Transcription
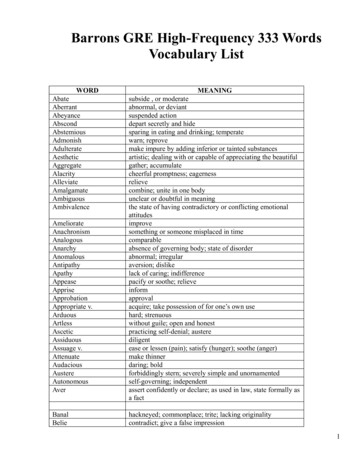
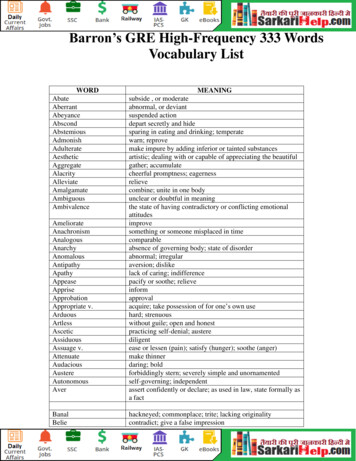
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYacceleration- The rate of change invelocity (a change in direction or achange in speed).acid- A substance that produceshydrogen ions in solution; thesesolutions have a pH less than 7.alternating current (AC) - Electriccurrent that reverses its direction in aregular pattern; the 60-Hz AC in ourhomes changes direction 120 times eachsecond.acid rain - Rain with a pH less than 5.6;produced by substances in the airreacting with rainwater.acoustics -The study of sound.actinide- Any of the 14 radioactiveelements having atomic numbers 90103; used in nuclear power generationand nuclear weapons.active solar heating - Collecting thesun's energy with solar panels, heatingwater with that energy, and storing theheated water to use the energy later.aerosol -A liquid sprayed from apressurized container; for example, a canof insect spray.air resistance - Frictional force airexerts on a moving object; acts oppositein direction to the object's motion.alchemist -A medieval version of themodern chemist; a practitioner whoblended primitive chemistry with magic,seeking to turn ordinary metals intogold.alcohol -Type of compound formedwhen -OH groups replace one or morehydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon.allotropes -Different structural forms ofthe same element; for example, somecarbon molecules form soft graphite,whereas others form hard diamonds.alloy -A mixture consisting of a metaland one or more elements.alpha particle - A particle of nuclearradiation emitted from a decayingatomic nucleus; has a charge of 2 , anatomic mass of 4, and is the largest,slowest, and least penetrating form ofradiation.amalgam- An alloy containing theelement mercury; an example is dentalfillings.ammeter- A galvanometer thatmeasures electrical current passingthrough in amperes; connected in aseries with the circuit.amorphous- Something that has nospecific shape; for example, a liquid orgas.ampere -The unit of measuring current,the rate of flow of electrons in a circuit.amplification- The process of increasingthe strength of an electric signal.amplitude- In a wave, the distance fromthe rest position of the medium to eitherthe crest or trough.amplitude modulated - (AM) waves Radio waves whose amplitude is variedwith voice, music, video, or data fortransmission over long distances.angle of incidence - In waves, the angleformed by the incident wave and thenormal.angle of reflection - In waves, the angleformed by the reflected wave and thenormal (perpendicular).anhydrous- A chemical compound thatnormally has water molecules attachedto its ions but from which water has beenremoved.antacid -An "anti-acid," or a chemicalthat changes an acid substance to aneutral substance.antifreeze -A solute added to a solventto lower the temperature at which thesolvent will freeze.aqueous -Describes a solution madewith water.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYArchimedes' principle - This Greekmathematician stated that the buoyantforce on an object in a fluid is equal tothe weight of the fluid displaced by theobject.aromatic compounds - Chemicalcompounds that contain the benzene ringstructure; most have distinctive odors.artificial satellite - Human-made devicethat orbits Earth; used forcommunication, weather-monitoring,military, and scientific purposes.atomic number - The number ofprotons in an atom's nucleus.average speed - A rate of motiondetermined by dividing the total distancetraveled by the total travel time.average atomic mass - The averagemass of the mixture of an element'sisotopes.balance -A device used in laboratoriesto measure mass; it works by balancing amass to be determined with a standardmass that is known.balanced chemical equation - Achemical equation that has the samenumber of atoms of each element onboth sides of the equation.balanced forces - Forces that are equalin size and opposite in direction.bar graph - A type of graph used toshow information collectedby counting; uses vertical orhorizontal bars of differentlengths to help peoplecompare quantities.base -A substance thatproduces hydroxide ions (OH-) insolution; these solutions have a pHover 7.Bernoulli's principle - The Swissscientist Daniel Bernoulli stated that asthe velocity of a fluid increases, thepressure exerted by the fluid decreases.beta particle - A negatively chargedelectron or positively charged positronemitted from a decaying atomic nucleus.binary compound - A chemicalcompound composed of two elements;for example, sodium chloride.biogas Mixture of gases, mostlymethane, produced when biomass isallowed to rot in the absence of air.biomass -Organic material from suchsources as wood, corn, and wastes fromanimals and crops.bionics The science of designingartificial replacements for parts of thehuman body that are not workingproperly.boiling point - Thetemperature at which vaporbubbles form in a liquid andrise to the surface,increasing evaporation.Boyle's law - Britishscientist Robert Boylestated that volume of a gas decreaseswhen the pressure increases, providedthe temperature stays the same.bubble chamber - Device filled withsuperheated liquid; used to detect andmonitor the path of charged nuclearparticles, which leave a trail of bubblesas they pass though the chamber.buoyant force - Ability of a fluid toexert an upward force on an objectimmersed in the fluid.butane -A flammable gas; part ofnatural gas.byte -A basic unit of computer memorythe represents a character (number,symbol, or alphabet letter); consists of 8bits.calorimeter- An instrument used tomeasure changes in thermal energy.carbohydrate An organic compoundhaving twice as many hydrogen atoms asoxygen atoms.