Transcription
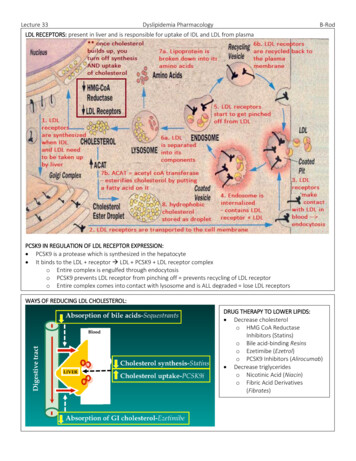
Lecture 33Dyslipidemia PharmacologyB-RodLDL RECEPTORS: present in liver and is responsible for uptake of IDL and LDL from plasmaPCSK9 IN REGULATION OF LDL RECEPTOR EXPRESSION: PCSK9 is a protease which is synthesized in the hepatocyte It binds to the LDL receptor LDL PCSK9 LDL receptor complexo Entire complex is engulfed through endocytosiso PCSK9 prevents LDL receptor from pinching off prevents recycling of LDL receptoro Entire complex comes into contact with lysosome and is ALL degraded lose LDL receptorsWAYS OF REDUCING LDL CHOLESTEROL:DRUG THERAPY TO LOWER LIPIDS: Decrease cholesterolo HMG CoA ReductaseInhibitors (Statins)o Bile acid-binding Resinso Ezetimibe (Ezetrol)o PCSK9 Inhibitors (Alirocumab) Decrease triglycerideso Nicotinic Acid (Niacin)o Fibric Acid Derivatives(Fibrates)
Lecture 33Dyslipidemia PharmacologyB-RodHMG CoA REDUCTASE INHIBITORS: (“Statins”)EFFECTIVENESS: First line agents to reduce cholesterol –major effect on livero Reduces plasma LDL by 18-55%o Minor reduction in VLDLtriglyceride (7-30%)o Marginal elevation of HDL (5-15%) Effective with once daily administrationNON-CHOLESTEROL RELATED ACTIONS:1. Improving endothelial function – decreased oxidative stress(prevents atherosclerosis)2. Modulate inflammatory response – reduction of inflammationat site of plaque (prevent infiltration of monocytes)3. Maintain plaque stability – reduced degradation ofextracellular matrix (blocks action of MMPs which degradethe plaque)4. Prevent thrombus formation – reduced platelet aggregationADVERSE EFFECTS: Myopathy (minor muscle weakness &tenderness) rhabdomyolysiso Monitor serum CPK in symptomatic patients Hepatic toxicityo Monitor with liver function tests (serumtransaminases) in symptomatic patients) Metabolzed:o CYP3A4: Atorva, Lova, Simova GRAPEFRUIT INHIBITSo CYP2C9: Fluva, Rosuva WARFARINo No CYP: Prava Pregnancy: skeletal malformation in fetus
Lecture 33Dyslipidemia PharmacologyB-RodBILE ACID SEQUESTRANTS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: Interactions:o Binds negatively charged drugs reduced absorption (digoxin,beta blockers, warfarin, thiazide)o Prevents re-absorption of fat soluble vitaminso Take other PO meds either an hr before or 4h after resin GI (bloating, constipation) Two availableo Colestipol HCl(Colestid) Granules: mix withfluid/pulpy fruits,soups, cereals Tablets: swallowwhole with fluidso Colesevelam HCl(Lodalis) Tablets: swallowwhole with fluidsDecreases LDLso Weakly stimulateshepatic triglyceridesynthesisWith time, efficacy of resinscan become bluntedo Up-regulation of HMGCoA reductaseo in hepaticcholesterol synthesiso in hepatic LDLreceptorsBiologically inertRarely used in therapeuticsEZETIMIBE: novel inhibitor of intestinal cholesterol absorption at the brush border Rapidly metabolized toglucuronide (active metabolite)o 400x potency of EZE prolongs actionNo important adverse effects ORsignificant drug interactionsMonotherapy/combination withstatino 25% reduction in LDLPLANT STENOLS: veggies, fruits Normally bile acids makecholesterol into micelles whichallow it to be absorbed Plant stenols look like cholesterolbut are more hydrophobic, sothey displace cholesterol fromthe micelles cholesterolexcreted
Lecture 33Dyslipidemia PharmacologyB-RodPCSK9 INHIBITORS: ROLE OF TRIGLYCERIDES:TRIGLYCERIDE MOVEMENT FROM STORAGE LIVER:Alirromumabo Injected sc once every 2 wksEvolocumabo Injected sc once every 4 wks Can reduce LDL-C by up to 65%o Very good for familialhypercholesteremia Modest side effects (URTI, rash,injection site reactions)
Lecture 33NICOTINIC ACID (Niacin):Dyslipidemia PharmacologyB-RodEFFECTS: Reduced HSL Reduced FA release Reduced VLDL synthesiso Results in reduced LDL Increase LPL Decrease TGs by 20-50% Reduction in cholesterol: 25% AGENT WITH LARGEST IMPACTON HDL (increase ApoA1)ADVERSE EFFECTS: Flushing: caused by activationof GPR109A on skin whichreleases prostaglandinso To counter, give aspirin 30mins before HyperglycemiaFIBRIC ACID DERIVATIVES (Fibrates):EFFECTS: Most effective at reducingVLDL (TG): 20-25% Less effective in reducingLDL (10-15%) Increases HDL (increasedtranscription of ApoA1)MOA: Increases FA oxidation inliver/muscle (PPARα) andincreases LPLADVERSE EFFECTS: GI intolerance Gallstones
Lecture 33 Dyslipidemia Pharmacology B-Rod LDL RECEPTORS: present in liver and is responsible for uptake of IDL and LDL from plasma PCSK9 IN REGULATION OF LDL RECEPTOR EXPRESSION: PCSK9 is a protease which is synthesized in the hepatocyte It binds











