Transcription
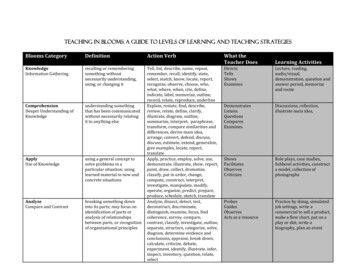
Teaching in Blooms: A guide to levels of learning and teaching strategiesBlooms CategoryDefinitionAction VerbWhat theTeacher DoesKnowledgeInformation Gatheringrecalling or rememberingsomething withoutnecessarily understanding,using, or changing itDirectsTellsShowsExaminesLecture, reading,audio/visual,demonstration, question andanswer period, memorizeand reciteComprehensionDeeper Understanding ofKnowledgeunderstanding somethingthat has been communicatedwithout necessarily relatingit to anything scussions, reflection,illustrate main idea,ApplyUse of Knowledgeusing a general concept tosolve problems in aparticular situation; usinglearned material in new andconcrete situationsShowsFacilitatesObservesCriticizesRole plays, case studies,fishbowl activities, constructa model, collection ofphotographsAnalyzeCompare and Contrastbreaking something downinto its parts; may focus onidentification of parts oranalysis of relationshipsbetween parts, or recognitionof organizational principlesTell, list, describe, name, repeat,remember, recall, identify, state,select, match, know, locate, report,recognize, observe, choose, who,what, where, when, cite, define,indicate, label, memorize, outline,record, relate, reproduce, underlineExplain, restate, find, describe,review, relate, define, clarify,illustrate, diagram, outline,summarize, interpret, paraphrase,transform, compare similarities anddifferences, derive main idea,arrange, convert, defend, discuss,discuss, estimate, extend, generalize,give examples, locate, report,translateApply, practice, employ, solve, use,demonstrate, illustrate, show, report,paint, draw, collect, dramatize,classify, put in order, change,compute, construct, interpret,investigate, manipulate, modify,operate, organize, predict, prepare,produce, schedule, sketch, translateAnalyze, dissect, detect, test,deconstruct, discriminate,distinguish, examine, focus, findcoherence, survey, compare,contrast, classify, investigate, outline,separate, structure, categorize, solve,diagram, determine evidence andconclusions, appraise, break down,calculate, criticize, debate,experiment, identify, illustrate, infer,inspect, inventory, question, relate,selectProbesGuidesObservesActs as a resourcePractice by doing, simulatedjob settings, write acommercial to sell a product,make a flow chart, put on aplay or skit, write abiography, plan an eventLearning Activities
EvaluateJudging the Outcomejudging the value of materialor methods as they might beapplied in a particularsituation; judging with theuse of definite criteriaCreateOriginal or new creationcreating something new byputting parts of differentideas together to make awhole.Coordinate, judge, select/choose,decide, debate, evaluate, justify,recommend, verify, monitor,measure, the best way, what worked,what could have been different, whatis your opinion, test, appraise, assess,compare, conclude, contrast, criticize,discriminate, estimate, explain,grade, interpret, rate, relate, revise,score, summarize, support, valueCreate, hypothesize, design,construct, invent, imagine, discover,present, deduce, induce, bringtogether, compose, pretend, predict,organize, plan, modify, improve,suppose, produce, set up, what if,propose, formulate, solve (more thanone answer), arrange, assemble,categorize, collect, combine, devise,explain, generate, manage, perform,prepare, rearrange, reconstruct,relate, reorganize, revise, argue forAdapted from these col/id/doc/BloomPolygon.pdfAcceptsLays bare the criteriaHarmonizesUse in real situations, on thejob training, create a newproduct, write a newlanguage code and write init, persuasively present anidea, devise a way to solve aproblem, compose a rhythmor put new words to a songReflectsExtendsAnalyzesEvaluatesSelf study, learning throughmistakes, create criteria tojudge material, conduct adebate, write a half yearlyreport,L. W. Anderson and D. R. Krathwohl (eds). A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing (based on Bloom’s Taxonomy), 2001.