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYcarbon 14 dating - Age-determiningmethod for carbon-containing objects upto 50,000 years old.catalyst-A substance that speeds achemical reaction without itself beingpermanently changed.cathode ray tube (CRT) - Sealed glassvacuum tube that uses electrons andfluorescent material to produce imageson a screen.central processing unit - The maincircuit board inside acomputer that performs thecalculating and holds themain memory.centripetal acceleration Acceleration toward thecenter of a circle by an object movingalong a circular path.centripetal force - The force that causesan object moving along a circular path tomove toward the center of the path.ceramic A material made from driedclay or claylike mixtures.cermet A tough, heat-resistant materialthat has the properties of both a ceramicand an alloy; ceramic-metal.chain reaction - A continuing series offission reactions in which neutrons fromfissioning nuclei cause other nuclei tosplit, releasing more neutrons, whichsplit more nuclei, and so on.Charles's law - The volume of a gasincreases when temperature increases,provided the pressure stays the same.chemical bond - The force that holdstogether the atoms in a compound; itoccurs because atoms of most elementsbecome more stable by losing, gaining,and sharing electrons.chemical change - Thechange of substances todifferent substances.chemical formula - Aprecise statement that tellswhich elements are in a compound andtheir ratios.chemical property - A characteristic ofa substance that indicates whether it canundergo a specific chemical change.chemical reaction - A change in whichone or more substances are converted todifferent substances.chemical symbol - A shorthand way towrite the name of an element; forexample: C for carbon, Ag for silver.chemically stable - Describes an atomwhose outer energy level is completelyfilled with electrons.chemically unstable - Describes anatom whose outer-most energy level isnot filled with electrons so it seekselectrons from other atoms and thusforms compounds.chloro Prefix that indicates presence ofchlorine, as in tetrachloroethylene orchlorofluorocarbon.CFC A group of compounds whosedecomposition releases chlorine atomsthat destroy ozone molecules in theupper atmosphere.circuit A closed path through whichelectrons flow.circuit breaker - A device that protectsan electrical circuit; if too much currentflows, the device opens the circuit,stopping the current.cloud chamber - Device filled withwater- or ethanol-saturated air; used todetect charged nuclear particles, whichleave a trail as they pass through.coagulation Process that destroyscolloid structure; can be used to reduce acolloidal form of air pollution.coal A rock formed of ancient decayedplants; burned as a fossil fuel.coefficient In a chemical equation, thenumber that represents the number ofunits of each substance taking part in achemical reaction.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYcoherent light - A beam of light inwhich all the electromagnetic wavestravel with the crests and troughsaligned; thus, the beam does not spreadout.colloid A heterogeneous mixturecontaining tiny particles that never settleout; for example, milk and gelatin.compression In compressional waves,the dense area of the wave.compressional wave - A type of wavewhere matter vibrates in the samedirection the wave travels.computer A device you can program todo calculations, make logical decisions,and manipulate data.computer virus - Type of programdesigned to infect a computer, erasedata, scramble other programs, or fill upso much memory that the system isharmed.concave lenses - Lenses that are thinnerin the middle and thicker at the edgesand thus curve inward; form virtual,upright, smaller images of an object.concave mirror - A mirror whosesurface curves inward; produces realimages.concentrated solution - A solution inwhich the amount of solute is near themaximum the solvent can hold at thattemperature.concentration Generally, the proportionof a solute dissolved in a solvent.condensation The change of a substancefrom a gas to a liquid, which usuallytakes place when a gas is cooled to orbelow its boiling point.condense To go from the gas state to theliquid state, due to a loss of heat.conduction The transfer of energythrough matter in which energy movesfrom particle to particle.conductor A material that allowselectrons to move easily through it.constant