Transcription
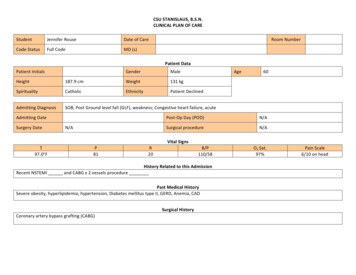
CSU STANISLAUS, B.S.N.CLINICAL PLAN OF CAREStudentJennifer RouseDate of CareCode StatusFull CodeMD (s)Room NumberPatient DataPatient InitialsGenderMaleAgeHeight187.9 cmWeight131 kgSpiritualityCatholicEthnicityPatient DeclinedAdmitting DiagnosisSOB, Post Ground level fall (GLF), weakness; Congestive heart failure, acuteAdmitting DateSurgery DateN/A60Post-Op Day (POD)N/ASurgical procedureN/AVital SignsT97.0 FP81R20B/P110/58History Related to this AdmissionRecent NSTEMI and CABG x 2 vessels procedurePast Medical HistorySevere obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, Diabetes mellitus type II, GERD, Anemia, CADSurgical HistoryCoronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)O2 Sat.97%Pain Scale6/10 on head
DietActivityNG/Feeding TubeDiabetic Diet (carbcontrol)NoIsolationDVT ProphylaxisVascular AccessSafety ConsiderationsRestraintsDressing ChangesOxygen TreatmentsRespiratory treatmentsFoleyNoneAdvance directivesAmbulatory withassistive devicesNoneDrains/ TubesNoneNoVS frequencyQ4hGlucose MonitoringYes, Q6hNo, patient isambulatoryPCA/EpiduralNoneTelemetryYesIV Site:right antecubitalType of access-- 20 gaugeIV Solution:-- N/AMorse Fall Scale 70 (High risk for falling)Patient has assistive devices, a call light, adequate lighting in room, upper side rails x 2, nonskid slippers and has been educatedregarding fall prevention. His safety needs are assessed qh.No restraintsAbdominal dressing (from previous chest tube) dry, clean and intact. Dressing was placed on and was changed on.Supplemental O2 2L/min via nasal cannula FiO2 28% LPM: 4 Maintain O2 at 95%Labs for clinical dayAlbuterol Nebulizer 2.5 mg q6hIncentive Spirometer 5-10 breathes qh while awakeBMP, BNP, CBC, Ionized Calcium, Magnesium level, POC whole blood glucose q6h, and daily weightScheduled ProceduresNoneProcedures done thisadmissionNoneNotes on pathophysiology: Patient was admitted to the ER with Acute CHF and tenderness on the posterior side of the head resulting from a post ground levelfall due to SOB. He recently had a NSTEMI on and then a CABG x2 vessels on . His heart has undergone a large amount of stress due to a recentMI and an invasive open heart procedure. His admitting diagnosis of acute CHF is likely due to his heart not being able to effectively pump because of thedamage to the heart during the MI. The MI has caused a decreased cardiac output and decreased stroke volume, so the heart compensates by driving up theheart rate in order to increase myocardial contractility to move the blood forward as needed. Unfortunately, the heart can only handle this for so long andcannot meet the demands of the body. Eventually, the ventricles are taxed (especially the left ventricle) and unable to gain a strong contraction to pump bloodforward, so blood backflows into the left atrium and then into the lungs. The fluid now in the lungs causes pulmonary congestion and edema (left-sided heartfailure). With pulmonary congestion, gas exchange is impaired because the lungs have been overcrowded with fluid instead of moving O2 in and CO2 out. Thiscauses weakness, confusion and fatigue because not enough O2 is getting to the brain and peripheral tissues. This patient became SOB due to pulmonarycongestion and fell because of weakness due to poor gas exchange.
