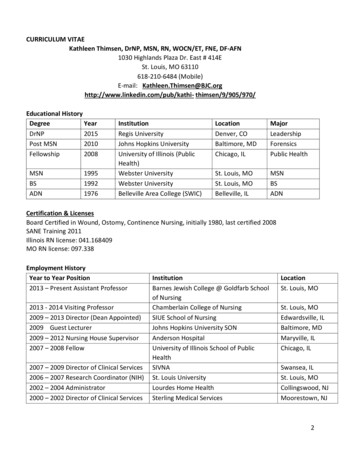
Transcription
VINCENT B. FARRELL MSN MBA RN FNP-CChamberlain College of Nursing1
This program has been developed solely for thepurposes of describing knowledge regardingbarriers and facilitators for providers discussingsexual issues in primary care with men screenedfor erectile dysfunction, before and afterparticipation in an online educational interventionwith a one-month practice-change follow-up. Theprogram is posted as a part of this project’seducational intervention and is intended only forsuch use. The study has been approved for thispurpose by the Chamberlain College of NursingInstitutional Review Board. Please find the link toreturn to the survey at the end of the slides.
Discern perceived barriers to ED discussion inthe areas of: Knowledge Comfort Environment Patient variables Other barriersDescribe perceived facilitators to ED discussionDetermine practice change factors that mightimprove healthcare for patients with ED3
The need for addressing barriers and facilitators forproviders discussing sexual issues in primary care withmen screened for erectile dysfunction has beenestablished in the nursing literature (MartinezPiedrola, Castro-Molina, & Saez-Crespo, 2005).However, increasing evidence reveals that there is alack of knowledge regarding best practices in relationto the treatment of erectile dysfunction (Abdulmohsen,et al., 2004; Wilbanks, 2008; Wilbanks, 2009). Givenemerging recommendations for evaluation, treatment,and management of erectile dysfunction, updates inprimary care provider knowledge is warranted(Albersen, Mwamukonda, Shindel, & Lue, 2011;Barnett, Robleda-Gomez, & Pachana, 2012; Nehra et al.,2012; Perelman, 2011).4
ED Erectile Dysfunction (ED)affects millions of menworldwide withimplications that go farbeyond sexual activityRecognized as an earlymarker of cardiovasculardisease, diabetes mellitus(DM) and depressionED Commonly missedwhen evaluating malepatients in clinic settingMissed due toembarrassment on thepart of the patient andthe clinician5
Sedentary LifestyleObesitySmokingDrug and Alcohol UseUntreated Hypertensionand HyperlipidemiaMetabobolic Syndrome HYPERTENSIONNot controlled or treated canlead to Stroke, Heart AttackPeripheral Vascular Disease(PVD), & Erectile Dysfunction6
THE INABILITY TO DISCUSS ED ISSUES WITH PROVIDERS Misinterpretation of questionsasked by provider to patientOptions in ED managementConcerns about ED treatmentImpact of treatment on pt’ssexual function Concerns in talking to one’spartner about sexual functionor future sexual relationshipsBody imageHow to carry out a testicularexamImpact of impotenceImpact of ED outcomesOptions of prosthesisEjaculatory difficulties7
Misinterpretation ofthe intentions of theproviderConcerns fortreatment andmanagementVerbal interactionsCouple sexcounsellingBody image Testicular self examsMonthly, after warmshower, in front of amirrorImpact of EDoutcomesEjaculatory difficultiesEarly, Delayed &Retrograde ejaculation8
9
Lack of private environmentLack of services to refer ptsHeavy workload – lack of timeToo short encounter window todiscuss sexual issues Sexual concerns too sensitive todocument in health record Lack of support from colleaguesand management 10
ED is when men have troublegetting or keeping an erectionED can be a sign of healthproblemsED becomes more common asyou get olderBlood vessels are clogged andone may have nerve damagefrom diabetesMale sexual dysfunction is nota natural part of aging (Grant &Jackson, 2013).ED problem will go untreatedif a man does not see hisdoctor or healthcare provider(Harvard Men’s Health Watch, 2013).11
Pt with mental healthissuesDifferent cultureDifferent ReligionYounger than me Older than meDifferent GenderDifferent SexualOrientationIs single12
Embarrassed/offended ifprovider initiated conversationFamily member or relativepresentPrefer nurses wait until ptraises own concernsBelieves that the impact of EDis the role of the provider Becomes emotionallydistressedDoes not want to talk aboutsexual issuesDoes not want female providerto talk about sexual concernsDoes not want to talk to afemale provider about sexualconcernsColleague thinks it is infringingon pt’s right to privacy aboutsexual issuesMight interpret questions assexual advance or seductivegestureRefuses to answer questions13
Knowledge of sexualED difficultiesHaving privateenvironmentSufficient time to talkto ptBeing told by anotherprovider that pt hassexual concernsCommunicationWorkshop – Role Play ClinicalPolicies/Procedureson how to addresssexual issuesKnowing pt toestablish a rapportHave colleagues talkto ptBeing prompted inEMR14
Regardless of our gender, medical providers needto have confidence for our clients to make themfeel comfortable to discuss any medical topic andcomfort to accept our suggestions and treatmentrecommendations . Our goal should be to helpour clients to changefrom this or this .to this15
Abdulmohsen, M., Abdulrahman, I., Al-Khadra, A., Bahnassy, A., Taha, S., Kamal, B., & . AlElq, A. (2004). Physicians' knowledge, attitude and practice towards erectile dysfunction inSaudi Arabia. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 10(4/5), 648-654.Albersen, M., Mwamukonda, K., Shindel, A., & Lue, T. (2011). Evaluation and treatment oferectile dysfunction. Medical Clinics of North America, 95(1), 201-212.Barnett, Z., Robleda-Gomez, S., & Pachana, N. (2012). Viagra: The little blue pill with bigrepercussions. Aging & Mental Health, 16(1), 84-88.Martinez-Piedrola, M., Castro-Molina, M., & Saez-Crespo, A. (2005). Erectile dysfunction:Objectives and interventions in the nursing consultation. Enfermeria Clinica, 15(1), 43-49.Moore, A., Higgins, A., & Sharek, D. (2013). Barriers and facilitators for oncology nursesdiscussing sexual issues with men diagnosed with testicular cancer. European Journal ofOncology Nursing, 17(4), 416-422.Nehra, A., Jackson, G., Miner, M., Billups, K., Burnett, A., Buvat, J., & . Wu, F. (2012). ThePrinceton III consensus recommendations for the management of erectile dysfunction andcardiovascular disease. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 87(8), 766-778.Perelman, M. (2011). Erectile dysfunction and depression: Screening and treatment. UrologicClinics of North America, 38(2), 125-139.Wilbanks, S. (2008). Test your knowledge: Erectile dysfunction. Journal for Nurse Practitioners,4(10), 800.Wilbanks, S. (2009). Test your knowledge. answer key for erectile dysfunction crossword.Journal for Nurse Practitioners, 5(1), 71-72.16
Thank you for participating in this project!Please slowly drag your mouse over the livelink below to activate and then click on theURL to return to the post-test (you may need towait briefly for the link to connect):https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/5B36YYM
VINCENT B. FARRELL MSN MBA RN FNP-C Chamberlain College of Nursing . This program has been developed solely for the purposes of describing knowledge regarding barriers and facilitators for providers d