Checklist for Student Learning Outcomes Are the student learning outcomes aligned with the vision, mission, values, and goals? Are the student learning outcomes measuring something useful and meaningful? Is it clear what the student learning outcomes are assessing? Can assessment of the student learning outcomes be used to identify areas to improve? Are they written using action verbs to specify clear, observable behaviors? Is it possible to collect accurate and reliable data for each student learning outcome? Are they written so that more than one measurement method can be used? Are the student learning outcomes simply stated? Are they written in “student-friendly”language? Are there a reasonable number of learning outcomes so that advisors and students aren’toverwhelmed? Are the learning outcomes listed sequentially in order of developmental achievement-least tomost complex? Are the learning outcomes reasonable for advisors to facilitate and students to achieve? Forexample, if advisors have no strategies for teaching advisees to be better world citizens, don'tlist it as a learning objective. When will the students initially be told about the student learning outcomes? How often willthey be referred to again? When will you plan to review and revise the student learning outcomes to ensure they reflectchanges to the student body, advising program, and institution?Adapted from:Bresciani, M. (2001). Writing Measurable and Meaningful Outcomes. Retrieved sions/200708/Session es-%20Bresciani%20Article.pdfHow to Write Program Objectives/Outcomes. University of Connecticut. Retrieved ectivesOutcomes.pdfMartin, H. (2007) Constructing Learning Objectives for Academic Advising. Retrieved from NACADAClearinghouse of Academic Advising Resources Web tcomes.aspx#sthash.ZOBjBZRQ.dpuf
Worksheet 1Reasons for Assessment & StakeholdersReasons for Assessment:What are Your Three Main Reasons for Designing anAssessment Plan for Your Academic Advising Program?Stakeholder in the process:Who Needs to Be Involved in Your Process and Why?1.1.2.2.3.3.
Worksheet 2Values, Vision and MissionWhat Are the Values of YourAcademic Advising Program?What Is Your Vision for YourAcademic Advising Program?What is the Mission Statement for YourAcademic Advising Program?
Worksheet 3Goals and Programmatic OutcomesWhat Are Your Programmatic Outcomes for YourAcademic Advising Program?What Are Your Goals for Your Academic AdvisingProgram?1.1.2.2.3.3.4.4.5.5.6.6.
Worksheet 4Advisor OutcomesAcademic Advisor OutcomesWhat Expectations for Academic Advisor?
Worksheet 5Student Learning Outcomes - CognitiveStudent Learning Outcomes for Academic AdvisingExamples: Know the general education requirements of yourinstitution. Know how to get involved in service learning experiences. Know about the campus procedures related to academicappeals.What do you want students to demonstrate that they KNOWas a result of participating in academic advising?1.2.3.4.
Worksheet 6Student Learning Outcomes – Skills/PsychomotorStudent Learning Outcomes for Academic AdvisingExamples: Read a degree audit. Identify courses that will add value to their intended majorsand/or careers. Use campus resources when they need assistance. Use your institution’s automated registration system.What do you want students to demonstrate that they AREABLE TO DO as a result of participating in academicadvising?1.2.3.4.
Worksheet 7Student Learning Outcomes - AffectiveWhat do you want students to demonstrate theyVALUE/APPRECIATE as a result of participating inacademic advising?Student Learning Outcomes for Academic AdvisingExamples: Value/appreciate the role of internships as part of theirundergraduate experience. Value/appreciate general education as liberal education. Value/appreciate the role of their academic advisor in helping toshape their educational plans.1.2.3.4.
Worksheet 8Mapping, Gathering Evidence, and Setting Expected Levels of PerformanceAdvisor OutcomesWhere the Process is toOccurAdvisor Outcomes(relates to whereassessment evidence willbe obtained)From Whom, Whenand How Often willEvidence BeGathered?Where or How WillYou Gather Evidence?(quantitative, qualitative;direct, indirect)Level of ExpectedPerformance(Performance Criteria)
Worksheet 9Mapping, Gathering Evidence, and Setting Expected Levels of PerformanceStudent Learning OutcomesWhat Should BeLearned?(Student LearningOutcomes)Where to Learn it?(What Experiences areProvided for Learning?)By When ShouldLearning Occur?(First-Year, SophomoreYear, Junior Year,Senior Year, etc.)*From Whom,When and HowOften willEvidence BeGathered?Where or HowWill You GatherEvidence?(quantitative,qualitative; direct,indirect)Level of ExpectedPerformance(Performance Criteria)
Worksheet 10Sharing and Acting on ResultsInterpret How Results Will Inform theAcademic Advising Process, StudentLearning and Decision MakingDetermine How and With Whom YouWill Share InterpretationsDecide How You Will Follow-up onImplemented Changes
A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing (based on Bloom’s Taxonomy), 2001. Evaluate Judging the Outcome judging the value of material or methods as they might be applied in a particular situation; judging with the use of definite criteria Coordinate, judge, select/choose, decid