Transcription
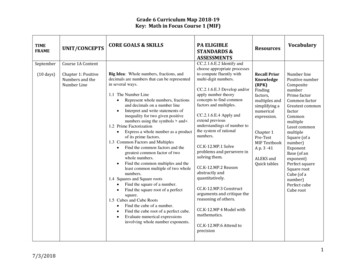
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)TIMEFRAMEUNIT/CONCEPTSSeptemberCourse 1A Content(10 days)Chapter 1: PositiveNumbers and theNumber LineCORE GOALS & SKILLSBig Idea: Whole numbers, fractions, anddecimals are numbers that can be representedin several ways.1.1 The Number Line Represent whole numbers, fractionsand decimals on a number line Interpret and write statements ofinequality for two given positivenumbers using the symbols and 1.2 Prime Factorization Express a whole number as a productof its prime factors.1.3 Common Factors and Multiples Find the common factors and thegreatest common factor of twowhole numbers. Find the common multiples and theleast common multiple of two wholenumbers.1.4 Squares and Square roots Find the square of a number. Find the square root of a perfectsquare.1.5 Cubes and Cube Roots Find the cube of a number. Find the cube root of a perfect cube. Evaluate numerical expressionsinvolving whole number exponents.7/3/2018PA ELIGIBLESTANDARDS &ASSESSMENTSCC.2.1.6.E.2 Identify andchoose appropriate processesto compute fluently withmulti-digit numbers.CC.2.1.6.E.3 Develop and/orapply number theoryconcepts to find commonfactors and multiples.CC.2.1.6.E.4 Apply andextend previousunderstandings of number tothe system of rationalnumbers.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.ResourcesRecall PriorKnowledge(RPK)Findingfactors,multiples andsimplifying anumericalexpression.Chapter 1Pre-TestMIF TextbookA p. 3 -41ALEKS andQuick tablesVocabularyNumber linePositive numberCompositenumberPrime factorCommon factorGreatest commonfactorCommonmultipleLeast commonmultipleSquare (of anumber)ExponentBase (of anexponent)Perfect squareSquare rootCube (of anumber)Perfect cubeCube rootCC.K-12.MP 4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecision1
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)CC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.Initial Knowledge Check –ALEKSChapter 1 Test – Math inFocusSeptember(7 days)Chapter 2: Negativenumbers and thenumber lineBig Idea: Negative numbers are theopposites of positive numbers. For everypositive number there is a correspondingnegative number.2.1 Negative numbers Use negative numbers to representreal-world quantities. Represent compare and orderpositive and negative numbers on anumber line,2.2 Absolute value Understand the absolute value of thenumber is its distance from 0 on thenumber line. Interpret absolute value asmagnitude for a positive or negativequantity in a real-world situation.CC.2.1.6.E.4 Apply andextend previousunderstandings of number tothe system of rationalnumbers.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.RPK:Representingpositivenumbers on anumber linep. 43Chapter 2pre-testMIF TextbookA p. 42-61NegativenumberOppositeAbsolute valueALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP 4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.Chapter 2 Test – Math inFocus7/3/20182
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)October(14 days)Chapter 3:Multiplying andDividing Fractionsand DecimalsBig Idea: Whole number concepts can beextended to fractions and decimals whenmore precise calculations are needed.3.1 Dividing Fractions Divide a fraction, whole number, ormixed number by a fraction or amixed number.3.2 Multiplying Decimals Multiply a decimal by a decimal.3.3 Dividing Decimals Divide a whole number or a decimalby a decimal.3.4 Real-world problems: Fractions andDecimals Sole problems involving fractionsand decimals.CC.2.1.6.E.1 Apply andextend previousunderstandings ofmultiplication and division todivide fractions by fractions.CC.2.1.6.E.2 Identify andchoose appropriate processesto compute fluently withmulti-digit numbers.CC.2.1.6.E.3 Develop and/orapply number theoryconcepts to find commonfactors and multiples.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.RPK:add/subtractdecimals &improperfractions asmixednumbersp. 63reciprocalsChapter 3pre-testMIF TextbookA p. 62-110ALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP 4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.Chapter 3 Test – Math inFocus7/3/20183
