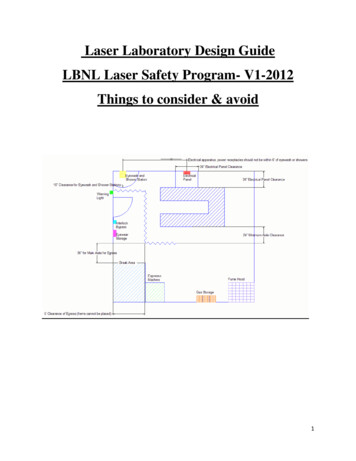
Transcription
UnderstandingLaser Illuminated ProjectorSafety RegulationsAn Informational WebinarPresented by:Pete Ludé, Mission Rock Digital LLCPete@MissionRockDigital.comOctober 17, 2019October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 1
A Word from our sponsor About the Laser Illuminated Projector AssociationMISSION: LIPA will speed the adoptionof laser illuminated projectors throughcooperative industry activity Education Regulatory Affairs SafetyOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 2
A Word from our sponsor About the Laser Illuminated Projector AssociationGOAL: Advocate for a positive regulatoryenvironment that will facilitate commercialadoption of laser illuminated projectors. Represent the leading projector manufacturers and supply chain companies October 17, 2019Projector manufacturers (both laser- and lamp-based)Component manufacturers (laser & micro-displays)Integrators / InstallersEnd Users (Theater-owners, film studios, and theme parks)LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 3
LIPA MembershipOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 4
Join us!www.LIPAinfo.org NewslettersEventsMeetingsDiscountsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 5
Today’s agenda About Laser Illuminated Projectors Understanding Brightness Measurements Regulatory Background The new FDA Laser Notice 57 About “Variances” Installation Considerations Summary and Q&AOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 6
For Avixa Members: By completing this webinar course, participants can earn the followingAVIXA Renewal Units for each designation I1October 17, 2019Not a member?Find out more A Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 7
Laser Illuminated Projector (LIP) BasicsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 8
Lamp based Optical Architecture9October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 9
RGB Laser Projector Optical Architecturelamp-like lightlaser-like light10October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 10
Laser-pumped Phosphor Optical Architecture11October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 11
Why Laser Illuminated?A “Laser Projector”October 17, 2019A “Laser Illuminated Projector”LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 12
Laser Safety In normal operation, LIPs are fundamentally as safe as lamp projectors Assuming radiance and beam geometry are equivalent LIPs are designed to emit light nearly identical to a lamp projector But – “raw”, collimated laser beams can be harmful Since laser sources are inside the projector, care must be taken Particular considerations during maintenance access Since laser sources are used, special safety regulations applyConsult your manufacturer for specific safetyrequirements, and to answer any questionsabout your particular situationOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 13
Understanding Brightness Measurements“How many lumens does a projector need to bebefore stricter regulations kick in? “October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 14
Understanding Brightness measurementsRadiometryThe measurement of light waves in the opticalportion of the electromagnetic spectrum (includingUV, visible and IR light).PhotometryA special subset of radiometry weighted for atypical human eye responseExample of typical RadiometerExample of typical ch/optics/me557/Radiometry.pdfOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 15
Understanding Brightness measurementsRadiometryThe measurement of light waves in the opticalportion of the electromagnetic spectrum (includingUV, visible and IR light).PhotometryA special subset of radiometry weighted for atypical human eye responseUnits of Measure October 17, 2019Radiant power (Watts)Irradiance (W/m2)Radiance (W/m2/steradian)Units of Measure Luminous flux (lumens)Illumination (lux lumen/m2)Luminance (cd/m2 lumen/m2/steradian)LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 16
Understanding Brightness measurementsLuminance FluxIn photometry, luminance flux is a measure of the total quantity of visible light emitted by a source,Measured in:The lumen (symbol: lm)1 lm 1 cd sr1 lux 1 lumen/m2For Projectors: "ANSI Lumens"Source: ctober 17, 2019Defined in IEC 61947-1:2002LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 17
Understanding Brightness measurementsRadianceIn radiometry, radiance is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a givensurface, per unit solid angle per unit projected area.Measured in:Watts per steradian per square meter(W·sr 1·m 2)Source: s/rsnote/cp1/cp1-6.htmOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 18
