Transcription
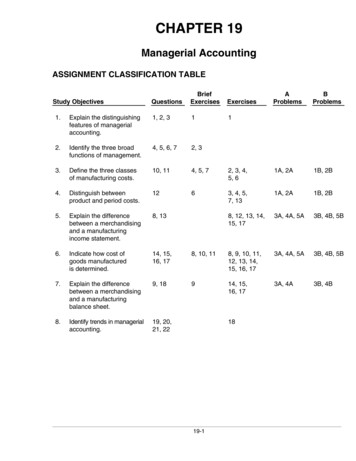
CHAPTER 19Managerial AccountingASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLEStudy sBProblems*1.Explain the distinguishingfeatures of managerialaccounting.1, 2, 311*2.Identify the three broadfunctions of management.4, 5, 6, 72, 3*3.Define the three classesof manufacturing costs.10, 114, 5, 72, 3, 4,5, 61A, 2A1B, 2B*4.Distinguish betweenproduct and period costs.1263, 4, 5,7, 131A, 2A1B, 2B*5.Explain the differencebetween a merchandisingand a manufacturingincome statement.8, 138, 12, 13, 14,15, 173A, 4A, 5A3B, 4B, 5B*6.Indicate how cost ofgoods manufacturedis determined.14, 15,16, 178, 10, 118, 9, 10, 11,12, 13, 14,15, 16, 173A, 4A, 5A3B, 4B, 5B*7.Explain the differencebetween a merchandisingand a manufacturingbalance sheet.9, 18914, 15,16, 173A, 4A3B, 4B*8.Identify trends in managerialaccounting.19, 20,21, 221819-1
ASSIGNMENT CHARACTERISTICS lotted (min.)1AClassify manufacturing costs into different categories andcompute the unit cost.Simple20–302AClassify manufacturing costs into different categories andcompute the unit cost.Simple20–303AIndicate the missing amount of different cost items, andprepare a condensed cost of goods manufactured schedule,an income statement, and a partial balance sheet.Moderate30–404APrepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule, a partialincome statement, and a partial balance sheet.Moderate30–405APrepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule and acorrect income statement.Moderate30–401BClassify manufacturing costs into different categories andcompute the unit cost.Simple20–302BClassify manufacturing costs into different categories andcompute the unit cost.Simple20–303BIndicate the missing amount of different cost items, andprepare a condensed cost of goods manufactured schedule,an income statement, and a partial balance sheet.Moderate30–404BPrepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule, a partialincome statement, and a partial balance sheet.Moderate30–405BPrepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule and acorrect income statement.Moderate30–4019-2
19-3Q19-9E19-15Explain the difference between amerchandising and a manufacturingincome statement.Indicate how cost of goodsmanufactured is determined.Q19-18Explain the difference between amerchandising and a manufacturingbalance sheet.Identify trends in managerialaccounting.*5.*6.*7.*8.Broadening Your PerspectiveE19-15Q19-14Distinguish between productand period costs.*4.Q19-10Define the three classesof manufacturing costs.*3.Q19-22E19-18Real-World 9E19-10E19-11E19-12E19-13P19-5BP19-5BDecision MakingAcross theOrganizationCommunicationManagerial AnalysisExploring the WebE19-17 P19-3AP19-4A P19-3BP19-4BE19-14 E19-8E19-16 E19-10E19-17 E19-11P19-4A P19-3AP19-4B P19-5AP19-3BP19-4B plicationBE19-7 E19-4E19-2 E19-5E19-3 E19-6Q19-4Q19-5Q19-6Identify the three broad functionsof management.*2.Q19-1Q19-2Q19-3ComprehensionExplain the distinguishing featuresof managerial accounting.Knowledge*1.Study ObjectiveEthics CaseAll AboutYouSynthesis EvaluationCorrelation Chart between Bloom’s Taxonomy, Study Objectives and End-of-Chapter Exercises and ProblemsBLOOM’S TAXONOMY TABLE
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS1.(a) Disagree. Managerial accounting is a field of accounting that provides economic and financialinformation for managers and other internal users.(b) Mary is incorrect. Managerial accounting applies to all types of businesses—service, merchandising,and manufacturing.2.(a)(b)(c)3.Financial accounting is concerned primarily with external users such as stockholders, creditors,and regulators. In contrast, managerial accounting is concerned primarily with internal users suchas officers and managers.Classified financial statements are the end product of financial accounting. The statements areprepared quarterly and annually. In managerial accounting, internal reports may be prepared daily,weekly, monthly, quarterly, annually, or as needed.The purpose of financial accounting is to provide general-purpose information for all users.The purpose of managerial accounting is to provide special-purpose information for a particularuser for a specific decision.Differences in the content of the reports are as follows:FinancialManagerial Pertains to business as a whole and is highlyaggregated. Limited to double-entry accounting and costdata. Generally accepted accounting principles. Pertains to subunits of the business andmay be very detailed. May extend beyond double-entry accountingsystem to any relevant data. Standard is relevance to decisions.In financial accounting, financial statements are verified annually through an independent auditby certified public accountants. There are no independent audits of internal reports issued bymanagerial accountants.4.Budgets are prepared by companies to provide future direction. Because the budget is also usedas an evaluation tool, some managers try to game the budgeting process by underestimatingtheir division’s predicted performance so that it will be easier to meet their performance targets.On the other hand, if the budget is set at unattainable levels, managers sometimes take unethicalactions to meet targets to receive higher compensation or in some cases to keep their jobs.5.Karen should know that the management of an organization performs three broad functions:(1) Planning requires management to look ahead and to establish objectives.