Transcription
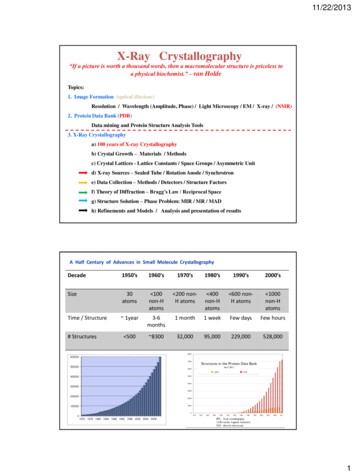
11/22/2013X-Ray Crystallography“If a picture is worth a thousand words, then a macromolecular structure is priceless toa physical biochemist.” – van HoldeTopics:1. Image Formation (optical illusions)Resolution / Wavelength (Amplitude, Phase) / Light Microscopy / EM / X-ray / (NMR)2. Protein Data Bank (PDB)Data mining and Protein Structure Analysis Tools3. X-Ray Crystallographya) 100 years of X-ray Crystallographyb) Crystal Growth – Materials / Methodsc) Crystal Lattices - Lattice Constants / Space Groups / Asymmetric Unitd) X-ray Sources – Sealed Tube / Rotation Anode / Synchrotrone) Data Collection – Methods / Detectors / Structure Factorsf) Theory of Diffraction – Bragg’s Law / Reciprocal Spaceg) Structure Solution – Phase Problem: MIR / MR / MADh) Refinements and Models / Analysis and presentation of resultsA Half Century of Advances in Small Molecule ��s1990’s2000’sSize30atoms 100non-Hatoms 200 nonH atoms 400non-Hatoms 600 nonH atoms 1000non-HatomsTime / Structure 1year3-6months1 month1 weekFew daysFew hours 500 830032,00095,000229,000528,000# Structures1
11/22/2013What happened?1913 – 1963 vs. 1963 - 20131) Sources2) Instrumentation diffractometers / computers / detectors3) Software / Computers FORTRAN programming SHELX, CCP4, Phenix, etc.4) Molecular Biology - cloning / expression systems; sequencing5) Automation - robotics6) Methods Phasing: Patterson / Heavy atom; MIR; SIR; MR; MAD; SADModel Building: Contour tracing, Richards Box, FRODO, COOTRefinement and ValidationX-ray Sources:X-ray tubes:the “sealed” tube2
11/22/2013Origin of Non-characteristic X-raysOrigin of characteristic X-rays3
11/22/2013Characteristic X-rays arise from electronic transitionsMLCharacteristic X-rays have definedKKl4
11/22/20135
11/22/2013Another Source of “X-rays”6
11/22/2013“X-ray” Sources: X-ray tubes22177Advanced Photon Source (APS) synchrotron near Chicago.7
11/22/2013DetectorsFilmVisual intensity estimationPrecession film ofPhosphorylaseFrom Blundell and Johnson p.156Ron Hamlin – Supper Award talk8
11/22/2013Concept drawing of a film scannerOptronics P-1000 film scannerRossmann, Methods in Enzymology 1985, p. 242Ron Hamlin – Supper Award talkPhoto provided by Dieter Schneider, Brookhaven National LaboratoryDiffractometer: automatic butmeasured only one hkl reflection at a timeRobert Sweet, Methods inEnzymology 1985Ron Hamlin – Supper Award talk9
11/22/2013Omega scan of a single reflectionRon Hamlin – Supper Award talkArea Detectors: Typical coverage of diffractionpattern by a pair of ADSC multiwire detectorsXuong Nguyen-huuRon Hamlin – Supper Award talkRon Hamlin10
11/22/2013Era of Multiwire Area DetectorsParts of first ADSCmultiwire countersystem in Ron’s livingroom in early 1984The two-detector Mark IIsystem started operation inXuong’s lab in about 1982Motor driven twotheta tableU. Texas Austin 1988Ron Hamlin – Supper Award talkMAR 180 with cover removedRon Hamlin – Supper Award talk11
11/22/2013Image Plate Detectorsbrute force solid angle coverageRon Hamlin – Supper Award talkFiberoptic TapersRon Hamlin – Supper Award talk12
11/22/2013Basic Principle of Operation(3.7:1 TAPER RATIO)81Å24450Ron Hamlin – Supper Award talkQuantum 1 cover removedRon Hamlin – Supper Award talk13
