Transcription
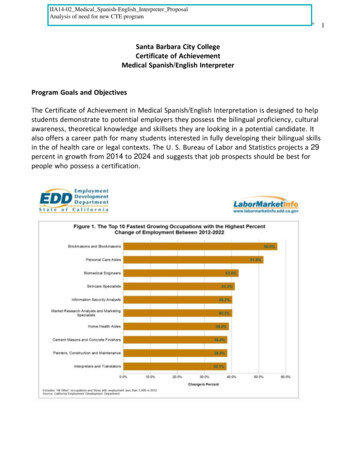
IIA14-02 Medical Spanish-English Interpreter ProposalAnalysis of need for new CTE programMedical Spanish/English InterpretationSanta Barbara City CollegeCertificate of AchievementMedical Spanish/English InterpreterProgram Goals and ObjectivesThe Certificate of Achievement in Medical Spanish/English Interpretation is designed to helpstudents demonstrate to potential employers they possess the bilingual proficiency, culturalawareness, theoretical knowledge and skillsets they are looking in a potential candidate. Italso offers a career path for many students interested in fully developing their bilingual skillsin the of health care or legal contexts. The U. S. Bureau of Labor and Statistics projects a 29percent in growth from 2014 to 2024 and suggests that job prospects should be best forpeople who possess a certification.1
Medical Spanish/English Interpretation2The Medical Spanish/English Interpretation program is designed to meet the needs of boththe students and local hospitals, clinics and the various healthcare providers. It also enhancesthe chances for better qualification and salary increases for currently employed workers.The Medical Spanish/English Interpretation program ultimately prepares students for theNational Board of Certification for Medical Interpreters examination. This examination allowsprofessional medical interpreters demonstrate they have met nationally set standards toensure patient safety and compliance with federal guidelines and requirements. Once acandidate passes the certification exams from the National Board, they are bestowedthe CMI Credential (Certified Medical Interpreter).Interpreters convert information from one spoken language into another. The goal of aninterpreter is to have people hear the interpretation as if it were the original language.Interpreters usually must be fluent speakers or signers of both languages, because theycommunicate back and forth among people who do not share a common language.There are three common modes of interpreting: simultaneous, consecutive, and whispered.* Simultaneous. Simultaneous interpreters cannot begin interpreting until the generalmeaning of the sentence is understood. Simultaneous interpreting requires interpreters tolisten or watch and speak or sign at the same time someone is speaking or signing. It requiresa high level of concentration. For that reason, simultaneous interpreters usually work inpairs, each interpreting for about 20 to 30 minutes and then resting while the other
Medical Spanish/English Interpretation3interprets. Simultaneous interpreters are often familiar with the subject matter, so they cananticipate the end of the speaker’s sentences.* Consecutive. Consecutive interpreting begins only after the speaker has said or signed agroup of words or sentences. Consecutive interpreters may take notes while listening to orwatching the speakers before presenting their interpretation. Note taking is an essential partof consecutive interpreting.* Whispered. Interpreters in this mode sit very close to the listeners and provide asimultaneous interpretation in a quiet voice.The following are examples of types of interpreters:Community interpreters work in community-based environments, providing vital languageinterpretation one-on-one or in small-group settings. Community interpreters often areneeded at parent-teacher conferences, immigration courts, motor vehicle administrations,social security offices, business meetings, new-home purchases, and many other communitysettings.Conference interpreters work at conferences that have non-English-speaking attendees. Thework is often in the field of international business or diplomacy, although conferenceinterpreters can interpret for any organization that works with speakers of foreign languages.Conference interpreters often do simultaneous interpreting. Attendees at a conference whodo not understand the language of the speaker wear earphones tuned to the interpreter whospeaks the language they want to hear. The interpreter listens to a bit of the speaker’s talkand then translates that bit. Simultaneous interpreters must be able to listen to the speaker’snext bit of talk while translating the previous bit.Health or medical interpreters and translators typically work in healthcare settings and helppatients communicate with doctors, nurses, technicians, and other medical staff. Interpretersand translators must have knowledge of medical terminology and of common medical termsin both languages.Health or medical interpreters must be sensitive to patients’ personal circumstances, as wellas maintain confidentiality and ethical standards. In the absence of local interpreter,interpretation is frequently provided remotely, either by video relay or over the phone.Health or medical translators often do not have the same level of personal interaction withpatients and providers that interpreters do. They translate primarily informational brochures,