Understanding Brightness measurementsRadianceIn radiometry, radiance is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a givensurface, per unit solid angle per unit projected area.Measured in:Watts per steradian per square meter(W·sr 1·m 2)The steradian (symbol: sr) or squareradian is the SI unit of a solid angleSource: Coles Physics II iwebsite/light-and-colorOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 19
Understanding Brightness measurementsIn Summary Hazard assessment doesn’t directly relate to Lumensbecause:1) Color spectrum measured “Brightness” is characterized by human-visible wavelengths Safety is evaluated by all wavelengths of light2) Geometry of light rays Radiance consider apparent source size Luminance flux does notOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 20
Regulatory BackgroundOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 21
US Laser Regulations Federal Laser ProductPerformance Standard (FLPPS) 21CFR subchapter parts 1040.10and 1040.11 Administered by the Center forDevices and Radiological Health(CDRH)October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 22
US Laser Regulations ANSI Z136.1 – 2014Safe Use of Lasers Part of a Suite of Standards Referenced by October 17, 2019CDRH VariancesState RegulationsOSHAOthers ANSI Z136.2 - Fiber OpticANSI Z136.3 - HealthcareANSI Z136.4 - Safety MeasurementsANSI Z136.5 - Educational InstitutionsANSI Z136.6 - OutdoorANSI Z136.7 - Test/Label EquipmentANSI Z136.8 - R&D/TestingANSI Z136.9 – ManufacturingLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 23
US Laser Regulations IEC 60825-1:2014Safety of laser productsPart 1: Equipment classificationand requirements Referenced by FDA Regulations Worldwide regulators IEC 62471-5:2015Photobiological safety of lampsand lamp systemsPart 5: Image projectorsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 24
US Laser Regulatory LandscapeLaserNotice57US21 ode115FireMeasureZ136.3MedicalOctober 17, 2019Z136.4EducationStatesPart AALIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsPub 8-1.7Ch. 17CRCPDModelStateSlide 25
Laser classifications according to FDA and IECLaser ClassFDAIIEC11MIntended for "raw" (collimated) laser beamsDescriptionNotesExample ProductsConsidered non-hazardous in normal operationHazard increases if viewed with optical aids,including magnifiers, binoculars, or telescopes. Laser printers CD / DVD playersEye protection normally through aversion responseHazard increases when viewed directly for long Bar code scannersperiods of time, or if viewed with optical aids.Depending on power and beam area. Risk ofinjury increases when viewed with optical aids.II2IIa2MIIIa3RMay be momentarily hazardous when viewed directly orwith specular reflection.IIIb3BImmediate skin hazard from direct beam and immediateeye hazard when viewed directly.IV4October 17, 2019Immediate skin hazard and eye hazard from exposure to May also produce laser-generated aireither the direct or reflected beam; Potential a fire hazard. contaminates and hazardous plasma radiationLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety Regulations Laser Pointers laser light show projectors industrial lasers research lasers laser light show projectors industrial / research lasers surgical lasersSlide 26
Definitions MPE(General to laser safety regulations)Maximum Permissible Exposure the maximum limit to which a person may be exposed without suffering adverse effects NOHD Nominal Ocular Hazard Distance The distance from the projector where the light exceeds the MPE SNHZ Skin Nominal Hazard Zone The area where skin burns are possibleOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 27
Definitions(Used in LIP Regulations) AEL Accessible Emission Limit maximum accessible emission permitted within a particular risk group HDHazard Distance distance from the projector's nearest point of human access, where the beamradiance or irradiance exceeds the applicable exposure limit HZHazard Zone the 3-dimensional space encompassing the region that is considered RG-3based on the Hazard DistanceOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 28
LIPS vs Lamp based projectors The eye injury mechanism is identical for laser or lamp projectors Thermal induced retinal injury model 0.25s accidental exposurethrough 7mm eye pupilHuman eyeSourceL [W/m² sr]Thermal effect[W/m²] Risk Lamp projector Risk Laser projector For identical radiance and lens exit pupil geometryOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 29
How are LIPs different than laser beams?LIPs have an extended source, not a collimated beamA source that emits broadband incoherent radiation represents an extendedsource, producing a correspondingly large image on the retina.October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 30
Projector Safety RegulationsRisk Factors “Brightness” [lumens] Throw Ratio Angular subtense 𝛼 [Rad] Radiance L [W/m²sr] effect on the human eyeOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 31
