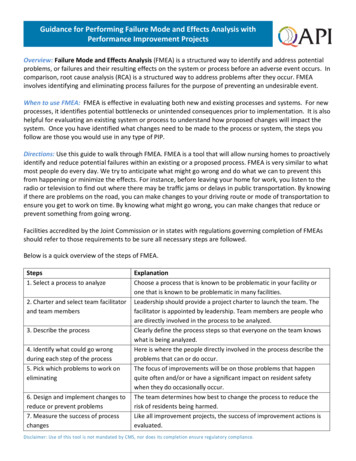
Transcription
(FAILUREFMEAMODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS)Course
Course Contente1. What is FMEA?2. Why to use FMEA?3. When to Use FMEA4. How to use FMEA5. FMEA benefits6. Improvement through FMEA7. FMEA Types8. FMEA Examples9. References11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-2
1. What is FMEA? In today global economy no failures are tolerated11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-3
1. What is FMEA? Goal is to eliminate (or extremely reduce) any type offailureGOAL ZEROFAILURES11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-4
1. What is FMEA? Failures are any errors or defects, especially onesthat affect the customer, and can be potential oractual11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-5
1. What is FMEA? Failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) is a step-by-step approach for identifying all possible failuresin a design, a manufacturing or assembly process, ora product or serviceFMEA «-»ERRORPREVENTION11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-6
1. What is FMEA? “Failure modes” means the ways, or modes, in whichsomething might fail es of those failures11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-7
1. What is FMEA?11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-8
1. What is FMEA? Failures are prioritized according to how serious theirconsequences are, how frequently they occur andhow easily they can be detected The purpose of the FMEA is to take actions toeliminate or reduce failures, starting with the highest-priority ones11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-9
2. Why to use FMEA? FMEAs are used by organizations to manage therisks associated with the failures and its effects FMEAs should be used as a preventive action andbe updated and redone regularly11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-10
2. Why to use FMEA? The costs associated with preventing failures aremuch less that the costs of correcting a failure after ithas occurred 11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-11
2. Why to use FMEA? FMEA alsodocuments current knowledge andactions about the risks of failures, for use incontinuous improvement11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-12
2. Why to use FMEA? FMEA started being used by the US Military in the1940s.11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-13
2. Why to use FMEA? Users of FMEA include NASA (since 1960s), FordMotor Company (since 1980s), AIAG (AutomotiveIndustry Action Group, since 1990s) and presentlythe Joint Commission for Accreditation of HealthcareOrganizations11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-14
3. When to use FMEA? FMEA is used during design to prevent failures Later it’s used for control, before and during ongoingoperation of the process Ideally, FMEA begins during the earliest conceptualstages of design and continues throughout the life ofthe product or service11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-15
3. When to use FMEA?ASQ (www.asq.org) recommends using FMEA in thefollowing situations :1. When a process, product or service is beingdesigned or redesigned, after quality functiondeployment2. When an existing process, product or service isbeing applied in a new way11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-16
3. When to use FMEA?3. Before developing control plans for a new ormodified process4. When improvement goals are planned for anexisting process, product or service11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-17
3. When to use FMEA?5. When analyzing failures of an existing process,product or service6. Periodically throughout the life of the process,product or service11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-18
3. When to use FMEA? FMEA is also used in Six Sigma Methodologyeither for DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze,Improve and Control) or DFSS (Design for SixSigma)Remark: Six Sigma is “a business improvementapproach that seeks to eliminate causes ofmistakes or defects in business processes byfocusing on outputs that are of critical importanceto customers” (Snee, 1999)11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-19
4. How to use FMEAThe following steps can used as a guideline to useFMEA (write the information on the FMEA table – thereis no fixed model - as is produced):1. Identify the scope of the FMEA: is it for a system,process or service? What are the boundaries andhow detailed should it be?11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-20
4. How to use FMEA2. Assemble a cross-functional team of people withdiverse knowledge about the system, process orservice (e.g., design, purchasing, manufacturing,engineering, quality, sales, marketing, customerservice )3. Study the system, process or service and identifythe several functions: What is the purpose? Whatare the expectations of the customers?11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-21
4. How to use FMEA4. For each function identify all the ways the failurecould happen, the potential Failure Modes5. For each Failure determine how serious the failureeffect can be. This is the Severity Rate, usuallyrated on a scale from 1 to 10, where 1 isinsignificant and 10 is catastrophic11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-22
4. How to use FMEAExample of Severity Rates11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-23
4. How to use FMEA6. For each Failure mode identify all the potential rootcauses and list them on the FMEA table7. For each Failure mode rate the Occurrence Level(O) that estimates the probability of failureOccurring during the lifetime of the scope and thatis usually rated from 1 (extremely unlikely) to 10(inevitable)11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-24
4. How to use FMEAExample of Occurrence Rates11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-25
4. How to use FMEA8. For each cause, identify the present processcontrols (e.g., tests, controls and mechanisms inplace to prevent that failures reach the customer)9. For each control identify the detection level (or D)that estimates how well the controls can detect thecause or its failure mode after they have occurredbut before the customer is affected. Usually this israted on a scale from 1 (control will surely detectthe problem) to 10 (control surely will not detect theproblem)11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-26