Medical Spanish/English Interpretation4materials that patients must read and sign, website information and patients’ records fromone language into another.Liaison or escort interpreters accompany either U.S. visitors abroad or foreign visitors in theUnited States who have limited English proficiency. Interpreting in both formal and informalsettings, these specialists ensure that the visitors can communicate during their stay.Frequent travel is common for liaison or escort interpreters.Program CompetenciesSuccessful completion of the program will provide the student with the ability todemonstrate the following competencies:* The ability to convert medical concepts in the source language to equivalent concepts in thetarget language and compile them into glossaries and terminology databases to be used intranslations and interpretation sessions.* The ability to speak, read, and write fluently in at least two languages, one of which isEnglish, accurately, quickly, and clearly, and relaying the style and tone of the originallanguageProgram Student Learning Outcomes (PSLO)Successful completion of the program will provide student with the ability to: Develop a personal and complete glossary of English medical terms and its equivalentsin Spanish. Accurately Render a printed document or form from one language to another anddeliver the rendering with accuracy, clarity, proper intonation and voice modulation. Accurately take written notes or create ideogramic symbology (in a languageindependent form) of a speech in one language, in preparation for its verbal deliveryin another language. Accurately identify and translate idiomatic expressions from Spanish to English andEnglish to Spanish documents, reflecting nuances, pragmatic meaning and levels offormality.
Medical Spanish/English Interpretation5 Apply appropriate medical interpretation techniques and procedures based on varioussituations and client’s needs. Read and analyze medical documents, recognizing specialized medical terminology andfinding its closest equivalent in the other language. Accurately translate from specialized medical documents in English or Spanish,applying various strategies available to the translator for solving typical translationfrom-or-to-English problems.Occupational PreparednessPrerequisites for this program are based on language competency in both English andSpanish, with introductory and terminology courses being open to all students. There are noadditional fees for students beyond the standard community college registration fees, tuition,and textbooks.Students who successfully complete the program will be trained to work as a medicalSpanish/English interpreter. Those interested in being certified, will be prepared to take theState and National credentialing board examinations.Catalog DescriptionThe Medical Spanish/English Interpretation program will help the student master the skillsneeded to become a Spanish-English / English-Spanish medical interpreter and will preparethem for State and National credentialing board examinations. Through a combination oftheory and practice, students will gain knowledge and experience in translating andinterpreting in situations where a specialized health care skillset is required.Required Courses:Medical Spanish/English InterpretationTRS 101TRS 102TRS 103TRS 104TRS 105Intro to Translation & InterpretationEnglish and Spanish for TranslationConsecutive Interpretation and Sight TranslationSimultaneous InterpretationEnglish Translation of Specialty Areas4 units3 units3 units3 units3 units
Medical Spanish/English InterpretationTRS 106TRS 107TRS 116TRS 117TRS 118Spanish Translation of Specialty AreasTechnology for Translation and Interpret.Basic Medical Terminology, SpanishMedical Spanish/English InterpretationInterpretation Techniques3 units3 units3 units3 units3 unitsTotal Units for Certificate31 unitsProgram RequirementsCertificate of Achievement in Medical Spanish/English RS103TRS104TRS105Class NameIntro. to Translation &InterpretationEnglish and Spanish forTranslationConsecutive Interpretationand Sight TranslationSimultaneousInterpretationEnglish Translation ofSpecialty AreasUnitsCSUGEIGETCSequence4.0YR 1 Fall3.0YR 1 Fall3.0YR 1 Fall3.0YR 1 Spring3.0YR 1 SpringSpanish Translation ofSpecialty Areas3.0TRS107Technology for Translationand Interpretation3.0YR 2 FallTRS116Medical Spanish/EnglishInterpretation3.0YR 2 FallTRS117Basic Medical Terminology,Spanish3.0YR 2 FallTRS106YR 1 Spring6