IEC Laser Regulations Previously, all laser productrequirements were definedin IEC 60825-1 MedicalIndustrialLaboratory useLaser WeldingLaser Illuminated ProjectorsIEC 60825-1 Ed 2 (2007)Safety of Laser ProductsPart 1: Equipment classification & RequirementsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 32
IEC Laser RegulationsBut under the latest revision(Edition 3), laser productsintended to behave as lampdevices may be carved out IEC 60825-1 Ed 3 (2014)Safety of Laser ProductsPart 1: Equipment classification & RequirementsCarve-out for devices with irradiance October 17, 20191MW·sr 1·m 2αLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 33
IEC Laser RegulationsIEC 60825-1 Ed 3 (2014)IEC 62471 Ed 1 (2006)Safety of Laser ProductsPart 1: Equipment classification & RequirementsPhotobiological safety of lamps and lamp systemsCarve-out for devices with irradiance October 17, 20191MW·sr 1·m 2αLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety Regulations and regulated underLamp standardsSlide 34
IEC Laser RegulationsIEC 60825-1 Ed 3 (2014).and this new standard wasforprojectorsSafety of Laser ProductscreatedspecificallyPart 1: Equipment classification& RequirementsIEC 62471-5 Ed 1 (2015)Photobiological safety of Lamp Systemsfor Image ProjectorsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 35
Evolution of LIP regulations The international community TC 76 optical radiation safety expertscreated a specific classification path for Laser products which aredesigned to function as conventional lamps. Risk from a Lamp projector is the same as from a Laser projector Assuming identical radiance and lens exit pupil geometry SOLUTION: Dual classification Laser based Class and Lamp based Risk Group Example: “Class 1 – Risk Group (RG) 3”October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 36
Why was IEC 62471-5:2015 created? Lower classification power to consider, newICNIRP limits Clear line what is considered safe for consumer useor not Guidance in what separation height to maintain forRG 3 Projectors: Cinema: Hazard Zone to be 2m above floor Non Cinema: Hazard Zone to be 3m above floor Clear labels and user information instructionsgeneric for projectorsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 37
Evolution of LIP regulationsExample: “Class 1 – Risk Group (RG) 3”1mIEC 60825-1:2014section 4.4Emission evaluated underIEC 62471-5: 2015Photobiological safety ofLamp Systemsfor Image ProjectorsEmbedded lasersinside enclosure maybe Class 3B or 4October 17, 2019But enclosure isprotected by lightstops and interlockswitchesSo product is ratedas Class 1 LaserProductLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 38
Risk Group ClassificationsOctober 17, 2019RISKGROUPSafety ImplicationRisk Group 0Risk Group 1Risk Group 2Risk Group 3Inherently safeSafe, for intended useSafe, based on aversion response (eye blink)Potential hazardous for eye and skin exposureat close distanceLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 39
Regulations define “exit pupil”Irradiance distribution of the image of the exitpupil (taken as the apparent source).From IEC 62471-5: Photobiological safety of lampsand lamp systems – Part 5: Image projectorsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Report: Risk Analysis Data Base and Case Study,Karl Schulmeister, PhDLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 40
Apparent Source SizeUsed in the calculation of Radiance (and therefore Risk Group)From IEC 62471-5: Photobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems – Part 5: Image projectorsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 41
Risk Group Classifications 1𝑀𝑊𝑚 2 𝑠𝑟 1ൗ𝛼 RG 3 – Potentially hazardous at close distanceHazardDistanceProfessional Use Projectors – with FDA VarianceIEC 62471-5:2015 requires: Sold only to professionals. Warning labels No access to beam within hazard distance Use & installation requirements, Soft startRG3 1m Over 10Klmdepends onexit pupilRG2 SeveralHundred lmRG1RG0For throw ratio 2.0October 17, 2019RG 2 - Safe based on aversion response (blink reflex)Home/office use projectorsIEC 62471-5:2015 requires: Caution labels, Soft start, User information andinstructionRG 0/1 - Inherently SafePico ProjectorsIEC 62471-5:2015 requires: User information0 lmLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 42
Introducing: Laser Notice 57!October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 43
Timeline for Regulatory 2017201820192020LIPA FoundedFDA Laser Notice 50LIP Guidance DocumentLN 57 DraftFirst Laser LightShow Variance for LIPLIP DevelopmentLIP PrototypesLIP Commercial DeploymentIEC 60825-1 Ed 2New LN 57LIP exceed lampIEC 60825-1:2014 (Ed 3)IEC 62471-5:2015 (Ed 1)October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 44