speed - Speed that does notchange.contraction Movement of moleculestoward one another, so that they occupya smaller space.combustion Rapid burning.composite A mixture of two materials,one of which is embedded in the other.compound Substance made of thecombined atoms of two or moreelements.compound machine - A combination oftwo or more simple machines.constant In an experiment, a factor thatdoes not change.control In an experiment, a standard forcomparison that is often needed to drawa meaningful conclusion.convection The transfer of energy by thebulk movement of matter in whichparticles move from place to place influid, carrying the energy with them.convex lenses - Lenses that are thickerin the middle than at the edges; canproduce both real and virtual images.convex mirror - A mirror with a surfacethat curves outward; produces upright,smaller, virtual images of an object.corrosive Hazardous compound thatattacks and alters metals, human tissue,or other materials; for example, ovencleaners and battery acid.coulomb The charge carried by 6.24billion billion electrons.covalent bond - A type of chemicalbond formed by atoms when they shareelectrons.crest The highest point of a wave.critical temperature - Insuperconductors, the very lowtemperature at which a material ceases tohave any electrical resistance.crystals In most solids, the arrangementsof particles in repeating geometricpatterns.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYcurrent The flow of electrons through awire or any conductor; measured inamperes with an ammeter.deceleration The rate of change invelocity (speed and/or direction) whenvelocity is decreasing; also callednegative acceleration.decibel The unit of measure for soundintensity, abbreviated dB.decomposition reaction - A chemicalreaction in which a substance breaksdown into two or more simplersubstances.dehydrating agent - A substance thatcan remove water from materials.density The mass per unit volume of amaterial; describes how tightly packed asubstance's molecules are.dependent variable - In an experiment,the factor whose value changes becauseof a change in the independent variable.derived - Unit of measurement obtainedby combining SI units.detergent An organic salt similar tosoap, except that detergents do not formsoap scum in hard water.diatomic molecule - A moleculecomposed of two atoms of the sameelement.diesel engine - An internal combustionengine that compresses a fuel-airmixture so much that it ignites from theheat of compression without a spark.diffraction The bending of wavesaround a barrier.diffraction grating - A piece of glass orplastic with many parallel slits that actslike a prism, causing white light thatpasses through it to separate into itscomponent colors.dilute solution - A solution in which theamount of solute is much less than themaximum the solvent can hold at thattemperature.diode A type of rectifier that allowselectric current to flow in only onedirection.direct current - Electrical current thatflows in only one direction through awire.disinfectant A chemical that killsbacteria, such as alcohol.dissociation – The breaking apart of anionic compound into positive andnegative ions when dissolved in water.doping Adding an impurity to asemiconductor to increase its electricalconductivity.Doppler effect - An increase or decreasein wave frequency, caused by motion ofthe source and/or motion of the observer;applies to all waves.dot diagram - A diagram to representelectrons in the outer energy level of anatom; uses the element symbols anddots.double displacement reaction - Achemical reaction in which two ioniccompounds in solution react, forming aprecipitate, gas, or water.dry cell - A power source that acts as anelectron pump and generates electriccurrent by a chemical reaction; usesthick, pasty electrolyte.ductile – ability of metals to be pulledinto wireseffort arm - The part of a lever onwhich an effort force is applied.effort force - The force applied to amachine when a machine is used to dowork.electric field - An area surrounding anelectron that exerts a force on anythingnearby with an electric charge; strongestnearest the electron and weakens withdistance.electric motor - A device that contains arotating electromagnet that changeselectrical energy to mechanical energy.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYelectrical power - The rate at whichelectrical energy is converted to anotherform of energy; electrical power isexpressed in watts or kilowatts.electrolyte A substance that separates orforms ions in a water solution, makingthe solution an electrical conductor.electromagnet Strong temporarymagnet made by inserting an iron coreinto a wire coil and passing an electriccurrent through the coil.electromagnetic induction - Process bywhich electrical current is induced in awire when it is moved through amagnetic field.electromagnetic radiation - Transversewaves that transfer energy by radiation;vary in length from very long radiowaves to extremely short gamma waves.electron arrangement - In an atom,how the electrons are distributed in theatom's various