(2) Directing involves coordinating the diverse activities and human resources of a company toproduce a smooth-running operation.(3) Controlling is the process of keeping the company’s activities on track.6.Disagree. Decision making is not a separate management function. Rather, decision making involvesthe exercise of good judgment in performing the three management functions explained in theanswer to question five above.7.CEOs and CFOs must now certify that financial statements give a fair presentation of the company’soperating results and its financial condition and that the company maintains an adequate systemof internal controls. In addition, the composition of the board of directors and audit committees receivesmore scrutiny, and penalties for misconduct have increased.19-4
Questions Chapter 19 (Continued)8.9.The differences between income statements are in the computation of the cost of goods sold asfollows:Manufacturingcompany:Beginning finished goods inventory plus cost of goods manufactured minusending finished goods inventory cost of goods sold.Merchandisingcompany:Beginning merchandise inventory plus cost of goods purchased minus endingmerchandise inventory cost of goods sold.The difference in balance sheets pertains to the presentation of inventories in the current assetsection. In a merchandising company, only merchandise inventory is shown. In a manufacturingcompany, three inventory accounts are shown: finished goods, work in process, and raw materials.10.Manufacturing costs are classified as either direct materials, direct labor, or manufacturing overhead.11.No, Matt is not correct. The distinction between direct and indirect materials is based on two criteria:(1) physical association and (2) the convenience of making the physical association. Materials whichcan not be easily associated with the finished product are considered indirect materials.12.Product costs, or inventoriable costs, are costs that are a necessary and integral part of producingthe finished product. Period costs are costs that are identified with a specific time period ratherthan with a salable product. These costs relate to nonmanufacturing costs and therefore are notinventoriable costs.13.A merchandising company has beginning merchandise inventory, cost of goods purchased, andending merchandise inventory. A manufacturing company has beginning finished goods inventory,cost of goods manufactured, and ending finished goods inventory.14.(a)(b)15.Raw materials inventory, beginning .Raw materials purchases .Total raw materials available for use .Raw materials inventory, ending.Direct materials used . 12,000170,000182,00015,000 167,00016.Direct materials used.Direct labor used .Total manufacturing overhead.Total manufacturing costs . 240,000200,000180,000 620,00017.(a)(b) 646,000 614,00018.The order of listing is finished goods inventory, work in process inventory, and raw materials inventory.19.The value chain refers to all activities associated with providing a product or service. For a manufacturer, this includes research and development, product design, acquisition of raw materials, production,sales and marketing, delivery, customer relations, and subsequent service.x total cost of work in process.x cost of goods manufactured.Total cost of work in process ( 26,000 620,000).Cost of goods manufactured ( 646,000 – 32,000) .19-5
Questions Chapter 19 (Continued)20.In a just-in-time inventory system the company has no extra inventory stored. Consequently, ifsome units that are produced are defective, the company will not have enough units to deliver tocustomers.21.The balanced scorecard is called “balanced” because it strives to not over emphasize any oneperformance measure, but rather uses both financial and non-financial measures to evaluate allaspects of a company’s operations in an integrated fashion.22.Activity-based costing is an approach used to allocate overhead based on each product’s relativeuse of activities in making the product. Activity-based costing is beneficial because it results inmore accurate product costing and in more careful scrutiny of all activities in the value chain.19-6
SOLUTIONS TO BRIEF EXERCISESBRIEF EXERCISE 19-1Financial AccountingManagerial AccountingPrimary usersExternal usersInternal usersTypes of reportsFinancial statementsInternal reportsFrequency of reportsQuarterly and annuallyAs frequently as neededPurpose of reportsGeneral-purposeSpecial-purpose informationfor a particular user fora specific decisionContent of reportsGenerally acceptedaccounting principlesRelevance to decisionsVerificationAnnual audit by certifiedpublic accountantNo independent auditsBRIEF EXERCISE 19-2One implication of SOX was to clarify top management’s responsibility forthe company’s financial statements. CEOs and CFOs must now certify thatfinancial statements give a fair presentation of the company’s operating results and its financial condition. In addition, top management must certifythat the company maintains an adequate system of internal controls tosafeguard the company’s assets and ensure accurate financial reports. Also,more attention is now paid to the composition of the company’s board ofdirectors. In particular, the audit committee of the board of directors mustbe comprised entirely of independent members (that is, non-employees) andmust contain at least one financial expert. Finally, to increase the likelihoodof compliance with these and other new rules, the penalties for misconductwere substantially increased.19-7
