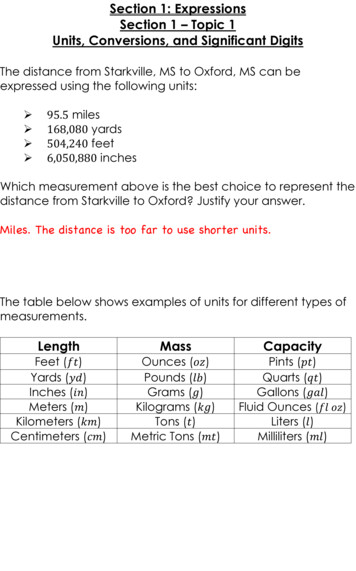
Transcription
Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1MAFS.912.G-SRT.1.1The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be coveredin this section:MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1Know precise definitions of angle,circle, perpendicular line, parallel line,and line segment, based on theundefined notions of point, line,distance along a line, and distancearound a circular arc.MAFS.912.G-CO.1.2 Represent transformations in the planeusing, e.g., transparencies andgeometry software; describetransformations as functions that takepoints in the plane as inputs and giveother points as outputs. Comparetransformations that preserve distanceand angle to those that do not.MAFS.912.G-CO.1.4 Develop definitions of rotations,reflections, and translations in terms ofangles, circles, perpendicular lines,parallel lines, and line segments.MAFS.912.G-CO.1.5 Given a geometric figure and arotation, reflection, or translation,draw the transformed figure. Specify asequence of transformations that willcarry a given figure onto itself.MAFS.912.G-CO.3.10 Prove theorems about triangles. Usetheorems about triangles to solveproblems: measures of interior anglesof a triangle sum to 180.MAFS.912.G-MG.1.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures,and their properties to describeobjects.Verify experimentally the properties ofdilations given by a center and ascale factor. A dilation takes a line notpassing through the center of thedilation to a parallel line and leaves aline passing through the centerunchanged. The dilation of a linesegment is longer or shorter in the ratiogiven by the scale factor.Topics in this SectionTopic 1:!Topic 2:!Topic 3:!Topic 4:!Topic 5:!Topic 6:!Topic 7:!Topic 8:!Introduction to Polygons – Part 1Introduction to Polygons – Part 2Angles of PolygonsTranslation of PolygonsReflection of PolygonsRotation of polygons – Part 1Rotation of Polygons – Part 2Dilation of PolygonsSection 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1!77
Section 4 – Topic 1Introduction to Polygons – Part 1Consider the polygon again.The word polygon can be split into two parts:!! “poly-” means .!! “gon” means .Consider the polygon below.The interior angles of a polygon are the angles on the insideof the polygon formed by each pair of adjacent sides.Use ! to label the interior angles of the polygon above.Are polygons closed or open figures? Explain your answer.How many sides does a polygon have?78An exterior angle of a polygon is an angle that forms a linearpair with one of the interior angles of the polygon.Use " to label the exterior angels of the polygon above.Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
Draw a representation of each of the polygons itionAll angles and sides of thispolygon are congruent.All angles and sides of thispolygon are notcongruent.This polygon has no anglespointing inwards. That is,no interior angles can begreater than 180 .This polygon has an interiorangle greater than 180 .This polygon has oneboundary and doesn’tcross over itself.RepresentationWe can also classify a polygon by the number of sides.# SidesNames34Names85pentagon7heptagon6# Sides9nonagon11hendecagon10dodecagon12Let’s discover some facts about angle measures of polygons.How many sides does a triangle have?What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 179
Let’s Practice!1.! Determine whether the following shapes are polygons.Classify the polygons by their number of sides.!!!!!!!!!!!!Try It!2.! Complete the table below.Number of sides34567/80Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1Sum of interior angles
Try It!3.! A convex pentagon has exterior angles with measures 66 ,77 , 82 and 62 .a.! Draw a representation of the pentagon.b.! What is the measure of an exterior angle of thepentagon at the fifth vertex?c.! Classify the pentagon as regular or irregular. Justifyyour answer.!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 181
82Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
Let’s Practice!Section 4 – Topic 3Angles of PolygonsIn the previous video, you learned the formula to find the sumof the angles of a polygon.1.! What are the measures of each interior angle and eachexterior angle of regular hexagon B05CDE?How can you use the sum of interior angles formula to find thenumber of sides of a polygon?2.! The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 1080 .a.! Classify the polygon by the number of sides.How can you use the sum of interior angles formula to find themeasure one angle of a regular polygon?b.! What is the measure of one interior angle of thepolygon?Can the same process be used to find the measure of oneangle of an irregular polygon? Explain your reasoning.c.! What is the measure of one exterior angle of thepolygon?!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 183
84Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
5.! If the measure of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is24 , how many sides does the polygon have?6.! Given a regular decagon and a regular dodecagon,which one has a greater exterior angle? By how much isthe angle greater?BEAT THE TEST!1.! A teacher showed the following exit ticket on theprojector.1.!What is the sum of the interior angle measures of a regular24-gon?2.! Pentagon ABCDE has interior angles that measure 60 and 160 and another pair of interior angles that measure 130 each.What is the measure of an interior angle at the fifth vertex?A student completed the following exit ticket.Which of the following statements is true?A! Both answers are correct.B! Answer #1 is incorrect. The student found theC!D!individual angle, not the sum of the angles. Theanswer should be 3960 . Answer #2 is correct.Answer #1 is correct. Answer #2 is incorrect. There aretwo angles measuring 130 , but only one was countedin the sum. The answer should be 60 .Both answers are incorrect. In #1 the student foundthe individual angle, not the sum of the angles. Theanswer is 3960 . In #2 there are two angles measuring130 , but only one was counted in the sum. Theanswer should be 60 .!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 185
86Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 187
88Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 189
90Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 191
92Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 193
Try It!2.! Samuel rotated 0B"E 270 Iclockwise about the origin togenerate 0j Bj "′E′ with vertices at A′(1, 5), B′(1, 0),"′( 1, 1), and E′( 3, 2).What is the sum of all Y-coordinates of 0B"E?3.! What happens if we rotate a figure around a differentcenter point instead of rotating it around the origin?Section 4 – Topic 7Rotation of Polygons – Part 2Use the following steps to rotate polygon 0123 155 clockwiseabout 2. Use the figure on the following page.Step 1.! Extend the line segment between the point ofrotation, 2, and another vertex on the polygon,towards the opposite direction of the rotation.Step 2.! Place the center of the protractor on the point ofrotation and line it up with the segment drawn instep 1. Measure the angle of rotation at 2. Mark apoint at the angle of rotation and draw a segmentwith your straightedge by connecting the point withthe center of rotation, 2.Step 3.! Use a compass to measure the segment used instep 1. Keeping the same setting, place the compasson the segment drawn in step 2 and draw an arcwhere the new point will be located. Label the newpoint with a prime notation.Step 4.! Copy the angle adjacent to the angle of rotation.Mark a point at the copied angle in the new figure.Draw a segment by connecting the point at the newangle with the point created in step 3.Step 5.! Use a compass to measure the segment adjacent tothe one used in step 1. Keeping the same setting,place the compass on the segment drawn in step 4and draw an arc where the new point will be located.Label the new point with a prime notation.Step 6.! Repeat steps 4-5 with the two other angles tocomplete the construction of the rotated polygon.94Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 195
96Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
!Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 197
98Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
Let’s Practice!1.! Pentagon 6"En0 has coordinates 6 0, 0 , " 4, 4 , E 8, 4 ,In 8, 4 , and 0 4, 4 and is dilated at the origin with aoscale factor of .pWhat are the coordinates of 6′"′E′n′0′?Try It!2.! Quadrilateral 6!En is dilated at the origin with a scaleqfactor of .oDescribe Quadrilateral 6!EnIand Quadrilateral 6’!’E’n′Ibyfilling in the table below with the most appropriate answer.Quadrilateral 6!En(F, Y)Quadrilateral I)E(IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII,IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII)E′(15, 5)6(3,3)!(IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII,IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII)n( 3, n 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 199
2.! Triangle 650 was dilated by a scale factor of 3 centeredat the origin to create triangle 6′5′0′, which hascoordinates 6′ 6, 12 , 5′ 18, 6 , 0′ 6, 6 . Write thecoordinates of the vertices of triangle 650 in the spacesprovided below.6(I , I)5(I , I)0(I , I)100Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1
Section 4: Introduction to Polygons – Part 1. The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.