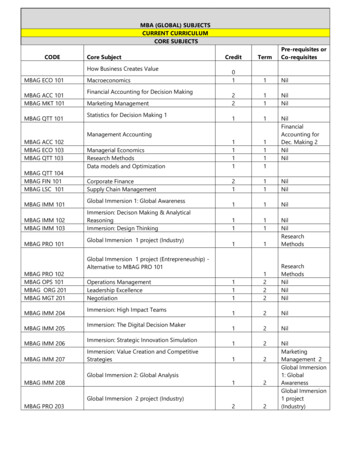
Transcription
INTRODUCTION TO OPERATIONSMANAGEMENT
Outline of topics Definition of operations managementOperations management levelsTransformation processesOperations as a serviceService in manufacturingImportance of operations managementFuture of operations management
What is operations management? Design, operation, and improvement ofsystems that create and deliver products andservices Functional field of business with clear line ofmanagement responsibilities Operation managers use tools of OR/MS/IE fordecision-making
Operations management levels Strategic issues i.e. broad-based– How to make product? Class examples? Tactical issues i.e. intermediate, constrainedby strategy– What resources? Class examples? Operational planning and control i.e. shortterm and narrow– What schedules? Class examples?
Transformation processes Uses resources to convert inputs into somedesired output– Physical--manufacturing– Locational--transportation– Exchange--retailing– Storage--warehousing– Physiological--health care– Informational--telecommunications
Physiological exampleSystem: rmationDesiredFunctionOutputPatients MDs, Nurses, HealthcareMedicalSuppliesHealthypeople
Supply chain of OEM exampleSource: Jacobs, Chase, Aquilano
Disintermediation exampleThe typical distribution channel has several intermediary layers, each ofwhich adds to the final cost of a product, such as a sweater. Removinglayers lowers the final cost to the consumer.
Higher education example Massive open online courses (MOOCs) Coursera – partners with universities to offer theircourses online Udacity – online education venture edX – online education initiative by MIT and Harvard Increasing enrollment in online courses Same or superior learning outcomes
Operations as a service Service is an intangible process while a good is aphysical output of a process Service requires some interaction with the customerhence location is often important Services are perishable and time dependent Services are inherently heterogeneous Emerging model in industry is that every business isin the service business
Service in manufacturing Service can be divided into core and valueadd services provided to internal andexternal customers of the factoryCore services: products made to meetcustomer demand for quality, flexibility,speed and priceValue-add services: supports externalcustomers & helps internal customers to dotheir jobs
Value-add services Information: ability to furnish data on product tointernal groups and external customers Problem solving: ability to help internal and externalgroups to solve problems, i.e. quality Sales support – ability to enhance sales andmarketing efforts, i.e. demonstrations Field support – ability to offer after-sales support i.e.replace defective parts quickly
Goods-services continuum
International growth in services
Why care about operations? Operations account for 60-80% of directexpenses of companies Organizations are now flat rather thanfunctional Companies are organized by customer andproduct groups Success of mergers/acquisitions mainlydepend on operational processes
Where is OM headed? Coordination – main activity of the future– Fast and cheap communications– Dramatic surge in outsourcing– Contract manufacturing on the rise Optimization - global supplies, production anddistribution networks– Implementation of global ERP systems– Optimal control of resources, i.e. inventory,transportation and production equipment
Where is OM headed? cont. Co-production - increased co-production– Internet allows direct contact of customers and producers– Use of IT gets rid of inefficient functions, reduces cost andimproves service Customer Management - managing customer touchpoints– Balance between staffing and customer service– Capture the implicit costs of lost customers and direct costof staffing Competitive weapon – need for awareness to useoperations for competitive advantage
Key thought Raise senior management awareness ofoperations as a significant competitiveweapon
Mind exercise 1 A major objective of OM is to show how smartmanagers can do which of the following?a.b.c.d.e.Improve efficiency by lowering costsImprove effectiveness by creating valueIncreasing value by reducing pricesServing customers wellAll of the above
Mind exercise 2 In the Input-Transformation-Output Relationship, atypical “input” for Nakumatt is which of thefollowing?a. Displaysb. Stocks of goodsc. Sales clerksd. All of the abovee. None of the above
Case: Wal-Mart What approaches did Wal-Mart use to createcompetitive advantage? How did K-Mart respond to the onslaught byWal-Mart? What is your assessment of K-Mart’s chancesof success in its attempts to contain WalMart?
Source: Jacobs, Chase, Aquilano. . Removing layers lowers the final cost to the consumer. Higher education example Massive open online courses (MOOCs) Coursera - partners with universities to offer their courses online Udacity - online education venture . -Implementation of global ERP systems -Optimal control of resources .