4. How to use FMEAExample of Detection Levels11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-27
4. How to use FMEA9. Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN S x O xD) and prioritize the order potential failures shouldbe addressed11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-28
4. How to use FMEA11. Identify and implement improvement actions (e.g.,design or process changes to lower severity oroccurrence; additional controls to improvedetection; also define responsible for the actionsand completions dates). Re-evaluate the RPNs12. Update the FMEA Table based on the actionscompleted and re-evaluation of the RPNs11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-29
4. How to use FMEAExample of simplified FMEA Table (source: ASQ)11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-30
5. FMEA benefitsThe benefits of a FMEA when used in the right wayInclude (ASQ CSSGB Primer):1. Improved product or service functions2. Reduced manufacturing problems3. Lower warranty and after service costs4. Increased safety and reliability of products andprocesses5. Improved customer satisfaction6. Decreased business problems11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-31
6. Improvement through FMEABongiorno (2000) proposes a 4-step process toimprove organizations performance:1. Measure the current FMEA performance for abaseline2. Agree on a projected FMEA performance level(e.g., RPN level)3. Develop a plan to close the gaps4. Implement the recommended methods to achievethe target11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-32
7. FMEA typesAccording to Stamatis (1995) there are four types ofFMEA:1. System FMEA, applicable to systems, subsystemsand components and the interactions betweensystems and elements of the system2. Design FMEA, analyzing products prior to therelease of production drawings for tooling andmanufacturing, emphasis is on the failure modescaused by design deficiencies11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-33
7. FMEA types3. Process FMEA: studying the manufacturing andassembly process, emphasis is on the failuremodes caused by process or assembly operations4. Service FMEA: studying the services before theyreach the customer, focus on the tasks, errors,and mistakes, caused by process deficiencies thatcover non manufacturing services11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-34
8. FMEA examplesAn example of a Process FMEA on a Bank ATMmachine is partially presented adapted fromwww.asq.org): Function: “Dispense cash” Failure Modes: Does note dispense cash, According to RPN “machines jams” and “heavycomputer network traffic” are the 1st and 2nd highestrisks11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-35
8. FMEA examples The FMEA also shows criticality rating an approachthat when used transform the FMEA into FMECA(Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis) TheTeam should use their knowledge andexperience to decide on the appropriateimprovements actions and prioritization11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-36
8. FMEA examples11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-37
8. FMEA examplesAnother example of a Process FMEA on the possible failures of a toasteris partially presented adapted from www.asq.org).An FMEA looks for all the ways a process or product can fail. Forexample, a toaster could fail in several ways: There is a short in the power cord The coils burn the bread no matter which setting is used The pop-up mechanism is too sensitive and flings toast onto thecounter11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-38
8. FMEA examplesFailures can also occur when the user makes a mistake, and it is wise toinclude both types of failures in an FMEA. Anything that can be done toassure the product works correctly, regardless of how the user operates it,will move the product closer to 100% satisfaction.A product/design FMEA can uncover problems that will result in safetyhazards, product malfunctions or a shortened product life. They keyquestion to ask here is, "How can the product fail?" A process FMEAuncovers process problems related to the manufacture of the product.The key question to ask here is, "How can process failure affect theproduct, processing efficiency or safety?"11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-39
8. FMEA examplesA short in the power cord of a toaster has a “hazardous effect without warning” soSeverity is rated as 10.The Team in charge of the FMEA has considered that the probability ofoccurrence of this failure is High, with repeated failures, leading to an OccurrenceRaking of 7.Concerning the likelihood of Detection, the Team has considered that it is veryremote, so Detection Level 9 was chosen.Final RPN is S x O x D 10 x 7 x 9 630.Because RPN is too high, the Team recommend the adoption of better packagingmaterials (heavy duty packaging foam) that will bring O to 2 (Low)and D to 5(Moderate), with a final RPN of 100.11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-40
8. FMEA examples11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-41
9. ReferencesReferences1. www.asq.org2. Bongiorno, J. (2000), “Improving FMEAs: FMEAscan Transform Compliance into CompetitiveAdvantage”, Quality Digest, 37-4011/03/2021-Presentation of the website-42
9. References3. CSSGB, Quality Council of Indiana, (2006,) ASQ4. Nancy R.T., 2004, The Quality Toolbox, 2nd Ed.,(2004), ASQ Quality Press11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-43
9. References5. Potential Failure Modes and Effects Analysis(FMEA) Reference Manual, 3rd. Ed.(2001)Southfield, MI, AIAG6. Stamatis, D. (1995), Failure Mode and EffectAnalysis: Failure From Theory to Execution,Milwaukee, ASQC Quality Press11/03/2021-Presentation of the website-44
8. FMEA examples . 11/03/2021 Presentation of the website 38. Another example of a Process FMEA on the possible failures of a toaster is partially presented adapted from www.asq.org). An FMEA looks for all the ways a process or product can fail. For example, a toaster could