energy levels.electron cloud - Region where electronsmost probably are found surrounding thenucleus of an atom.electrons Negatively charged particlesthat move around the nucleus of anatom.electroscope A device containing twosuspended metal leaves in a jar thatmove apart when charged; used to detectthe presence of electric charges.element Substance in which all theatoms in a sample are alike.endothermic reaction - A chemicalreaction in which energy is absorbed.energy The ability to cause change.energy farming - The growing of plantsfor use as fuel.energy transfer - The movement ofenergy from one object to another; forexample, thermal energy flowing as heatfrom a heated stove to a skillet.ester An organic compound formed byreacting an organic acid with an alcohol.evaporation The gradual change of asubstance from a liquid to a gas attemperatures below the boiling point.exothermic reaction - A chemicalreaction in which energy is released.Outward movement of molecules awayfrom one another so that they occupy alarger space.expansion combustion engine - Anengine in which the fuel is burnedoutside the engine.experiment An organized procedure fortesting a hypothesis; typically has acontrol and dependent and independentvariables.farsighted Describes a person who seesfaraway things clearly, but has troublefocusing on nearby objects.fiberglass Hairlike strands of glass thatmake a good insulator when arranged inpuffy layers.filter In working with light, a device thatallows one or more colors to betransmitted while others are absorbed orblocked.flammable A chemical characteristic ofa substance that allows it to oxidizerapidly.fluid Any material that flows, such asliquids and gases.fluorescence Occurs when a materialabsorbs ultraviolet radiation thatstimulates it to radiate visible light.fluorescent light - Light produced whenultraviolet radiation inside a fluorescentlight bulb causes its fluorescent coatingto glow.focal length - The distance from thecenter of a lens or mirror to its focalpoint.focal point - A point on the optical axisof a concave mirror or convex lenswhere the light rays come together.force A push or pull one body exerts onanother.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYfractional distillation - A process basedon boiling points used in oil refineries toseparate the chemical compounds incrude oil into gasoline, kerosene, andother products.fractionating towers - Towers at oilrefineries used for fractional distillationof petroleum.free fall - How an object moves in spacewhen it is influenced only by gravity.freon A refrigerant gas used inrefrigerators and air conditioners.frequency The number of wave creststhat pass a point during one second;expressed in hertz.frequency modulated - Radio waveswhose frequency is varied with voice,music, video, or data for transmissionover long distances.friction The force that opposes motionbetween two surfaces that are touchingeach other.fuel rod - A metal rod filled withuranium pellets, used as the fuel in anuclear reactor.fulcrum The fixed point around which alever pivots.fuse A device that protects an electricalcircuit.galvanometer An instrument used todetect electric currents.gamma rays - High frequencyelectromagnetic waves that travel at thespeed of light, have no mass or charge,and are the most penetrating form ofradiation.gamma rays - High frequencyelectromagnetic waves that travel at thespeed of light, have no mass or chargeand are the most penetrating form ofradiation.gaseous solution - A homogeneous gasthat is composed of two or more gases.gasohol A mixture of ethanol andgasoline that is a useful substitute forgasoline, but whose production may bedamaging to the environment; a biomassfuel.gear A wheel with teeth around its edgedesigned to mesh with teeth on anothergear so as to transfer force and motion.gelatin A substance obtained by boilinganimal bones; used in glues and goods.generator A device that useselectromagnetic induction to induceelectrical current by rotating loops ofwire through a magnetic field.geothermal energy - Thermal energysource located far below Earth's crust.glass A ceramic mixture with no regularcrystal structure.graduated cylinder - A cylinder markedwith volume scale, used in laboratoriesfor measuring liquid volumes.graph A visual display of information ordata organized to help people interpret,understand, or quickly find information.graphite A mineral made of carbonatoms arranged in layers that easily slidepast one another, forming a drylubricant.gravity Force exerted by every object inthe universe on every other object. Theamount of force depends on the massesof the objects and the distance betweenthem.grounded Electrically connected toEarth, either directly or through a wire orother metal object.group In the periodic table, each of the18 vertical columns of elements; eachgroup is made up of elements withsimilar properties.hacker A person who uses a computerto break into other computer systemswithout permission.half life - The amount of time requiredfor one-half of the nuclides in a sampleof radioactive isotope to decay.