11/22/2013The Quantum 315 uses 9 instead of 4 of exactly thesame modules as used in the Quantum 210.315 mm210mm315 mm210 mm2104K by 4KQuantumQuantum 3156K by 6KRon Hamlin – Supper Award talkDiffraction pattern from a Quantum 315Early Image Plate(MAR 180)Single counterdiffractometerADSC multiwireCounter systemRon Hamlin – Supper Award talk14
11/22/2013X-Ray Crystallography“If a picture is worth a thousand words, then a macromolecular structure is priceless toa physical biochemist.” – van HoldeTopics:1. Image Formation (optical illusions)Resolution / Wavelength (Amplitude, Phase) / Light Microscopy / EM / X-ray / (NMR)2. Protein Data Bank (PDB)Data mining and Protein Structure Analysis Tools3. X-Ray Crystallographya) 100 years of X-ray Crystallographyb) Crystal Growth – Materials / Methodsc) Crystal Lattices - Lattice Constants / Space Groups / Asymmetric Unitd) X-ray Sources – Sealed Tube / Rotation Anode / Synchrotrone) Data Collection – Methods / Detectors / Structure Factorsf) Theory of Diffraction – Waves, Fourier / Bragg’s Law / Reciprocal Spaceg) Structure Solution – Phase Problem: MIR / MR / MADh) Refinements and Models / Analysis and presentation of resultsWaves ( Amplitudes & Phases )Adding waves / phase effect15
11/22/2013Joseph Fourier / Fourier Series 180816
11/22/2013Fourier Series Applethttp://www.falstad.com/fourier/17
11/22/2013Euler's formula (Leonhard Euler, 1707-1783) gives the relationshipbetween the complex exponential function and common trig terms. Forany real number “j”Replace list ofan / bn with Fn and jnFnbnjnanna bFj17 07020 889035 5 7.1 ?48 6? 36.918
11/22/2013Fourier Series / Fourier TransformsorNow consider electron density (as a function or a set of coefficients)orReal SpaceReciprocal SpaceAND – Fhkl can also be calculated as the resultant scattering or the sum of theindividual scattering atoms!!ObjectTransformImageTransform / Reciprocal SpaceElectronDensityMapsX-rays Object / Real SpaceModels19
11/22/2013Diffraction: Scattering from (two) “atoms”Represent a waveas an amplitude phase.Scattering from “many atoms”CalculatedExperimentalF(hkl) SQRT [cI(hkl)]The structure factor for a reflection may be thought of as the vector sum of the x-ray scatteringcontributions from many atoms.Each of the j contributions may be represented as a vector in the complex plane, with amplitude fj andphase phij.20
11/22/2013Scattering from “atoms in two unit cells”X-ray apparatusSodium Chloride (NaCl)Bragg’s Law (nl 2d sinq )21
11/22/2013Crystals: Scattering from “planes”Resultant scattering of resultant scattering!Bragg Equationnλ 2 d sin(θ)PQ QR nλScattering will only be “observed” at discrete Bragg angles(q)The spacings of the Bragg reflectionsLattice Constants(1 2)Planes and Indices(1 1)22
11/22/2013ReciprocalSpace Lattice2,13,11,10,13,02,0b*1,01,0a*2,-11,-1Real SpaceLattice0,-11 Set Bragg Planes b1 Spot (Diff. Max.)aPlanes in direct space represented by points in reciprocal space.Electron Density FunctionMeasure thousands of Amplitudes - [Fhkl ]‘s - ? How do we obtain Phases ahkl ?Phase Problem23
11/22/201324
11/22/201325
11/22/2013Effect ofResolutionReduced Disorder atLower TemperaturesX-Ray Crystallography“If a picture is worth a thousand words, then a macromolecular structure is priceless toa physical biochemist.” – van HoldeTopics:1. Image Formation (optical illusions)Resolution / Wavelength (Amplitude, Phase) / Light Microscopy / EM / X-ray / (NMR)2. Protein Data Bank (PDB)Data mining and Protein Structure Analysis Tools3. X-Ray Crystallographya) 100 years of X-ray Crystallographyb) Crystal Growth – Materials / Methodsc) Crystal Lattices - Lattice Constants / Space Groups / Asymmetric Unitd) X-ray Sources – Sealed Tube / Rotation Anode / Synchrotrone) Data Collection – Methods / Detectors / Structure Factorsf) Theory of Diffraction – Waves, Fourier / Bragg’s Law / Reciprocal Spaceg) Structure Solution – Phase Problem: MIR / MR / MADh) Refinements and Models / Analysis and presentation of results26