BRIEF EXERCISE 19-3(a) (1) Planning.(b) (2) Directing.(c) (3) Controlling.BRIEF EXERCISE 19-4(a)(b)(c)(d)DMDLMOMOFrames and tires used in manufacturing bicycles.Wages paid to production workers.Insurance on factory equipment and machinery.Depreciation on factory equipment.BRIEF EXERCISE 19-5(a)(b)(c)(d)(e)(f)(g)(h)Direct materials.Direct materials.Direct labor.Manufacturing overhead.Manufacturing overhead.Direct materials.Direct materials.Manufacturing overhead.BRIEF EXERCISE .Product.Product.19-8
BRIEF EXERCISE 19-7Product OverheadXXXXBRIEF EXERCISE 19-8(a) Direct materials used.Direct labor .Total manufacturing overhead .Total manufacturing costs. 180,000229,000208,000 617,000(b) Beginning work in process .Total manufacturing costs.Total cost of work in process . 25,000617,000 642,000BRIEF EXERCISE 19-9DIEKER COMPANYBalance SheetDecember 31, 2008Current assetsCash .Accounts receivable .InventoriesFinished goods.Work in process .Raw materials.Prepaid expenses .Total current assets .19-9 62,000200,000 71,00087,00073,000231,00038,000 531,000
BRIEF EXERCISE 19-10DirectMaterials Used(1)(2)(3)DirectLabor UsedFactoryOverheadTotalManufacturingCosts 136,000 81,000 144,000BRIEF EXERCISE 19-11TotalManufacturingCosts(1)(2)(3)Work inProcess(January 1)Work inProcess(December 31) 136,000Cost of GoodsManufactured 174,000 123,000 58,00019-10
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISESEXERCISE 19-11. False. Financial accounting focuses on providing information to externalusers.2. True.3. False. Preparation of budgets is part of managerial accounting.4. False. Managerial accounting applies to service, merchandising andmanufacturing companies.5. True.6. False. Managerial accounting reports are prepared as frequently asneeded.7. True.8. True.9. False. Financial accounting reports must comply with Generally AcceptedAccounting Principles.10. False. Managerial accountants are expected to behave ethically, and thereis a code of ethical standards for managerial accountants.EXERCISE c)(a)Direct labor.*Manufacturing overhead.Manufacturing overhead.Manufacturing overhead.Direct materials.Direct labor.Manufacturing overhead.Manufacturing overhead.Manufacturing overhead.Direct materials.*or sometimes (c), depending on the circumstances19-11
EXERCISE 19-3(a) Materials used in product. DM Advertising expense .PeriodDepreciation on plant. MOH Property taxes on plant. MOHProperty taxes on store.Period Delivery expense .PeriodLabor costs of assemblySales commissions.Periodline workers . DL Salaries paid to sales clerks.PeriodFactory supplies used . MOH(b) Product costs are recorded as a part of the cost of inventory, becausethey are an integral part of the cost of producing the product. Product costsare not expensed until the goods are sold. Period costs are recognizedas an expense when incurred.EXERCISE 19-4(a) Factory utilities .Depreciation on factory equipment .Indirect factory labor .Indirect materials .Factory manager’s salary.Property taxes on factory building .Factory repairs.Manufacturing overhead. 11,50012,65048,90080,8008,0002,5002,000 166,350(b) Direct materials.Direct labor.Manufacturing overhead.Product costs . 137,60069,100166,350 373,050(c) Depreciation on delivery trucks .Sales salaries .Repairs to office equipment .Advertising .Office supplies used .Period costs . 19-123,80046,4001,30018,0002,640 72,140
EXERCISE .or sometimes (c), depending on the circumstances.EXERCISE c)(c)EXERCISE 19-7(a)(b)Delivery service (product) costs:Indirect materialsDepreciation on delivery equipmentDispatcher’s salaryGas and oil for delivery trucksDrivers’ salariesDelivery equipment repairsTotal 5,40011,2005,0002,20011,000300 35,100Period costs:Property taxes on office buildingCEO’s salaryAdvertisingOffice suppliesOffice utilitiesRepairs on office equipmentTotal 87012,0001,600650990180 16,29019-13(c)(c)
EXERCISE 19-8(a) Work-in-process, 1/1.Direct materials used.Direct labor.Manufacturing overheadDepreciation on plant .Factory supplies used.Property taxes on plant .Total manufacturing overhead .Total manufacturing costs.Total cost of work-in-process.Less: ending work-in-process .Cost of goods manufactured . 12,000 100,000110,000 60,00023,00014,00097,000(b) Finished goods, 1/1 .Cost of goods manufactured .Cost of goods available for sale .Finished goods, 12/31 .Cost of goods sold .307,000319,00015,500 303,500 60,000303,500363,50055,600 307,900EXERCISE 19-9Total raw materials available for use:Direct materials used.Add: Raw materials inventory (12/31).Total raw materials available for use. 190,00012,500 202,500Raw materials inventory (1/1):Direct materials used.Add: Raw materials inventory (12
(a) Disagree. Managerial accounting is a field of accounting that provides economic and financial information for managers and other internal users. (b) Mary is incorrect. Managerial accounting applies to all types of











