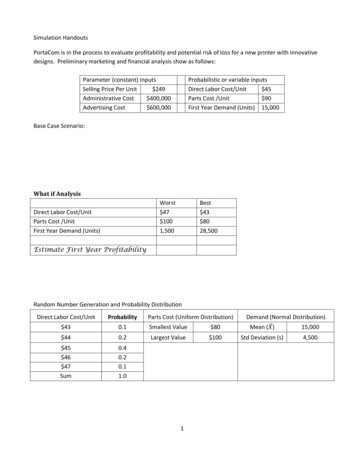
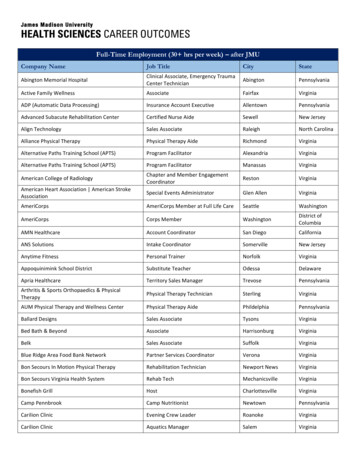
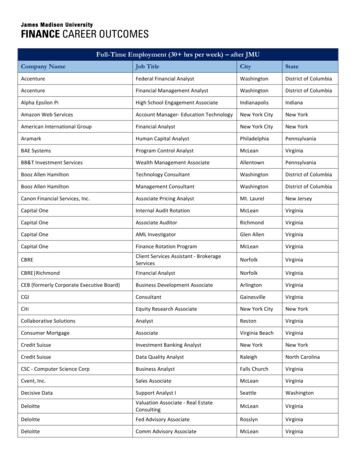
Transcription
Computer Science atJames Madison UniversityDr. Sharon Simmons, Department HeadDr. Chris Mayfield, Assistant ProfessorCHOICES 20161
What isComputer Science?2
What is Computer Science?CS is posingaproblem in such away that a computercan help us solve it. CommunicateSolve problemsDesign and imagineShare, store, retrieve or manipulateinformation3
Computer Science isengineering new productsDo youwant to:Createdevicesthat cando thework foryou?Google Glass4
Computer Science isInfrastructure and NetworksDo youwant tohelp:Keepcomputersystems upand running?Invent newways fortechnologiesto connect?5
Computer Science isvisualizing and creating imageryDo you like:Art?Science?Game Design?Theater?Movies?6
Computer Science isinformation systemsAre you someone who: Understandsrelationships? Likes to do thingsefficiently? Is interested inbusiness andconnecting people?7
Paths to CareersWhat skills does CS require?Computer Science might be right for you if youhave 8
What are thejob prospects?9
Some may think:The tech industry is desperatelytrying to hire computerprogrammers in California
The tech every industry isdesperately trying to hirecomputer programmers inCalifornia everywhere
Computing Connectsmusic business manufacturing communicationsadvertisingengineeringsafety systemssciencecriminal justice recreationveterinary medicinesportsagriculture ng the artsOnly 50% oftech jobs areat gn12health care
Computing Connects to Other CareersFor instance: Are you interested in healthYou might want to study fields? robotics and inventdigital prostheses computerengineering and buildthe next generation of lasersurgical tools bioinformatics anddesign a life-saving drug13
Computer Science isComputer Forensics and Cyber SecurityDo you wantto help:Solve crime?Keep ussafe?Secureinformation?14
Computer Science isDesignDo youwant 5
The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 1 million opencomputing jobs in the U.S. by 2024These are jobs inevery industry andevery state.Sources: Conference Board, Bureau of Labor Statistics
The value of a computer science educationSource: Brookings
The STEM workforce problemis in computer science:71%of all new jobsin STEM are incomputing8%of STEMgraduatesare in computerscienceSources: Bureau of Labor Statistics, National Center for Education Statistics
Where the STEM Jobs Will BeProjected Annual Growth of NEWLY CREATED STEM Job Openings 2010-2020* STEM is defined here to include non-medical occupations.Source: Jobs data are calculated from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), Employment Projections 2010-2020,available at http://www.bls.gov/emp/.August 2012
Where the STEM Jobs Will BeDegrees vs. Jobs AnnuallySources: Degree data are calculated from the National Science Foundation (NSF), Science and Engineering Indicators 2012,available at . Annual jobs data are calculated from the Bureau of LaborStatistics (BLS), Employment Projections 2010-2020, available at http://www.bls.gov/emp/. STEM is defined here to include nonmedical degrees and occupations.August 2012
https://cew.georgetown.edu/stem The District of Columbia will have thehighest proportion of STEM jobs as afraction of job openings through 2018(10%), followed by Virginia (8%). In most states, computer occupations(computer technicians, computerprogrammers, and computer scientists)are the largest of STEM occupations.21August 2012
What is CSlike at JMU?22
23
CS at JMU B.S. in CS and M.S. in CS500 undergraduates, 60 graduates18 CS FacultyProgram strengths:Software Engineering, Computer Networking,Robotics (minor), Telecommunications (Minor),Database Systems, Information Security, DigitalForensics. Embedded systems, and more!24
CS Department (Jan 2015)25
DepartmentalCulture and Opportunities Student-FacultyRelationships Friendly Environment Small class sections Undergraduatelaboratory assistants Undergraduatesworking on researchgrants Independent studywith CS facultymembers Summer Internships Programming TeamCompetitions CyberDefense TeamCompetitions26
Student Support and Enrichment Student organizations– ACM Student Chapter– Cyber Defense Club &Team– Programming Team– Cyber Forensics Group– Women in Technology– Unix Users Group– Robotics Club UPE – CS Honor Society DepartmentalScholarships TA Consultants forthe introductoryprogrammingsequence Independent Study Research Projects27
Scholarship Opportunities JMU Scholarships– Malcolm Lane– SWIFT– Industrial Partners– Second Century– Madison Achievement– Dingledine Scholar National Scholarships– DoD Information DepartmentalAssuranceScholarships– NSF Scholarship for– Computer ScienceService– TAG– FGM28
120 Credit Hours53-57 hours in CS38-40 hours GenEd24-27 hours elective29
Core Courses CS 139 Programming FundamentalsCS 159 Advanced ProgrammingCS 227 Discrete Structures ICS 240 Algorithms and Data StructuresCS 260 Technical CommunicationCS 261 Computer Systems ICS 327 Discrete Structures IICS 345 Software EngineeringCS 361 Computer Systems IICS 430 Programming LanguagesCS 474 Database Design & ApplicationMATH 220 Elementary StatisticsMATH 235 Calculus I30
Elective Courses CS 347 Web-Based Information SystemsCS 349 Developing Interactive MultimediaCS 354 Intro to Autonomous RoboticsCS 432 CompilersCS 442 Logic in Computer ScienceCS 444 Artificial IntelligenceCS 448 Numerical AnalysisCS 450 Operating SystemsCS 452 Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsCS 456 Computer ArchitectureCS 457 Information SecurityCS 458 Cyber DefenseCS 470 Parallel and Distributed Systems31
Q&A withcurrent students32
33
Contact Information Dr. Sharon Simmons– Office: ISAT/CS 222– Phone: 540-568-4196– simmonsj@jmu.edu Dr. Chris Mayfield– Office: ISAT/CS 208– Phone: 540-568-3314– mayfiecs@jmu.edu34
CS at JMU B.S. in CS and M.S. in CS 500 undergraduates, 60 graduates 18 CS Faculty Program strengths: Software Engineering, Computer Networking, Robotics (minor), Telecommunications (Minor), Database Systems, Information