11/22/2013Solving the Phase ProblemEarly Days:Centric structures (all phases 0o or 180o) Heavy atom / Patterson methodMacromolecular Crystallography1.MIR: Multiple Isomorphous Replacement (Heavy Atom)2.MR: Molecular Replacement3.MAD: multiwavelength anomolous **** Molecular Modeling (predicting starting structure from sequence alone)Use of Heavy Metal Ions for Phasing by MIR MethodsNative PhosphorylasePhosphorylase Ethyl Hgthiosalicylate27
11/22/2013Effect of adding 1 “heavy” atom with lots of electrons!(e.g. Hg, Pt)FPH FP FHMultiple Isomorphous Replacement (MIR) methodFPH FP FHFP FPH - FH28
11/22/2013Multiple Isomorphous Replacement (MIR) methodFP FPH - FHSolving the phase problem by “MolecularReplacement".If an approximate model of the protein structure is known in advance, approximatephases can be guessed, and the unknown parts of the structure can be calculatedin an iterative procedure.No heavy atom derivative required.BUT – need starting model and orientation (rotation and translation)For example, molecular replacement can be used to determine the structure of ancomplex with inhibitor bound to an enzyme active site, if the structure of the enzymeitself is already known. Also, MR is often used to solve the structures of closelyrelated proteins in a superfamily.29
11/22/2013http://www.ysbl.york.ac.uk/ cowtan/fourier/fourier.html30
11/22/2013X-Ray Crystallography“If a picture is worth a thousand words, then a macromolecular structure is priceless toa physical biochemist.” – van HoldeTopics:1. Image Formation (optical illusions)Resolution / Wavelength (Amplitude, Phase) / Light Microscopy / EM / X-ray / (NMR)2. Protein Data Bank (PDB)Data mining and Protein Structure Analysis Tools3. X-Ray Crystallographya) 100 years of X-ray Crystallographyb) Crystal Growth – Materials / Methodsc) Crystal Lattices - Lattice Constants / Space Groups / Asymmetric Unitd) X-ray Sources – Sealed Tube / Rotation Anode / Synchrotrone) Data Collection – Methods / Detectors / Structure Factorsf) Theory of Diffraction – Waves, Fourier / Bragg’s Law / Reciprocal Spaceg) Structure Solution – Phase Problem: MIR / MR / MADh) Refinements and Models / Analysis and presentation of results31
11/22/201332
11/22/2013Energy Refinement(Simulated Annealing)ETOTAL EEMPlRICAL EEFFECTIVEEEFFECTIVE EXREF ENOE EHARM ECDIH ENCS EDG ERELA EPLANEEMPIRlCAL ΣNp l [wpBONDEBOND wpANGLEANGL wpDIHEEDIHE wpIMPREIMPR wpVDWEVDW wpELECEELEC wpPVDW EPVDW wpPELEEPELE wpHBONEHBON].Difference FourierObs.Calc.33
11/22/201334
11/22/2013Examples of Difference FouriersM.C. EscherEscher sketch35
11/22/201336
Resolution / Wavelength (Amplitude, Phase) / Light Microscopy / EM / X-ray / (NMR) 2. Protein Data Bank (PDB) Data mining and Protein Structure Analysis Tools 3. X-Ray Crystallography a) 100 years of X-ray Crystallography b) Crystal Growth - Materials / Methods c) Crystal Lattices - Lattice Constants / Space Groups / Asymmetric Unit




![[AWS Black Belt Online Seminar] AWS X-Ray](/img/17/20200526-blackbelt-x-ray.jpg)