Transcription
Ransomware incident handling andmitigationCsaba VIRÁG – Cyber Security Competence Centre
Portfolio – Cyber Security ServicesPreventive (Proactive) Defence APPLIED INTELLIGENCE or CTI (CYBERTHREAT INTELLIGENCE) AWARENESS ETHICAL HACKING GAMIFICATION CYBER EXERCISESInformation ExchangeManaged Security Services EARLY WARNING (VULNERABILITYINFORMATION EXCHANGE) BUSINESS PROCESS REENGINEERING TEAM DEVELOPMENT DECISION SUPPORT 3rd PARTIES IIEX MONITORING LOG MANAGEMENT INCIDENT MANAGEMENT VULNERABILITY MANAGEMENT APT and ZERODAY MANAGEMENTMitigationIncident Response RISK AND IMPACT MITIGATION SYSTEM HARDENING SOFTWARE REFACTORING INCIDENT INVESTIGATION COMPUTER AND NETWORKFORENSICS MALWARE ANALYSIS
Advanced Cyber Security Services PortfolioProactive ch andDevelopmentEARLY WARNINGINCIDENTINVESTIGATIONRISK AND ENGINEERINGLOGMANAGEMENTPOLICYDEVELOPMENTETHICAL ICATIONCYBEREXERCISESCOMPUTER AGEMENTAPT and ORING3rd PARTIES IIEXCYBER DEFENCEMANAGEMENTSUPPORT ANDCONSULTINGBIGDATAANALYSISDEVELOPMENT
Ransomware familiesExtreme growth in families and variantsTrendmicro: 752% growth in a yearTimeline of appearing ransomware familiesSource: F-Secure, State of Cyber Security 2017
QuestionsHow can such a great threat be handled?What is the most important measure to take when a ransomware attack ison?How do you know who attacks and what method the attacker uses?Why not to pay ransom? If one does not pay, how can it be guaranteedthat the files can be restored?How does a ransomware attack look like?
Ransomware Cyber-kill ChainThe ransomware executable is delivered viaAttachments or web links in phishing emailsMalvertising on malicious web pagesDrive-by downloads (e.g. fake antivirus)The payload is executed on the end user’s deviceThe ransomware installs itself on the victim’s computerThe ransomware generates a unique encryption/decryption key pairThe ransomware contacts a C2 server on the Internet to deposit the decryption keyThe malware starts encrypting the files on the hard disk, mapped network drives and USB devices with the encryption keyOnce the process finishes, the files become inaccessible.The malware places a text file on the desktop and/or a splash screen pops-up with the instructions to pay and restore the original files.
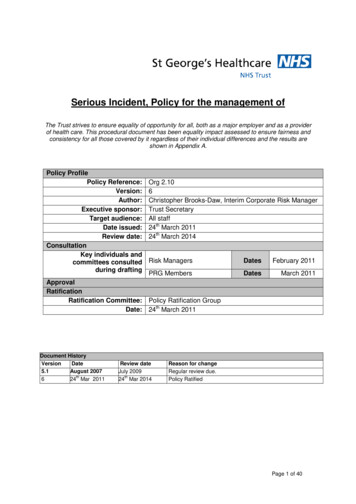
Incident handling procedureName of employeeDid a window pop upwith demanding aransom?Validate with the userwhether it is agenuine ransomwarecaseHas a text file withthe instructions beenplaced on theDesktop?Have the fileextensions beenchanged to .abc,.xxx or similar?Are the filesunavailable?Contact detailsAsk the user todisconnect the devicefrom the network. Ifthe user connects tothe network with awireless card, he/shemust turn it off.Computer nameTake the followingdetails from the enduser and registerthem into the ticketIP addressWhat happened?How was theproblem identifiedand when?Is the user aware ofhe/she clicked on asuspicious link orattachment lately?
Incident handling procedureTakequestionsMake a rawHDD(image)copy ofdesktop(s)Define estigateAnalyseCollect metainformationAnswer thequestions
Some questions to askSome questions to ask a national CERT tasked by examiningreceived files from an incident. What happened at these organisations?When did it happen?What kind of company assets have been involved?Which files can be evaluated?Which traces can be the ones originating from the attacker(s)?What is the timeline of events recorded?What is the attack vector?Are there possible further victims?Shall one pay for restoring the files to keep operations running? Has the attackerused a C&C (Command and Control) Server? Based on the analysis of the malicious files is it possible to restore the files bygetting passwords or keys from the attacker?
RecommendationsBlock incoming emails on the SMTP server, remove emails from user inboxes, warn users to not click on certain links andattachmentsBlock malicious URLs on the web proxy, identify computers that visited malicious websites on certain URLs using the proxy logsBlock malicious URLs on the web proxy, identify computers that visited malicious websites using the proxy logs, deploy customAV signatures to block certain files to be downloaded, identify PCs with ETDR that downloaded files with certain IoCsApply application whitelisting, identify PCs using the HIDS logs that executed certain filesIdentify and/or block traffic on NIDS and on the proxy(ies)Monitor end-user devices and shared folders for certain file extensions, such as .abc, .xxx, .yyy, .zzzMonitor endpoints for ransomware related text or HTML files in the desktop folder
Program ionSupported OSBitdefender AntiRansomwareyesnoCTBLocker, Locky, TeslaCryptyesnoall supported versions ofWindowsCryptoPreventyesnounknown, developer cites "largenumber of cryptoware"yesnoWindows XP to Windows 10HitmanPro.AlertnonoCryptoware protectionyesnoWindows XP to Windows 7HitmanPro.KickstartnonoLock Screen onlynoyesWindows XP to Windows 10Kaspersky AntiRansomwareyesnounknownyesrollbackall supported versions ofWindowsMalwarebytes AntiRansomwareyesyesCryptoLocker, CryptoWall,CTBLocker, TeslayesnoRansomFreeyesnoagainst more than 40 testedvariantsyesnoSBGuardyesnohardens the systemnonoTrend Micro AntiRansomwareyesnoLock Screen onlynoyesWinantiransomnonomost, if not all, ransomwareyesnoall supported versions ofWindowsall supported versions ofWindowsall supported versions ofWindowsall supported versions ofWindowsall supported versions ofWindowsSource: ghacks.net, By Martin Brinkmann on March 30, 2016 in Security - Last Update:December 20, are-overview/CommentsPaid versionsavailable,protects againstother Protectionagainst newransomwareHoneypotsystemLayeredprotection, File,network andRegistryprotection
Thank you for your attentionwww.cyber.services
vulnerability management apt and zeroday management incident response incident investigation computer and network forensics malware analysis . policy development cyber defence management support and consulting research and development startup incubation automated methods development bigdata analysis