AllergiesNo Known AllergiesMedicationsGeneric & Trade NameDrug Classification(Therapeutic uencyAction of drug andRationale(Why is patient onmedication?)650 mg oral q6hprn for mild pain (13) or temp 101Treatment of mild aches andpain and reduces fever. Thispatient was in pain uponarrival d/t respiratorydistress and GLF whichresulted in hitting thebackside of his head.Trade: TylenolTherapeutic:Antipyretic, nonpoiodanalegesicsSignificantSide Effects(Serious and/or frequent)Pruritis, Constipation,Nausea, Vomiting,Headache, Insomnia,Agitation, Atelectasis,HepatotoxicityNursing implications related toassessment, administration oreducation Generic:Acetaminophen HYDROcodoneTrade: NorcoTherapeutic: allergy, cold andcough remedies (antitussives),opioid analgesics325 mg tablet1 tablet q4h prn formoderate pain (4-7)Used to treat allergy, coldand cough remedies. Patienthas CHF and is SOB due topulmonary congestion. Thismedication helps relievecoughing. Patient recentlyunderwent an open,invasive heart surgery.Surgical site is still healingConfusion, dizziness,sedation, respiratorydepression, hypotension,constipation, dyspepsia,nausea. Have patient rate pain 1-10to determine whetherTylenol is appropriate 30-60min followingadministration.Assess temperature q4h oras needed when patient’sskin feels warm, wet, orconsciousness is altered.Check for signs of fever(diaphoresis, tachycardia,malaise).Monitor patient’s pain levelor temperature thereafterand for any adverse effectsAssess BP, pulse andrespirations before andperiodically duringadministration. If RR is 10/min, assess level ofsedation.Assess bowel functionroutinely.Assess type, location and
and sternum presentsinflammation and edema atsite. This medication is usedto control postoperativepain.Pharmacologic: opioidagonist/ nonopioid analgesiccombinationGeneric: Albuterol2.5 mg Nebulizerq6hTrade: Accuneb, AtroventTherapeutic: bronchodilatorPharmacologic: adrenergicsThis is used as abronchodilator to controland prevent reversibleairway obstruction andallow the patient to coughand breathe moreefficiently. Nervousness, restlessness,tremor, paradoxicalbronchospasm, chest pain,palpitations and tachycardia Generic: AsprinTherapeutic: antipyretics,nonopiod analgesicsPharmacologic: salicylates81 mg oral dailywith a meal (onetime per day)This patient is taking thismed as a prophylaxis whichis used for transientischemic attacks and MI.GI bleeding,hepatotoxicity, epigastricdistress, dyspepsia,anaphylaxis, laryngealedema intensity of pain prior to the1hr peak followingadministration.This medication suppressescough, so assess patient forcongestion and movementof secretions.Assess lung sounds, pulseand BP beforeadministration and duringpeak of medication.Note the amount, color andcharacter of sputumproduced.Monitor pulmonary fxn testsbefore and during therapy.Observe for paradoxicalbronchospasm (wheezing)and withhold med is thiscondition occurs.Also, assess for allergy toatropine and belladonnaalkaloids.Assess pain, fever andmonitor hepatic function,serum salicylate levels,prothrombin time, andhematocrit.Teach patient to take witha full glass of water, andto avoid use with alcoholand to avoid use withacetaminophen orNSAIDs.
Generic: atrovastatin20 mg oral 1 timeper day with a mealTrade: LipitorTherapeutic: lipid loweringagentsPharmacologic: HMG-CoAreductase inhibitorGeneric: carvedilol12.5 mg oral 2times per dayTrade: CoregTherapeutic:antihypertensivesHold for HR lessthan 55 and/or SBPless than 100Pharmacologic: beta blockersGeneric: famotidineTrade: PepcidTherapeutic: antiulcer agentsPharmacologic: histamine H2antagonists20 mg oral q12hPrimary prevention forcardiovascular disease (MIor stroke) in patients withCHD or type II diabetes.Used for revascularizationprocedures. Patient has ahistory of MI, currently hasCHF and type II diabetesmellitus and hyperlipidemia.Hypersensitivity, active liverdisease or unexplainedpersistent increase in AST orALT.The medication is used forhypertension and for heartfailure. It decreases HR andBP which improves cardiacoutput, slowing theprogression of HF anddecreased risk of death. Itblocks the stimulation ofbeta1 and beta 2 adrenergicreceptor sites.Dizziness, fatigue, weakness,diarrhea, erectiledysfunction, hyperglycemia,bradycardia, HF, pulmonaryedema, Stevens-Johnson’ssyndrome, toxic epidermalnecrolysis, anaphylaxis,angioedemaThe patient receives thismedication for managementof GERD. It inhibits theaction of histamine at theH2-receptor site locatedprimarily in gastric parietalcells, resulting in inhibitionof gastric acid secretion.Confusion, arrhythmias,dizziness, drowsiness,hallucinations, headache,constipation, diarrhea,agranulocytosis, aplasticanemia Evaluate serum cholesterollevels and triglyceridesbefore initiating, after 4-6wks of initiating andperiodically afterwards.Monitor liver function tests,including AST and ALT. Ifpatient develops muscletenderness during therapy,monitor CK levels. If CKlevels are 10 times theupper limit of normal, ormyopathy occurs,discontinue the drug.Monitor BP and pulsefrequently during doseadjustment period andperiodically during therapy.Assess for orthostatichypotension when assistingpatient up from supineposition.Monitor intake and outputratios and daily weight.Assess patient routinely forevidence of fluid overload.Assess for epigastric orabdominal pain and frank oroccult blood in the stool,emesis, or gastric aspirate.Monitor CBC withdifferential periodicallyduring therapy.For geriatric patients, assessthem routinely forconfusion.