Medical Spanish/English InterpretationTRS118Interpretation Techniques3.0Required Core Total31 unitsTotal Units31 units7YR 2 FallProposed Sequence units per semester:Year 1 Fall 10Year 1 Spring 9Year 2 Fall 12Total Units 31Master PlanningThe School of Modern Languages program at Santa Barbara City College has been a strongand exemplary program for many years. It is well respected by the community and providesmany students with second language instruction in many languages in Santa Barbara andsurrounding communities.The Labor Market Statistics (attachment B) shows a need for additional interpreters in theSanta Barbara region. The increase for the state is estimated to be 8.3%. The medianhourly salary for workers in the translation/interpretation sector in the region is 25.23 perhour which is above the national average. Consistent with Santa Barbara City College’s visionto strive to build a socially conscious community where knowledge and respect empowerindividuals to transform our world, would be serving its students and community well byproviding training for upcoming, desirable employment opportunities in this field.Santa Barbara City College’s mission and core principles honor its commitment to the spiritand intent of the foundational framework of the California Community Colleges, as describedin California Education Code §66010.4: Primary Mission: Academic and vocational instruction at the lower division level;advancement of California’s economic growth and global competitiveness througheducation, training, and services.Essential and Important Functions: Remedial instruction, ESL, adult noncreditinstruction (in areas defined as being in the state’s interest), and student supportservices.
Medical Spanish/English Interpretation8The Medical Spanish/English Interpretation program adheres to these core principles byteaching skills that advance students careers and competitiveness.Projected Enrollment (Estimated)Department#2018-2019Course TitleTRS 101Intro. to Translation & InterpretationTRS 102English and Spanish for TranslationConsecutive Interpretation and Sight TranslationSimultaneous InterpretationEnglish Translation of Specialty AreasSpanish Translation of Specialty AreasTechnology for Translation and InterpretationBasic Medical Terminology, SpanishMedical Spanish/English InterpretationInterpretation TechniquesTRS 103TRS 104TRS 105TRS 106TRS 107TRS 116TRS 117TRS 118# ted)50 (est.)25 (est.)111125 (est.)25 (est.)25 (est.)25 (est.)31175 (est.)25 (est.)25 (est.)This projected enrollment is based on a maximum class size of 25 students per class.Prerequisite section (TRS 101) will be taught every semester. Our Basic Medical Terminology inSpanish course could potentially attract HIT, Nursing students and health care workers fromthe community. English and Spanish for Translation is a class that is also attractive to proficientstudents who want to advance their bilingual language skills.Place of Program in Curriculum/Similar ProgramsThe Medical Spanish/English Interpretation program is new to Santa Barbara City College.Since it is an entirely new program all the classes are new, have been recently developed andare in the process of being approved by the Curriculum Committee and the district board.Being a new program it is not replacing any other classes or programs.Similar Programs at Other Colleges in the Service Area
Medical Spanish/English InterpretationCurrently there are no other Medical Spanish/English Interpretation programs in the collegeservice area. After surveying other colleges in Southern California, only two other offeringgeneric Spanish/English Interpretation programs were identified: UCLA and San Diego StateUniversity Extensions, well outside the Santa Barbara City College service area.Attachments:A. OES Wages for all areasB. Interpreters and Translators : Occupational Outlook Handbook:C. Occupational Employment Statistics9
The Medical Spanish/English Interpretation program is new to Santa Barbara City College. Since it is an entirely new program all the classes are new, have been recently developed and are in the process of being approved by the Curriculum Committee and the district board. Being a new program it is not replacing any other classes or programs.