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)Cumulative Review Chapters1-3OctoberNovember(10 days)Chapter 4: RatioBig Idea: You can use a ratio to comparetwo quantities and you can use ratios to solveproblems.4.1 Comparing two quantities Write ratios to compare twoquantities. Interpret ratios given in fractionform. Use a ratio to find what fraction onequantity is of another or how manytimes as great one is as the other.4.2 Equivalent ratios Write equivalent ratios. Write ratios in simplest form. Compare ratios.4.3 Real-world problems: Ratios Solve real-world problems involvingratiosCC.2.1.6.D.1 Understandratio concepts and useratio reasoning to solveproblems.CC.2.1.6.E.2 Identify andchoose appropriate processesto compute fluently withmulti-digit numbers.CC.2.1.6.E.3 Develop and/orapply number theoryconcepts to find commonfactors and multiplesRPK:Equivalentfractionsexpressed bymultiplicationand divisionp. 115RatioTermEquivalent ratiosSimplest formChapter 4pre-testMIF TextbookA p. 118-153ALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP 4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecision7/3/20184
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)CC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.Chapter 4 Test – Math inFocusNovember(8 days)Chapter 5: RatesBig Idea: You can use a rate to compare onequantity to another quantity, and use rates tosolve problems.5.1 Rates and unit rates Sole unit rate problems includingpricing and constant speed.5.2 Real-world problems involving rates andunit rates Solve problems involving unit ratesCC.2.1.6.D.1 Understandratio concepts and useratio reasoning to solveproblems.CC.2.1.6.E.2 Identify andchoose appropriate processesto compute fluently withmulti-digit numbers.RPK:Multiplyingwholenumbers,mixednumbers, andfractionsp. 155CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.Chapter 5pre-testMIF TextbookA p. 159-181CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.ALEKS andQuick tablesRateUnit rateSpeedAverage speedCC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP 4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.7/3/20185
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.December(9 days)Chapter 6: PercentBig Idea: Percent is a concept used tocompare quantities expressed per hundred6.1 Understanding percent Understand percent notation. Write equivalent fractions, decimals,and percents.6.2 Fractions, decimals, and percents Write more equivalent fractions,decimals, and percents.6.3 Percent of a quantity Find the percent of a number6.4 Real-world problems: Percent Sole problems involving percent6.5 Percent of change Sole problems involving percentincrease and decrease.CC.2.1.6.D.1 Understandratio concepts and useratio reasoning to solveproblems.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.RPK: mplifyingfractionsusing divisionp. 183PercentBaseSales taxCommissionInterestInterest rateMarkupDiscountChapter 6pre-testMIF TextbookA p. 185-213ALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.5 Reasonabstractly andquantitativelyCC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.7/3/20186
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)DecemberJanuary(12 days)Chapter 7: AlgebraicexpressionsBig Idea: Algebraic expressions can be usedto describe situations and sole real-worldproblems.7.1 Writing algebraic expressions Use variables to write algebraicexpressions.7.2 Evaluating algebraic expressions Evaluate algebraic expressions forgiven values of the variable.7.3 Simplifying algebraic expressions Simplify algebraic expressions inone variable. Recognize that the expressionobtained after simplifying isequivalent to the original expression.7.4 Expanding and factoring algebraicexpressions Expand simple algebraic expressions Factor simple algebraic expressions.7.5 Real-world problems: Algebraicexpressions Sole real-world problems involvingalgebraic expressions.CC.2.2.6.B.1 Apply andextend previousunderstandings ofarithmetic to algebraicexpressions.CC.2.2.6.B.2 Understandthe process of solving aone-variable equation orinequality and apply it toreal-world andmathematical problems.RPK: Usingbar modelsp. 219Chapter 7pre-testMIF TextbookA p. 221-252ALEKS andQuick tituteSimplifyCoefficientLike termsEquivalentexpressionsExpandfactorCC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.5 Reasonabstractly andquantitativelyCC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.7/3/20187
