Transcription
EP Ancient HistoryPrintables:Levels 1-4This book belongs to:
Lesson2Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Pyramid
Lesson3Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Timeline OrderCut out these timeline events and put them in order. Remember, in BC thebigger the number, the farther back in time you are.551 BCConfucius is born509 BCRoman Republic established500 BCAdena mounds are built inOhio206 BCHan Dynasty begins inChina221 BCShi Huangdi becomes firstemperor of China27 BCOctavian becomes ruler ofthe Roman Empire44 BCJulius Caesar is killed100 ADPaper invented in China476 ADRoman Empire falls500 ADHeight of Mayancivilization570 ADMuhammad is born600 ADIslam spreads to NorthAfrica800 ADArab traders brought paperfrom China960 ADSong Dynasty founded inChina1215 ADEnglish Magna Cartasigned2700 BCThe Old Kingdom beganin Egypt
Lesson4Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Egyptian HierarchyRead about Egyptian workers and look at the chart about Egyptian society. Fillin your own chart. You can write the words or cut out the pieces at the bottomof the pagePriestsCraftsmenVizier (religious advisor)NoblesPharaohSoldiersSlavesScribesFarmers
Lesson5Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Hieroglyphic Code BreakCrack the code!A K. B% L/ C& M0 U D' N1 V E( O2 W F) P3 X? G* Q4 Y@ H R5 ZA I, S6 J- T7 7 ( 3@5 0,'6 (5( % ,/7 72 %( 720%6 )25 7 ( 3 5 2 6 1' 7 (,5 ) 0,/,(6
Lesson6Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Rosetta StoneThe Rosetta stone was found in. It was found byFrench soldiers. The Rosetta stonehad writing carved on it. The sameorder, or proclamation, was writtenin three . They are:an ancient Egyptian script calledDemotic, Ancient Greek, and. This helpedpeople learn how to readhieroglyphics and the ancientEgyptian Demotic script.Jean Franҫois Champollion studiedthe Rosetta Stone and decipheredthe hieroglyphs. He read theWord Bank:writing and was able toGREEKmake educated guesses about theSCRIPTSmeaning of the hieroglyphs.Through a lot of study and work, hewas able to decipher thehieroglyphic and Demotic writingsystems.HIEROGLYPHICSEGYPT
Lesson7Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4PapyrusThe ancient Egyptians made a form of paper called papyrus. Draw a picture inthe box to match the directions for making papyrus.Gather a large amount of riverreeds. Cut off the outside layer ofthe reed. You may need to furthercut the inside portion of the reedsinto thinner strips.Weave the inside portions of thereeds like you are making aplacemat.Pound the mat area to flatten it.You can use a rock, hammer, orrolling pin.This also helpsremove water from the reeds.Make sure you flip it over andpound the other side as well.Leave your papyrus to dry. Youcan hang it in the sun to let it dryfaster. When it is completely dry,you can write or draw on it!
Lesson8Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Embalming the PharaohWhen the Pharaoh died, the body was prepared for burial. The embalmingprocess required certain organs to be removed and placed into jars. Labeleach jar with the organ it contains. Mark off the labels to find out which organswere NOT placed into jars.BRAININTESTINESSTOMACHHEARTLIVERLUNGS
Lesson9Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4King TutWrite something about what you have learned about King Tut.Draw a picture of one of thetreasures found in his tomb.
Lesson10Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Word FindRead these facts about ancient Egypt. Find the words in bold in the XDLife in ancient Egypt was centeredaround the Nile River. The mainform of transport in ancient Egyptwas the boat. Early Egyptians usedclay to make pottery.The ancient Egyptians developed awriting system called hieroglyphics.The Great Sphinx and the GreatPyramid at Giza were built duringthe “Old Kingdom” period.King Tut was a pharaoh that wasburied in the Valley of the Kings witha beautiful gold mask.
Lesson11Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4King TutColor the picture of King Tut.
Lesson12Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Ancient Egypt Timeline
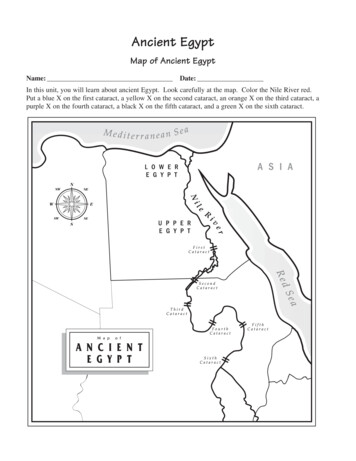
Lesson15Ancient HistoryLevels t/prochorient07.gifColor in the area known as Mesopotamia.
Lesson18Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Mesopotamia Timeline
Lesson20Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Current EventsAnswer each question about the article you read.What happened?Who was there?When did it happen?Where did it happen?Why did it happen?
Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson21
Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson21
Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson21
Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson21
Lesson22Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4ConfuciusRead and copy this quote from Confucius.Teaching from ConfuciusWhat you do not want done to you,do not do to others.
Lesson23Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Emperor QinCut around this as one longrectangle, including thepicture. Fold in the middle.This part gets glued down.Part of theEasy Peasy All-in-One Homeschool
Lesson24Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Terracotta WarriorsCut around the whole thing as one big rectangle, and fold down the middle.The blank rectangle gets glued down and the picture becomes the cover. Writeon the inside to tell about the Terracotta Warriors.
Lesson25Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Great Wall of ChinaCut out each box with its tabs. Don’t cut off the tabs!?
Lesson25Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Great Wall of ChinaCut out the Great Wall box. Cut out the box with the 4 tab (don’t cut off thetab!) Cut out the box with the “answers” tab. Stack all boxes with the picture ontop, then in order 1, 2, 3, 4, answers.
Lesson26Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4ConfuciusCopy the Confucius quote.A man who has committed a mistake and doesn’t correctit is committing another mistake.
Lesson27Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4ConfuciusCopy the Confucius quote.Consideration for others is the basis of a good society.
Lesson28Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Tangramsg
Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson28
Lesson30Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Silk RoadWrite information you learned about the Silk Road. You can cut this out anduse it as a lapbook piece or just use this page as a notebooking page.
Lesson41Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Indus ValleyUse this page to write notes about what you have learned about the Indus ValleyCivilization.Why did early civilizations begin around rivers? Whatwere some of the important uses of water?Label the Indus River and color itblue. Look back at the map inyour reading. Shade the IndusValley civilization area.Look at the pictures from your reading assignment. Use this space to recordyour observations of the archaeologists’ finds from the Indus Valley civilizations.
Lesson42-46Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Indus ValleyCut out the pieces of this tabbed booklet. Stack all the pieces together andstaple together at the bottom of the booklet.My discoveries about the ancient cities of the Indus ValleyWhy was the river important to the civilizations?Cover page, Lesson 42Daily lifePage 1, Lesson 42
Lesson42-46Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Trade/TravelArt/WritingPage 2, Lesson 43Jobs, Foodand FarmingPage 3, Lesson 44
Lesson42-46Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Games/ToysPage 4, Lesson 45What they didfor usPage 5, Lesson 46
Lesson47Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Map ActivityABCDEFG12345Color the dotted lines blue. Do you remember the name of the river? Label theriver on the map.Highlands are found in Pakistan, west of the Indus River. Color that area brownand label it “Highlands.”Draw a symbol to represent mountains in squares C1, D1, E1, F1, F2, and G2.Label the mountain range “Himalaya Mountains.”One major excavation site is Mohenjo-Daro. It is east of the Indus River insquare B3. Mark and label that area on the map.Another major area is Harappa. On your map, it is in square D2 between thelower 2 segments of the river system. Mark and label that area.
Lesson49Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Fill in the BlanksFill in the blanks using words from the word bank.Picture 1 shows an area excavated in Dholarvira. That is a reservoir that wouldhave been full of during the Indus Valley Civilization.Picture 2 shows a . These were baked and cut to use in buildingthe structures in the towns.The clay sculptures in picture 3 were likely used as .Picture 4 shows where a washroom would have been. The narrow, brick-linedarea would have been a taking dirty water away from thewashroom.The and weights in picture 5 would have been used in trade andsales.The seal in picture 6 has writing, an inscription of a deity with 3 faces, andseveral animals. The striped animal on the right is likely a.Word BankTIGERWATERDRAINTOYSBRICKSCALE
Lesson50Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Current EventsWhat happened?Who was there?When did it happen?Where did it happen?Why did it happen?
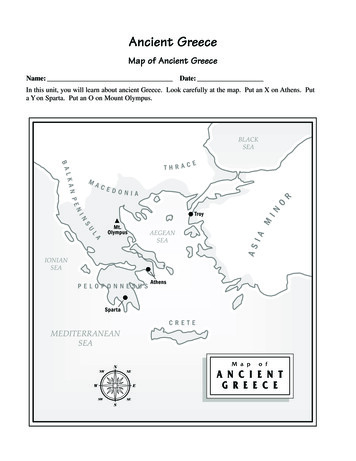
Lesson51Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4GreeceChoose a color to represent Greece.Choose a symbol to represent Athens and Sparta.Mark these places on the map.Label the major bodies of water on the map.Map Source: ifMap KeyGreeceAthens2Sparta
Lesson52Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Trojan HorseWrite about the story of the Trojan Horse.Trojjan Horse
Lesson53Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4by HomerThe OdysseyThe Odyssey
Lesson54Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Ancient GreeceAncientGreeceLife inCut on the solid lines. Fold on the dotted lines to make a booklet. Writeinformation about life in Ancient Greece.
Lesson55Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Coloring PageChoose one of the Greek gods you read about and color a design on thepottery to tell about him or her.