October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 45
Laser Notice 57 US Standards (finally!) harmonize with IEC Risk Groups! Applies to: Laser Illuminated Projectors (LIPs) A type of Demonstration Laser Product* That comply with IEC Standards during laser product classification Not a children’s toy laser product or medical device Designed to display an image without use of raster-scanned collimatedlaser beams*Demonstration Laser Product: “Any laser product manufactured, designed,intended, or promoted for purposes of demonstration, entertainment, advertisingdisplay or artistic composition.”- 21 CFR 1040.10(b)(13)October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 46
Summary of LN 57 GuidanceClassify Projectoraccording to IEC62471-5:2015AssignRGAEL - Accessible Emission LimitRG - Risk GroupOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 47
Summary of LN 57 GuidanceAppropriate Safety Labels,Manuals and ReportsRG 0, 1 or 2Classify Projectoraccording to IEC62471-5:2015AssignRGThe dual-classificationsystem is used – forexample: “Class 1, RG 2”AEL - Accessible Emission LimitRG - Risk GroupOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 48
Summary of LN 57 GuidanceAppropriate Safety Labels,Manuals and ReportsRG 0, 1 or 2Classify Projectoraccording to IEC62471-5:2015AssignRG 60%RG 2AEL?NOAEL - Accessible Emission LimitRG - Risk GroupOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 49
Summary of LN 57 GuidanceAppropriate Safety Labels,Manuals and ReportsRG 0, 1 or 2Classify Projectoraccording to IEC62471-5:2015AssignRG 60%RG 2AEL?NOYESWARNINGAEL - Accessible Emission LimitRG - Risk GroupOctober 17, 2019Additional ChildSafety LabelsMount Above theHeads of ChildrenLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 50
Summary of LN 57 GuidanceAppropriate Safety Labels,Manuals and ReportsRG 0, 1 or 2Classify Projectoraccording to IEC62471-5:2015AssignRG 60%RG 2AEL?YESRG 3AEL - Accessible Emission LimitRG - Risk GroupOctober 17, 2019NOObtain FDAVarianceLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsAdditional ChildSafety LabelsFollow VarianceStipulationsSlide 51
As explained by Laser Notice 57 “CDRH considers LIPS that are in RG3 to be equivalent to LaserClasses IIIb or IV (IEC Class 3B or 4)”“When laser products are Class IIIb or IV, a variance approval byFDA is required that permits the laser product to exceed the limit”October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 52
VariancesFirst, a brief history October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 53
October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 54
“It was the coolest show I'veever seen! Unbelievable. Theyhad those glitter balls you'd seelater in discos hung all over theplace and they'd shoot a laserinto one in the center which wasspinning and the laser wouldricochet to the other balls thatwere spinning and you felt likeyou were in a war zone. Theyseemed to be coming from alldirections. They had rings withlasers, guns with lasers andthose strobe light laser guns!”October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 55
Pittsburgh PressAugust 8, 1978October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 56
Original Laser Light Show Variance Requirements, circa 1978 (Partial list)– File specifications on laser equipment prior to use– Prior Reporting of every show– Annual Reporting of prior shows– Safety Checks before every show– Regular Variance Renewal, extensive paperwork and logging– Subject to Federal Show Inspection, each set-up– 3 to 6 meters minimum vertical separation distanceOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 57
Variances for LIPsFDA began issuing Laser LightShow Variances for LaserIlluminated Projectorsin December 2010October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 58
FDA Laser Light ShowVariance ApplicationOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 59
Variance ConditionsTemporary InstallationPermanent Installation Non-cinema Rental and Staging Trade ShowsOctober 17, 2019 Presentation rooms House of WorshipLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety Regulations Cinema Movie theater Premium Large FormatSlide 60
Example of Variance Application For temporaryvenues61October17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 61
and a Variance issuedOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 62
Variance requirements: Temporary Installs Temporary Show Installations containing RG3 LIPS May be installed by LIP (Branded) Manufacturer Or may be sold or leased to valid laser show FDA Variance holders Also applies to Dealers and Distributors Examples of Appropriate Operational Practice: Locate projectors so that all beam paths within Hazard Zone, and theaudience, can be observed at all times Maintain communications with personnel observing operations Terminate projection immediately upon any unsafe condition Provide readily accessible controls for termination63October17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 63
