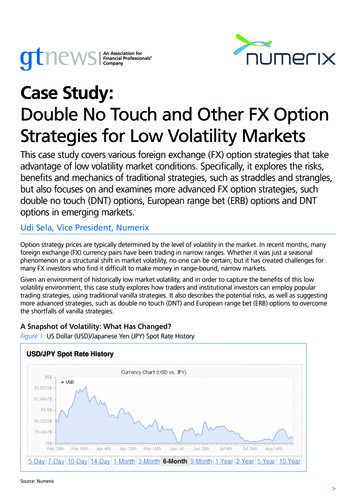
Transcription
Option Strategies Covered Lecture 1.2: Advanced Option StrategiesProfit equations and graphs for option spread strategies,including 01135532: FinancialInstrument and InnovationNattawut Jenwittayaroje, Ph.D., CFADepartment of Banking and FinanceFaculty of Commerce and AccountancyChulalongkorn University Bull spreadsBear spreadsCollarsButterfly spreadsProfit equations and graphs for option combinationstrategies including Straddles21Option Spreads: Basic Concepts (continued) Bull SpreadsNotation For spreads A bull spread consists of the purchase of the call option with the lower exerciseprice and the sale of the call option with the higher exercise price.C 1, C 2, C 3 That is, buy call with strike X1, sell call with strike X2. Let N1 1, N2 -1N1, N2, N3 Profit equation: Max(0,ST - X1) - C1 - Max(0,ST - X2) C2 X 1 X 2 X3 Bull SpreadsSee Table 7.1 below for DCRB option data3 -C1 C2if ST X1 X2 ST - X 1 - C 1 C 2if X1 ST X2 X 2 - X1 - C 1 C 2if X1 X2 ST Maximum profit X2 - X1 - C1 C2, Minimum - C1 C2 Breakeven: ST* X1 C1 - C24
Bull Spreads Bull Spreads Example See Figure 7.1 for DCRB June 125/130, C1 13.50, C2 11.35. That is, buy call with strike 125, sell call with strike 130. Let N1 1, N2 -1 Profit equation: Max(0,ST - 125) – 13.5 - Max(0,ST - 130) 11.35 -13.5 11.35 -2.15if ST 125 130 ST - 125 -13.5 11.35 ST – 127.15if 125 ST 130 130 – 125 -13.5 11.35 2.85if 125 130 ST Maximum profit 130 – 125 -13.5 11.35 2.85 Minimum -13.5 11.35 -2.15 Breakeven: ST* 125 13.5 – 11.35 127.15Long call at X 125A call bull spread has a limitedgain, which occurs in a bull market,and a limited loss, which occurs ina bear market.Short call at X 1305Bear SpreadsBull Spreads (continued) Bull Spreads (continued) A call bull spread has a limited gain, which occurs in a bullmarket, and a limited loss, which occurs in a bear market. In comparison to simply buying the 125 call, the spread traderreduces the maximum loss by the premium on the short 130call and lowers the breakeven, but gives up the chance for largegains if the stock moves up substantially.67Bear Spreads A bear spread is the mirror of a bull spread. We long the high-exercise-price putand short the low-exercise-price put. That is, buy put with strike X2, sell put with strike X1. Let N1 -1, N2 1 Profit equation: -Max(0,X1 - ST) P1 Max(0,X2 - ST) - P2 X2 - X1 P1 - P2if ST X1 X2 P1 X2 - ST - P2if X1 ST X2 P1 - P2if X1 X2 ST Maximum profit X2 - X1 P1 - P2. Minimum P1 - P2. Breakeven: ST* X2 P1 - P2.8
Bear Spreads (continued) Bear Spreads Example See Figure 7.3, p. 225 for DCRB June 130/125, P1 11.50, P2 14.25. That is, buy put with strike 130, sell put with strike 125. Let N1 -1, N2 1 Profit equation: -Max(0,125 - ST) 11.5 Max(0,130 - ST) – 14.25 130 - 125 11.5 - 14.25if ST 125 130 11.5 130 - ST - 14.25if 125 ST 130 11.5 - 14.25if 125 130 ST Maximum profit 130 - 125 11.5 – 14.25. Minimum 11.5 - 14.25. Breakeven: ST* 130 11.5 - 14.25.Long put at X 130A put bear spread has a limited gain,which occurs in a bear market, and alimited loss, which occurs in a bullmarket.Short put at X 125(Return to text slide)910Bear Spreads (continued) Collars Bear Spreads (continued) A put bear spread has a limited gain, which occurs in a bearmarket, and a limited loss, which occurs in a bull market. In comparison to simply buying the 130 put, the spread traderreduces the maximum loss by the premium on the short 125 putand moves up the breakeven, but gives up the chance for largegains if the stock goes down substantially.11Collars A collar is a strategy in which the holder of a position in a stock buys a put with anexercise price lower than the current stock price and sells a call with an exercise pricehigher than the current stock price. The call premium is intended to reduce the cost ofthe put premium. Buy stock, buy put with strike X1, sell call with strike X2. NS 1, NP 1, NC -1. Profit equation: ST - S0 Max(0,X1 - ST) - P1 - Max(0,ST - X2) C2 X1 - S0 - P1 C2if ST X1 X2 ST - S0 - P1 C2if X1 ST X2 X2 - S0 - P1 C2if X1 X2 ST Maximum profit X2 - S0. Minimum X1 - S0. Breakeven: ST* S0.This term is usually set suchthat it is practically zero.12