Lesson56Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4ParthenonFill in the blanks with words from the WORD BANK to complete the sentences.Share with someone what you have learned about the Parthenon.WORD BANKsixtycolumnsAthenatempleThe Parthenon wasbuilt as afor worshipping the Greek gods.Inside the Parthenon, there is a statue of .The Parthenon is feet tall.The Parthenon has on all sides.Eight across the front and back and 17 along both of the other sides.
Lesson57Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Sparta and AthensCompare and contrast Sparta and Athens.SpartaBothAthens
Lesson58Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4MatchingMatch the Olympic event with the correct description.WrestlingThis event consisted of fivecompetitions: long jump, discus,javelin, running, and wrestling.PentathalonSome of these events took place onhorseback. Others took place onchariots pulled by two or fourhorses.BoxingThis event was throwing a woodenspear.Long jumpThis event was throwing an itemshaped similar to a Frisbee.Horse racingThis event took place in the sand.The match was over when acontestant was taken down threetimes.JavelinCompetitors would hold weights,swing them, then jump in a sandtrack.DiscusCompetitors were not allowed tohit below the belt. Hitting in thehead was allowed.
Lesson61Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Ancient Greek ColumnsRead the descriptions and write the name under the correct image.DORIC – plain tops, not very decorativeIONIC – a little more decorative than Doric, basic column with ascroll design addedCORINTHIAN – fancier column with leavesDraw your own Greek building. Which columns would you use?
Lesson62Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Ancient Greek City-StatesUse this graphic organizer to record what you learned about the ancient Greekcity-states.
Lesson63Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Famous GreeksSocratesHippocratesSophoclesFamous GreeksWrite information you learned about these famous Greeks. You can leave thisas a worksheet or you could cut it out and use it as a lapbook piece.
Lesson67Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Ancient Greek TheatreMatch the letter to the area being described.1.2.3.4.The two outer curved areas were seating areas. andThe higher/outer seating area was for ordinary citizens.The lower/inner seating area was for priests.From the seating area, you can see the skene behind the stage. Theskene was where actors would change or get ready.5. Between the stage and the seating area was the orchestra area. Thechorus would be in this area so they could be a part of the play andinteract with the audience.6. The stage was between the orchestra and the skene. Often it wouldbe a simple wooden platform.
Lesson70Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Current EventsWhat happened?Who was there?When did it happen?Where did it happen?Why did it happen?
Lesson95Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Current EventsWhy did it happen?
Lesson105Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Viking shipsColor these Viking ships.
Lesson116Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Knights and CastlesRecord what you have learned. You can leave this as a worksheet or cut it outto be a lapbook.Castles:Knights and Pages:
Lesson119Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Coat of Arms
Lesson121Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4JapanFind Japan on the top map and color it. Label the maps with the locationslisted.North KoreaSouth KoreaChinaSea of JapanPacific OceanMount FujiHokkaidoHonshuShikokuKyushu
Lesson122Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4JapanAdd notes to each class of the Japanese Feudal System.EMPERORDIAMYOSSAMURAIPEASANTS
What wasthe codeofbushido?List someof theirweapons.Who werethey?SamuraiAncient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson123Samurai
Lesson124Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Japan: Kimono and Fan Dance“Kimono” originally meant “something you“Kwear.”Kimonos are long robes shaped like a “T”Kand usually covered in colorful designs.Color the picture of the kimono.Draw a picture below of the fan youwould design for the traditional Japanesefan dance.
pe02.gifMongol EmpireAncient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson127
Lesson130Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Current EventsWho?What?Where?When?Why?
Lesson131Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Ottoman EmpireColor the area showing where the Ottoman Empire ruled. Label Africa, Asia,and ans03.gif
meriques02.gifAztec EmpireAncient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson133
Lesson134Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Aztec EmpireUse the timeline available online to fill in information on this timeline.Add information or events you found interesting on the blank lines.City of settled13251350Conquistador arrives1521built to improve travel1519Fall of
Lesson142Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4ItalyLabel Florence, Rome and Venice as closely as you can. Also label theMediterranean ie05.gif
F Ponce de LeonF Vasco Da GamaF CabotF De SotoF VerrazanoF HudsonF De entreeurope02.gifF Marco PoloF DrakeF MagellanChoose a color to use to draw the route for each explorer.Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Lesson153
Lesson167Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Research Report Note TakerTopic:Resource 1:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Resource 2:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Resource 3:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Resource 4:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:
Lesson167Ancient HistoryLevels 1-4Resource 5:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Resource 6:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Resource 7:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Resource 8:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Resource 9:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:Info:
Levels 1-4 Lesson 6 Rosetta Stone The Rosetta stone was found in _. It was found by French soldiers. The Rosetta stone had writing carved on it. The same order, or proclamation, was written in three _. They are: an ancient Egyptian script called Demotic, Ancient Greek, and _. This helped people learn how to read hieroglyphics and .