Variance requirements: Fixed Installs Permanent Installations Typical Variance specifies the Hazard zone not lower than: 3m for non-cinema 2m for cinema Horizontal clearance to Hazard Zone should be 2.5m Any human access to Hazard Zone restricted by barriers Installation by trained and authorized installersAlways check with your manufacturer or variance-holderFDA variances may differ!64October17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 64
October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 65
FDA Variance Exception RG 3 LIPS that prevent human access to theHazard Zone by use of engineering controlswill not require a Variance application Sensors which detect the location of the human bodyor objects within hazardous areas Output power is reduced automatically when personnelor reflective objects are detected entering the enter theHZ66October17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 66
Installation Considerations & RequirementsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 67
Hazard distance RG2 to RG3 For RG3 products, theHD is determined undermaximum emission powerat each throw ratio. For interchangeablelenses, the maximumforeseeable HD should beprovided68October17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 68
Hazard zone The region of space where the projectionlight is greater than Emission Limits forRG2.HZThe Hazard Distance is defined* ascollinear to the optical projection axisTherefore the Hazard Distance alone doesnot sufficiently describe a 3-dimensionalHazard Zone.The Hazard Zone encompasses the entireregion of space that is considered RG3HZ*Defined in IEC 62471-5:Ed 169October17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 69
Responsibilities of Cinema OwnersPREVIOUS SITUATION Implement local government safety regulation Laser light show variance Event safety regulation Requirements based on exposure limits LIP operator Training requirementsProjection booth requirements (restricted area, protectivebarriers)Risk based implementationHZ Cinema visitor (general public) October 17, 2019No exposure above safety limits is allowed in any case!Physical barrier or sufficient separation heightLIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 70
Responsibilities of Cinema OwnersTYPICAL VARIANCE REQUIREMENTS (for Class 1 / RG 3) Cinema theaters do not need a variance approval Because LIP Manufacturer has variance requiring them to provide adequate instruction Projector installed under restricted access location conditions Provide basic operator training Access to projector must be restricted by key or pass code lock Appropriate signage Installation test report to be provided to the theater manager No dedicated Laser Safety Operator required Falls under general safety management Not retroactive except for any retrofitOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 71
October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 72
Servicing While servicing, Class 4(collimated) laser sources could beexposed. Training required! Only qualified / certified personnel Safety features Safety interlocks Beamstop mechanism Fibreoptic interlocks Labeling and signage requiredOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 73
Summary and Q&AOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 74
Summary LIPs present hazard similar to lamp projectors Very unlike raw laser beams However, due to embedded laser, laser regulations apply US is now (nearly) harmonized to worldwide IEC standard Most high-power LIPs are RG3, and therefore require variance Variances are specific to a manufacturer & model family! Work closely with your supplier to understand the specific requirements Review safety instructions / Hazard Zone constraints carefully Special care / training required for servicing LIPsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 75
Join us!www.LIPAinfo.org NewslettersEventsMeetingsDiscountsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 76
Time for QuestionsOctober 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 77
UnderstandingLaser Illuminated ProjectorSafety RegulationsAn Informational WebinarPresented by:Pete Ludé, Mission Rock Digital LLCPete@MissionRockDigital.comOctober 17, 2019October 17, 2019LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety RegulationsSlide 78
But -"raw", collimated laser beams can be harmful Since laser sources are inside the projector, care must be taken Particular considerations during maintenance access Since laser sources are used, special safety regulations apply Laser Safety October 17, 2019 LIPA Webinar: Understanding LIPs Safety Regulations Slide 13