Collars (continued) A common type of collar is what is often referred to as a zero-cost collar. The callstrike is set such that the call premium offsets the put premium so that there is noinitial outlay for the options. See Figure 7.5 for DCRB July 120/136.165, P1 13.65, C2 13.65. That is, a callstrike of 136.165 generates the same premium as a put with strike of 120. This resultcan be obtained only by using an option pricing model and plugging in exerciseprices until you find the one that makes the call premium the same as the putpremium. This will nearly always require the use of OTC options Profit equation: 120 – 125.94 - 0if ST 120 136.165 ST – 125.94if 120 ST 136.165 136.165 – 125.94 - 0if 120 136.165 ST Maximum profit 136.165 – 125.94. Minimum 120 – 125.94. Breakeven: ST* 125.94.Long put at X 120Short call at X 136.16513Butterfly Spreads (continued) 14Butterfly Spreads (continued)Butterfly Spreads Butterfly spread is a combination of a bull spread and a bear spread. Specifically, buy call (put) with strike X1, buy call (put) with strike X3, sell twocalls (puts) with strike X2. X2 is usually the halfway between X1 and X3. Let N1 1, N2 -2, N3 1.Profit equation: Max(0,ST - X1) - C1 - 2Max(0,ST - X2) 2C2 Max(0,ST - X3)- C3 -C1 2C2 - C3if ST X1 X2 X3 ST - X1 - C1 2C2 - C3if X1 ST X2 X3 -ST 2X2 - X1 - C1 2C2 - C3if X1 X2 ST X3 -X1 2X2 - X3 - C1 2C2 - C3if X1 X2 X3 ST Maximum profit X2 - X1 - C1 2C2 - C3, minimum -C1 2C2 - C3 Breakeven: ST* X1 C1 - 2C2 C3 and ST* 2X2 - X1 - C1 2C2 - C3Butterfly Spread Using CallsProfitProfitX1 X2 X315Butterfly Spread Using PutsSTX1 X2 X3ST16
Butterfly Spreads (continued) A butterfly spread has a limited loss, which occurs on large stockmoves, either up or down, and a limited gain, which occurs if thesock price ends up at the middle exercise price. The butterflyspread is considered low-risk strategy in that its loss is limited. The butterfly spread strategy assumes that the stock price willfluctuate very little. Thus the butterfly spread strategy is one ofthe volatility strategies because it is based on the expectation ofhigh or low volatility rather than the direction of the stock.A butterfly spread has a limited loss,which occurs on large stock moves,either up or down, and a limited gain,which occurs if the sock price ends up atthe middle exercise price.See Figure 7.7 for DCRB July 120/125/130, C1 16.00, C2 13.50, C3 11.35.1817StraddlesStraddles Straddle: long an equal number of puts and calls Profit equation: Max(0,ST - X) - C Max(0,X - ST) - P (assuming Nc 1, Np 1) If ST X, then ST - 150A straddle is a strategy designedto profit if there is a large up ordown move in the stock.If ST X, then ST - X - C - Pif ST X X - ST - C - Pif ST X Breakeven: ST* X - C - P and ST* X C P Breakeven: Maximum profit: , minimum - C – P.ST* 100 and ST* 150 Maximum profit: , minimum - 25. See Figure 7.11 for DCRB June 125, C 13.50, P 11.50. The profit potential on a straddle is unlimited. However, we should be aware thatthe straddle normally requires a fairly large stock price move to be profitable. FromFigure 7.11, it would require about a 20% increase or decrease in the stock price inone month to make a profit.19 100 - ST20
Straddles (continued) Applications of Straddles Appropriate for situations in which one suspect that the stock price willmove substantially but does not know in which direction it will go.Based on perception of volatility greater than priced by marketA Short Straddle Expects the market to stay within a narrow trading range.Unlimited loss potentialBased on perception of volatility less than priced by market21
Lecture 1.2: Advanced Option Strategies Nattawut Jenwittayaroje, Ph.D., CFA Department of Banking and Finance Faculty of Commerce and Accountancy Chulalongkorn University 01135532: Financial Instrument and Innovation 2 Option Strategies Covered Profit equations and graphs for option sprea