Transcription
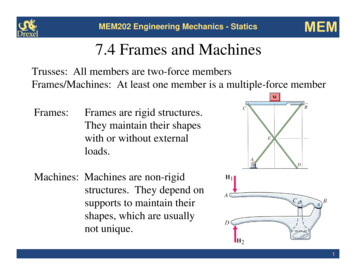
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsMEM7.4 Frames and MachinesTrusses: All members are two-force membersFrames/Machines: At least one member is a multiple-force memberFrames:Frames are rigid structures.They maintain their shapeswith or without externalloads.Machines: Machines are non-rigidstructures. They depend onsupports to maintain theirshapes, which are usuallynot unique.1
MEMMEM202 Engineering Mechanics - Statics7.4 Frames and MachinesWCyByBCCx F C B 0 F C B W 0 M 30B 15W 0xxyxyyAyADraw FBD of the entirestructure and set up theequilibrium equations todetermine the reactions F A 0 F A D W 0 M 24 D 12W 0x F A E B 0 F A E B 0 M 36B 27 BExyCBxBxDraw FBD ofB individual membersand set up theB y equilibrium equationsCCyEyAxyAxxyyyyxy 16 E x 12 E y 0CxEy F C E 0 F C E D M 20E 15ExExxyxyCyxy 0y 27 D y 0yyxAxyxDDy2
MEMMEM202 Engineering Mechanics - Statics7.4 Frames and MachinesEy2698 N F Fy 0 E y 1962 N x 2698 981 1717 0 N (Check!)TBx M 0 E 2700 N F 0 A 2700 N F 0 A E 981 NA F FByx 0 C x 981 N y 0 C y 981 N xxxyyAyCyByTyCxCx2698 NBxCy M 0 B 1962 N M 0 A 981 N F 0 B 1717 N xAyByxTTW3
MEMMEM202 Engineering Mechanics - Statics7.4 Frames and Machines M 0 E 1400 lb F 0 A 500 lb F 0 A 600 N Ayxxyy M 0 D 541.7 lb F 0 C 541.7 lb F 0 C 400 lb CCy500 lb Fx 0 Bx 541.7 lb Fy 0 By 1000 lb 500 lb600 lbCxBxBy M MDxxxyy 0 B y 1000 lb 0 D y 1000 lb DyByCxBDxBx2000 lbCyDxDy1400 lb4
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsMEMStatically Determinate and Indeterminate TrussesStatically Determinate TrussesStatically Indeterminate TrussesMember forces can be determined byusing only the equilibrium conditions.(In Statics we don’t have to know whatmaterial the structure is made of.)Equilibrium conditions alone are not enough todetermine member forces. Properties of thematerials, hence the deformation of thestructures, must be taken into consideration.Steel barRubber band5
MEMMEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsInternal Forces in Structural Members- A PrimerBTBDBDTBDTBETBEdFAdCdPEAAxTCECAydDFETCEFyPBD F A T T cos 45 T F A T sin 45 P 0 M A (2d ) Pd T d 0oxxBDyyBEBECE 0oAxAFCAyEP Fx Ax 0yEyBD F T T cos 45 T F T sin 45 F 0 M T d F d 0ox F A F M 2dAyFyEBDBECE 0oy P 0y Pd Fy d 0yBEEBDyy6
MEMMEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsInternal Forces in Structural Members- A Primerr F 0r F 0r F 0r F 0r F 07
MEMMEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsInternal Forces in Structural Members- A PrimerC y C x 541.7 lb C y 400 lb500 lbCxCxDyByAxByAx 500 lbAy 600 NAyDxDxDx 541.7 lbBx BxBx 541.7 lbB y 1000 lbCy2000 lbD y 1000 lbDyEyE y 1400 lbAll these forces at the joints are useful for designing the pins that connectmembers together. But they are useless for designing the members themselves.For the latter, we must know the “internal force distributions”, or the “stressdistributions” in all members.8
MEMMEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsInternal Forces in Structural Members- A PrimerD y 1000 lbB y 1000 lbB y 1000 lbBx 541.7 lb BFDDx 541.7 lb2000 lbBx 541.7 lbActual “stress”distributionBxResultants of the stressesB y 1000 lbM 1000x in - lb F 0 P 541.7 lb F 0 V 1000 lb M 0 M 1000 x in - lbxyBx 541.7 lbBP 541.7 lbxV 1000 lbxWhy is it important to know the internalforces in a structural member?9
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsMEMInternal Forces in Structural MembersHow to break a piece of Torsion10
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - StaticsMEMInternal Forces in Structural Members- A PrimerFx : Axial force (in x - direction)yV y : Shear force in y - directionVz : Shear force in z - directionT ( M x ) : TorqueM y : Bending moment about y - aixszVzV y M z : Bending moment about z - axisMzMyT ( M x )Fxx11
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - Statics MEM Internal Forces in Structural Members-A Primer 600 N 500 lb y x A A 1000 lb 541.7 lb y x D D Cx 541.7 lb Cy 400 lb 1000 lb 541.7 lb y x B B Bx By Cx Cy Bx By Cx Cy Dx Dy Dx Dy Ey Ay Ax 500 lb 2000 lb Ey 1400 lb All these forces at the