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYhalogens Highly active elements inperiodic table Group 17; they have sevenelectrons in their outer shells and readilycombine with Group 1 elements.heat Thermal energy that flows from awarmer material to a cooler material.heat engine - A device that convertsthermal energy that is produced byburning fuel into mechanical energy.heat mover - A device that movesthermal energy from one location andreleases it in another location having adifferent temperature.heat of fusion - The amount of energyneeded to change a material from thesolid state to the liquid state.heat of vaporization - The amount ofenergy needed to change a material froma liquid to a gas.herbicide A chemical poison that killsundesirable plants.hertz The unit of measure for frequency.heterogeneous mixture - A mixture inwhich different parts can be easilydistinguished.homogeneous mixture – A mixture inwhich different materials are blendedevenly so that the mixture is the samethroughout; also called a solution.hydrate A compound that has watermolecules chemically attached to its ionsand written into its formula.hydraulic Describes a system operatedby the energy of moving water.hydrocarbon A compound containingonly carbon and hydrogen atoms.hydronium ion - The ion that makes asolution acidic.hypothesis A testable prediction used tosee how something works or to solve aproblem.incandescent light - Light produced bya thin tungsten wire, or filament, that isheated in an incandescent bulb until itglows.inclined plane - A simple machineconsisting of a sloping surface used toraise objects.incoherent light - Light rays that arenearly parallel, but spread out becausetheir electromagnetic waves do nottravel in the same direction.ideal machine - A machine in whichwork input equals work output; such aperfect machine would be frictionlessand 100 percent efficientindependent variable - In anexperiment, the factor adjusted to adifferent value by the experimenter tosee what effect it will have on thedependent variable.indicator An organic compound thatchanges color in an acidic solution or abasic solution.induction Electrically charging anobject or creating an electrical current init, without physically touching it.inertia The tendency of an object toresist any change in its motion. Ifmotionless, it tends to remain at rest; ifmoving, it tends to keep moving at thesame speed and in the same direction.infrared radiation - Electromagneticwaves that have a wavelength slightlylonger than visible light; indicates thepresence of heat.infrasonic waves - Waves at frequenciesbelow the limit of human hearing.inhibitor A substance that slows orprohibits a chemical reaction.instantaneous speed - The rate ofmotion at a given instant in time.insulator A material that does not allowheat or electrons to move through iteasily.integrated circuit - A thin slice ofsilicon, often less than 1 cm on a side,which can contain thousands of resistors,diodes, and transistors; used in computerand electronic equipment.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYintensity In sound waves, the amount ofenergy in each wave.interference The ability of two or morewaves to combine to form a new wave.internal combustion engine - Anengine in which fuel is burned inside theengine in chambers.ion A positively or negatively chargeatom.ionic bond - A type of chemical bondformed by the attraction betweenopposite charges of the ions in an ioniccompound.ionization The breaking apart of certainpolar substances to form ions whendissolved in water.isomers Compounds that have identicalchemical formulas but differentmolecular structures and shapes.isotopes Atoms of the same element thathave different numbers of neutrons.joule The basic unit of energy and work.kelvin The SI unit of temperature.kilogram The SI unit of mass.kilowatt hour - The unit of electricalenergy.kinetic energy - Energy in the form ofmotion, as in a moving car or truck.kinetic theory of matter - The idea thatall matter is made up of constantlymoving, tiny particles.lanthanide Any of the 14 metallicelements having atomic numbers 58-71;used in magnets, ceramics, andtelevision picture tubes.laser A device that emits a beam ofphotons that travel in the same directionand phase, producing a beam of coherentlight.Law of conservation of energy - A lawstating that energy can change form butcannot be created or destroyed underordinary conditions.Law of conservation of mass - A lawstating that matter is neither created nordestroyed during a chemical change.Law of conservation of momentum - Alaw stating that the total momentum of agroup of objects is conserved unless anet force acts on the objects.lever A simple machine consisting of abar that is free to pivot around a fixedpoint.line graph - A type of graph used toshow trends or continuous change bydrawing a line that connects data points.lipids Fats, oils, and related organiccompounds.liquid solution - A liquid solvent thathas dissolved in it a gas, liquid, or solid.liter The unit of liquid volume thatoccupies the same volume as a cubicdecimeter and is slightly larger than aquart.loudness The human perception ofsound intensity.lubricant A substance used to reducefriction between two surfaces that movetogether; for example, oil,grease, or graphite.machine A device thatmakes work easier bychanging the size of theforce applied to it and/or the direction ofthe force.magnetic bottle - A powerful magneticfield that creates a container to hold thehydrogen plasma needed for a nuclearfusion reaction.magnetic domains - Groups of atomswith aligned magnetic poles.magnetic field - The region around amagnet where magnetic forces act.magnetic poles - The two ends of apiece of magnetic material where themagnetic forces are strongest, labelednorth pole and south pole.