Generic: furosemideinjectable60 mg IV q12h(ordered as Lasixinjectable)Trade: LasixTherapeutic: diureticsPharmacologic: loop diureticsGeneric: glipiZIDE20 mg oral BIDTrade: GlucotrolTherapeutic: antidiabeticPharmacologic: sulfonylureasGeneric: insulin aspart*(sliding scale)Trade: NovoLOG Mix 70/30Therapeutic: antidiabetics,hormonesPharmacologic: pancreaticsNote* HiGH ALERT MEDSubCutaneous 4times/day premeal/bedtime(use sliding scale)This patient receives thismed because he has CHF.This medication inhibits thereabsorption of sodium andchloride from the loop ofHenle and distal renaltubule. It increases theexcretion of water, sodium,chloride, magnesium,potassium and calcium. Italso decreases BP.Control of blood glucose intype 2 diabetes mellitus.This patient has diabetestype 2, so this medicationlowers blood glucose bystimulating the release ofinsulin from the pancreasand increasing thesensitivity to insulin atreceptor sites.Because this patient hasType 2 diabetes mellitus,this medication is used tolower blood glucose bystimulating glucose uptakein skeletal muscle and fatand inhibiting hepaticglucose production. Itcontrols hyperglycemia.Blurred vision, dizziness,headache, vertigo,hypotension, constipation,drymouth, increase in BUN,excessive urination,erythema multiforme,Stevens-Johnson Syndrome,toxic epidermal necrolysis,dehydration, mia,hyponatremia, hypovolemiaand metabolic alkalosis.Dizziness, drowsiness,photosensitivity,hypoglycemia, aplasticanemia Hypoglycemia, erythema,lipodystrophy, pruritis,swelling, allergic reactionsincluding anaphylaxis Assess fluid status prior todrug administration.Monitor daily weights,intake and output ratios,amount and location ofedema, lung sounds, skinturgor, and mucousmembranes.Monitor BP and pulsebefore and duringadministration.Observe for signs andsymptoms of hypoglycemia.Assess for allergies tosulfonamides.Monitor CBC periodicallyduring therapy and reportdrop in blood levels.Instruct patient on purposeand effects of antidiabeticdrugs and to not take thisdrug if unable to eat.Assess for symptoms ofhypoglycemia andhyperglycemia. (anxiety,restlessness, tingling inextremities, confusion,irritability, nausea,tachycardia, tremor,weakness or unsteady gait)Monitor body weightperiodically.Monitor glucose Q6h duringtherapy. Hemoglobin A1Cmay also be monitoredevery 3-6mo to determine
Generic: lisinopril2.5 mg oral dailyTrade: PrinivilHold is SBP 90Therapeutic:antihypertensivesPharmacologic: ACE inhibitorsGeneric: ondansetroninjectableTrade: ZofranTherapeutic: antiemeticsPharmacologic: 5-HT3antagonists4 mg IV q6h PRN fornausea/vomitingThis medication blocks theconversion of angiotension Ito the vasoconstrictorangiotensin II, which it turncauses systemic vasodilationand reduces BP. It is used toimprove symptoms inpatients with HF anddecreases the developmentof overt HF after MI.Dizziness, drowsiness,fatigue, couch, hypotension,taste disturbances,agranulocytosis,angioedemaUsed to prevent nausea andvomiting associated withhighly or moderatelyemetogenic chemotherapy.Headache, dizziness,drowsiness, fatigue,weakness, torsade depointes, constipation,diarrhea. effectiveness.If overdose occurs(hypoglycemia), give oralglucose to counteract theeffects.Monitor BP and pulsefrequently during initialdose adjustment andperiodically during therapy.Do not give medication ifSBP is less than 90 mmHg.Assess patient for signs ofangioedema (dyspnea, facialswelling).For HF patients, monitorweight and assess patientroutinely for resolution offluid overload.Assess for nausea, vomiting,abdominal distension andbowel sounds prior to andfollowing administration.Assess patient forextrapyramidial effects andmonitor ECG in patientswith hypokalemia.Teach patients to notifyhealth care professionalimmediately if symptoms ofirregular heart beat orinvoluntary movementoccurs.
Lab and Diagnostic Test DataLABSNormal Range(Fill in HospitalNorms)RESULT 1(3/17/150100)Reason for abnormal lab values r/t diagnosis & nursing implicationsCBC WBC4.5-1111.3 RBC3.8-5.83.39Hemoglobin (Hgb)12.6-17.49.7Hematocrit (Hct)35-5130.3 MCV MCH MCHC RDWPLT COUNT81-10027-3431-368928.531.8150-450490Slightly high. The WBC count is likely high because of recent trauma (surgery)and stress that the patient is currently experiencing. The WBC’s are probablyunder hormonal influence of epinephrine which is secreted by the sympatheticnervous system in response to stress. Also, the patient has undergone aninvasive surgical procedure which causes inflammation and migration of WBC’sto the area. Continue to monitor WBC’s and the surgical sites integrity.Slightly low. Patient has a history of anemia which would cause a decreasedlevel of RBC’s. Also, with a fluid overload (which is indicated by pulmonarycongestion and peripheral edema), the RBC’s are diluted and the number ofRBC’s per cubic millimeter is reduced. Continue to monitor RBC’s and treatanemia with Iron (if needed) as well as get fluid volume under control with useof diuretics which the patient is currently on.Low. RBC’s are re
Nursing implications related to assessment, administration or education Generic: Acetaminophen Trade: Tylenol Therapeutic: Antipyretic, nonpoiod analegesics 650 mg oral q6h prn for mild pain (1-3) or temp 101 Treatment of mild aches and pain and reduces fever. This patient was in pain upon arrival d/t respiratory distress and GLF which resulted in hitting the backside of his head. Pruritis .