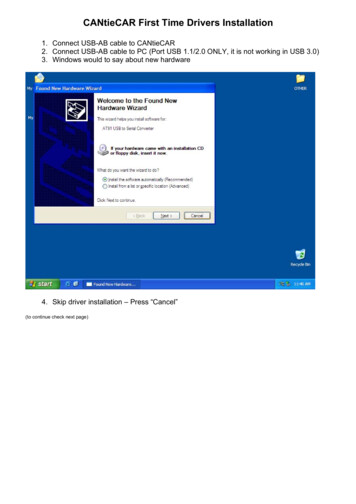
Transcription
LED DriversA Practical Understandingfor Lighting ApplicationsDr. Adan Hernandez, Philips-AdvanceAl Marble, Philips-Advance
Outline What is a driver? Design types Constant current vs. constant voltage Standards/compliance to codes Environmental/temperature ratings Power factor correction2
Typical SSL system Driver Bank of LEDs Fixture or lampDriverMainsFeedback orcontrol signals3LEDsFixtureor lampLight
Purpose and Function “Driver” term adopted from electronic componentterminology Similar function as ballast Processesline voltage into power usable by LED’s Regulatesand controls current to LED’sSwitch-mode electronic solutions4Magnetic solutions
Resistor/Cap/Diode combination Example Film capacitor to drop mains voltage Rectify signal with diodes Use resistor to limit current Advantages Inexpensive & small Disadvantages5 Limited power range Inefficient ( 50%) No LED brightness regulation No power factor correction Susceptible to line transients High LED ripple current (high crest factor)
Design Type: Magnetic Example Use 60Hz step down transformer Rectify signal with diode bridge Use capacitor to filter ripple Advantages Low cost (?) Disadvantages6 Limited LED current regulation Weight & Size Low power factor Power de-rating Safety concerns
Design Type: Switch-Mode Electronic Example Flyback PFconvertercorrection IC MOSFETor BJT switch Advantages Highefficiency Smallsize & weight Powerfactor correction Regulation& Controllability Disadvantages7 Highercost (?)
Operation Type:Voltage Regulated Fixed output voltage (12vdc or 24vdc) Load up to max current/power rating Driver50mAResistorResistor850mA120vac24vdc bus
Operation Type:Voltage Regulated Advantage Flexibility Simpleto connect variable LED loadapplication Disadvantage Moreparts on LED array (current limitingresistors) Not9as energy efficient
Operation Type: Current Regulated Fixed output current (e.g., 350mA)120vac10Xitanium Add load in series up to max outputvoltage 350mA
Operation Type: Current Regulated Advantage Greaterenergy efficiency (no current limitingresistors) Disadvantage Lessflexibility in connecting variable number ofLEDs In general,11 ConstantCurrent for high flux LEDs and, ConstantVoltage for low flux LEDs
Standards/Compliance to Codes UL “Recognized Component” status ULnot providing “Listing” for LED drivers Key:Listing in Sign Accessory Manual (SAM) Confusingto field inspectors UL Class 2 (defined in UL 1310) Loadvoltage 30vdc, load current 5 amps Shortcircuit protection: Secondary fusing or inherentpower limitation Impliesconduit on secondary not required, but manylocal codes require anyways12
Environmental/Temperature Ratings Environmental ratings Drylocation: Protected from any moisture Damplocation: Suitable for self-contained signs/racewayinstallationÚ Mount ½-inch from bottom of enclosure!Ú Referred in UL 935 as “Outdoor Type II” Wetlocation: Weatherproof housing/enclosure Temperature ratings13 Caseratings used by OEMs, impractical for field use Lookfor ambient rating for sign application
Power Factor Correction Best understood by thinking of it as“current factor correction” Powerfactor corrected drivers have lowerinput amperage draw Lighting industry standards Highpower factor (HPF): 90% Normaltypical14power factor (NPF): 90 60%
Power Factor CorrectionConcept:For a given LED load . . . HPF driver draws less inputamps than NPF driver Powerfactor correction is not related to:Ú WattageÚ Power supply losses (efficiency)Ú How the LEDs are driven15
Power Factor Correction60 Watt HPF DriverFrom Utility:75 watt 0.7 amp 120vacLED Load:60 watt 5 amp 12vdcDriver 60 Watt NPF DriverFrom Utility:75 watt 1.0 amp 120vacLED Load:60 watt 5 amp 12vdcDriver16
Power Factor CorrectionWho cares? The utility Userpays utility for “wattage” (i.e., inputpower) Utilitymust generate “amperage,” so NPFwith higher amperage more costly to utilityfor the same money received from customer17
Power Factor CorrectionWho cares? Whoever pays for installation 60watt example:HPF driver draws 0.7 ampsNPF driver draws 1.0 amps 20amp breaker: Load to 16 amps per NECÚ HPF: Load 22 drivers on one circuitÚ NPF: Load 16 drivers on one circuit Cost18of a running a circuit very high!
Power Factor CorrectionWho cares? Anyone concerned with the environmentLess amperageLess generation requirementLess pollutants19
What to look for in a Driver Performance Regulated Poweroutputfactor correction Efficiency Size Life and Reliability20 Environmental concerns Temperature range Dry, damp, or wet location Safety UL Recognition/SAMlisting Class 2
Questions?www.LEDcentral.com
LED Drivers A Practical Understanding for Lighting Applications A Practical Understanding for Lighting Applications Dr. Adan Hernandez, Philips-Advance Al Marble, Philips-Advance.