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYmagnetism A property of somematerials in which there is a force ofrepulsion or attraction between certainlike and unlike poles.magnifier A device thatmakes things appear larger sothat more detail can be seen;for example, a microscope.malleable Ability of metals to behammered or rolled into thin sheets.mass A measurement of the amount ofmatter in an object.mass number - Sum of the number ofprotons and neutrons in an atom'snucleus.mechanical advantage - The number oftimes a machine multiples the effortforce applied to it.mechanical energy - The total amountof kinetic energy and potential energy ina system.medium A material through which awave travels.melt The changing of a substance from asolid state to a liquid state when heatedabove the substance's freezing/meltingpoint.melting point - The temperature atwhich a solid changes to a liquid.metallic bonding - The type of chemicalbond in which positively charged ionsare surrounded by freely movingelectrons.metalloids Elements having propertiesof both metals and nonmetals.metals Elements usually having thesecommon properties: shiny, goodconductors of heat and electricity, aresolids at room temperature.meter The SI base unit of length.microprocessor The computer's "brain."It receives input and tells the computerhow to respond.microscope A opticalinstrument that uses twoconvex lenses withrelatively short focallengths to magnify small,close-up objects.microwaves Radio waves with thehighest frequency and energy; used incommunications and microwave ovens.mixture A material made of elements orcompounds stirred together but notcombined chemically.model A symbolic representation of anidea, system, or structure to makesomething understandable.modulation Process of adding voice,music, video, computer information, orother data to radio waves by usingelectrical currents to vary eitheramplitude or frequency.momentum A property of any movingobject; the product of an object's massand velocity.monomers Organic molecules that arestrung together to form polymers.music Sound created using specificpitches, sound quality, and regularpatterns.nearsighted Describes a person whosees nearby things clearly, but hastrouble focusing on distant objects.net force - The sum of the forces on anobject when unbalanced forces areapplied to it.neutralization A chemical reactionbetween an acid and a base.neutralize To change an acidic solutionor a basic solution so that it is neutral.neutron Atomic particle with no chargethat is part of an atom's nucleus.Newton's first law of motion Describes the relationship betweenvelocity and forces. An object moving ata constant velocity keeps moving at thatvelocity unless a net force acts on it.
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARYNewton's second law of motion Describes the acceleration of an object inthe direction of the net force applied toit.Newton's third law of motion Describes action-reaction pairs; forevery action force, there is an equal andopposite reaction force.NIMBY Not in my backyard; a point ofview that supports an issue such asnuclear generation of electricity as longas it does not take place close to home.noise Sound that has no regular patternor definite pitch.nonelectrolyte A substance, such aspure water, that does not conductelectricity.nonmetals Elements that usually aregases or brittle solids at roomtemperature; most do not conduct heat orelectricity well.nonpolar molecule - A molecule thatdoes not have oppositely charged ends.nonrenewable resources - Resourcessuch as coal, oil, and natural gas, whichcannot be replaced after they are usedup.normal In the study of light, animaginary line drawn perpendicular to areflecting surface or perpendicular to amedium that light is entering.nuclear fission - Process in which anatom's nucleus is split into two nucleiwith smaller masses.nuclear fusion - Process in which twoatomic nuclei with low masses are fusedinto a single nucleus of larger mass; alsoknown as a thermonuclear reaction.nuclear reactor - A device thatgenerates electricity from a controllednu
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY carbon 14 dating - Age-determining method for carbon-containing objects up to 50,000 years old. catalyst-A substance that speeds a chemical reaction without itself being permanently changed. cathode ray tube (CRT) - Sealed glass vacuum tube that uses electron