontal maintenance visits during orthodontic treatment.11Invisalign* therapy was planned to intrude theovererupted upper molars, thus gaining space forimplants and prosthetic replacement of the missinglower molars while aligning the anterior teeth (Fig.2B,C). To provide mechanical retention and supportfor the desired intrusion, attachments were orderedon the upper right second premolar, right first molar, left first premolar, and left second premolar—the teeth adjacent to those planned for intrusion(Fig. 2D). Lingual bite turbos were prescribed onthe upper incisors to help level the mild overbite;additional attachments were used on the lower premolars and molars to level the curve of Spee.Twenty pairs of aligners were delivered forthe initial treatment phase. In 40 weeks of treatment, the upper right second molar, left first molar,and left second molar were intruded enough toprovide an acceptable occlusal plane for prosthetic rehabilitation (Fig. 3). After consultation withthe restorative dentist, eight sets of refinement*Registered trademark of Align Technology, Inc., San Jose, CA;www.aligntech.com. 2016 JCO, Inc.JCO/JANUARY 2016
Dr. Barzilay is a staff member, Department of Orthodontics, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv,Israel. Dr. Dayan is Founder and President, Orthodontic Clinic Education Corp., 9 ForestRidge Drive, Toronto, Ontario, M6B 1G9 Canada; e-mail: drwilldayan@gmail.com. Dr.Dayan receives an honorarium from Align Technology to speak at conferences and otherevents. Dr. Barzilay wrote this article; Dr. Dayan provided the clinical treatment.Dr. Barzilayaligners were ordered for detailing (Fig. 4). Duringthis phase, the upper molars were tipped linguallyto create a more coordinated posterior archformwith the anticipated implant-supported crown replacements of the lower right second molar, leftfirst molar, and left second molar.Dr. DayanOverall treatment time was 56 weeks. Posttreatment records demonstrated anterior levelingand alignment, accompanied by intrusion of theovererupted upper molars without unwanted sideeffects on the adjacent teeth (Fig. 5). Followingreplacement of the missing lower molars, the pa-Fig. 1 69-year-old female patient with missing lower right second molar, left first molar, and left secondmolar and overerupted upper right second molar, left first molar, and left second molar before treatment.VOLUME L NUMBER 149
Clear-Aligner Treatment of Overerupted Upper Molarstient was instructed to wear a clear retainer in theupper arch at night, and a 3-3 fixed retainer wasbonded in the lower arch.**Trademark of Align Technology, Inc., San Jose, CA; www.aligntech.com.DiscussionOnly one previous case report has documented molar intrusion using the Invisalign system.12This esthetic technique does not compromise oralhygiene or periodontal health in adult patients, andit avoids the need for invasive coronal-reductionABFig. 2 ClinCheck** records. A. Pretreatment. B. Projected post-treatment (continued on next page).50JCO/JANUARY 2016
Barzilay and Dayanprocedures such as grinding or subapical osteotomy. Even without skeletal anchorage, it does notresult in extrusion of the adjacent teeth. This maybe due to a posterior bite-block effect from thealigners’ constant occlusal coverage, which enhances the active intrusion of the molars and ne-gates the extrusive vectors of force on the anchorage teeth from the attachments supporting themolar intrusion.Because the use of clear aligners for molarintrusion depends on patient compliance, case selection is an important issue—as in all InvisalignCDFig. 2 (cont.) ClinCheck** records. C. Superimposition of pretreatment and projected post-treatment.D. Labial attachments and lingual bite turbos.VOLUME L NUMBER 151
Clear-Aligner Treatment of Overerupted Upper Molarscases. Teamwork and an open line of communication between general dentist and orthodontist areessential in determining the patient’s needs andachieving treatment goals.A controlled clinical trial would not only addvalidity to the clinical experience presented in thisarticle, but would also enable more accurate assessment of the efficacy of this method, perhapsquantifying the amount of intrusion that can beachieved.Fig. 3 Upper-molar intrusion achieved in 40 weeks with 20 sets of aligners.Fig. 4 Superimposition of pre-refinement and projected post-refinement ClinCheck records.52JCO/JANUARY 2016
Barzilay and DayanFig. 5 Patient after 56 weeks of treatment, showing molars in normal occlusal plane.REFERENCES1. Belinfante, L.S. and Abney, J.M. Jr.: A teamwork approach tocorrect a severe prosthodontic problem, J. Am. Dent. Assoc.91:357-359, 1975.2. Spalding, P.M. and Cohen, B.D.: Orthodontic adjunctivetreatment in fixed prosthodontics, Dent. Clin. N. Am. 36:607629, 1992.3. Moon, C.H.; Wee, J.U.; and Lee, H.S.: Intrusion of overerupted molars by corticotomy and orthodontic skeletal anchorage,Angle Orthod. 77:1119-1125, 2007.4. Hwang, H.S. and Lee, K.H.: Intrusion of overerupted molarsby corticotomy and magnets, Am. J. Orthod. 120:209-216,2001.5. Schoeman, R. and Subramanian, L.: The use of orthognathicsurgery to facilitate implant placement: A case report, Int. J.Oral Maxillofac. Implants 11:682-684, 1996.6. Ng, J.; Major, P.W.; and Flores-Mir, C.: True molar intrusionattained during orthodontic treatment: A systematic review,Am. J. Orthod. 130:709-714, 2006.7. Kravitz, N.D.; Kusnoto, B.; Tsay, T.P.; and Hohlt, W.F.: TheVOLUME L NUMBER 18.9.10.11.12.use of temporary anchorage devices for molar intrusion, J.Am. Dent. Assoc. 138:56-64, 2007.Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Duan, P.; and Xu, C.: Asimple way to intrude overerupted upper second molars withminiscrews, J. Prosthod. 22:597-602, 2013.Ohura, R.; Kuroda, S.; Takahashi, T.; Tomita, Y.; and Tanaka,E.: Efficient usage of implant anchorage to treat overeruptedmaxillary first molar and mesially inclined mandibular molars, Am. J. Orthod. 139:113-122, 2011.Heravi, F.; Bayani, S.; Madani, A.S.; Radvar, M.; andAnbiaee, N.: Intrusion of supra-erupted molars using miniscrews: Clinical success and root resorption, Am. J. Orthod.139:S170-S175, 2011.Boyd, R.L.: Periodontal and restorative considerations withclear aligner treatment to establish a more favorable restorative environment, Compend. Cont. Ed. Dent. 30:280-291,2009.Giancotti, A. and Ronchin, M.: Pre-restorative treatment withthe Invisalign system, J. Clin. Orthod. 40:679-682, 2006.53
ed molar intrusion using the Invisalign system.12 This esthetic technique does not compromise oral hygiene or periodontal health in adult patients, and it avoids the need for invasive coronal-reduction Fig. 2 ClinCheck** records. A.