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.JanuaryFebruary(12 days)Chapter 8: Equationsand InequalitiesBig Idea: Equations and inequalities can beused to describe situations and solve realworld problems.8.1 Solving algebraic equations Solve equations in one variable8.2 Writing linear equations Express the relationship between twoquantities as a linear equation. Use tales and graphs to representlinear equations8.3 Solving simple inequalities Use substitution to determinewhether a given number is a solutionof an inequality8.4 Real- world problems: Equations andinequalities Solve real-world problems bywriting equations Sole real-world problems by writinginequalities.CC.2.1.6.E.4 Apply andextend previousunderstandings of numbersto the system of rationalnumbers.CC.2.2.6.B.2 Understandthe process of solving aone-variable equation orinequality and apply it toreal-world andmathematical problems.CC.2.2.6.B.3 Represent andanalyze quantitativerelationships betweendependent and independentvariables.RPK:Comparingsymbols andusingvariables towritealgebraicexpressionsp. 3EquationSolutionLinear lityChapter 8pre-testMIF TextbookB p. 3-37ALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.7/3/20188
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)CC.K-12.MP.5 Reasonabstractly andquantitativelyCC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.February(9 days)Chapter 9: Thecoordinate planeBig Idea: Every point on the coordinateplane can be represented by a pair ofcoordinates.9.1 Points on the coordinate plane Name and locate points on thecoordinate plane Draw and identify polygons on thecoordinate plane9.2 Length of line segments Find lengths of horizontal andvertical line segments on thecoordinate plane. Solve real-world problems involvingcoordinates and coordinate plane9.3 Real world problems: Graphing Solve real-world problems involvingequation sand coordinate plane.CC.2.2.6.B.3 Represent andanalyze quantitativerelationships betweendependent and independentvariables.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.RPK: Plottingcoordinatesp. 39Chapter 9pre-testMIF TextbookB p. 42-71CoordinatesCoordinate planex-axisy-axisquadrantsALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecision7/3/20189
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)CC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.March(12 days)Chapter 10Big Idea: The area of a polygon can befound by dividing it into smaller shapes andthen adding the areas of those shapes.10.1 Area of a triangle Use a formula to find the area of atriangle10.2 Area of parallelograms and trapezoids Use a formula to find the area of aparallelogram, given its base andheight. Use a formula to find the area of atrapezoid, given its bases and height.10.3 Area of other polygons Divide polygons into triangles Find the area of a regular polygon bydividing it into smaller shapes.10.4 Area of composite figures Recognize that a plane figure ismade up of polygons. Solve problems involving areas ofcomposite figures.CC.2.3.6.A.1 Applyappropriate tools to sole realworld and mathematicalproblems involving area,surface area, and volume.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.RPK: Findingarea oftriangles p.75Chapter 10pre-testMIF TextbookB p. 75-117ALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.April(11 days)7/3/2018Chapter 11:Circumference andArea of a CircleBig Idea: A circle is a geometric figure thathas many useful applications in the realworld.CC.2.1.6.E.2 Identify andchoose appropriate processesto compute fluently withRPK: Adding,subtractingandCenterRadius10
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)11.1 Radius, diameter and circumference of acircle Identify parts of a circle Recognize that a circle’s diameter istwice its radius Use the formula for thecircumference of a circle Identify semicircles and quartercircles and find the distance aroundthem11.2 Area of a circle Use the formula to calculate theareas of circles, semicircles, andquadrants.11.3 Real-world problems: Circles Sole real-world problems involvingcomposite figures. Solve real-world problems involvingsemicircles, quadrants, andcomposite figures.multi-digit numbers.CC.2.3.6.A.1 Applyappropriate tools to sole realworld and mathematicalproblems involving area,surface area, and volume.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.multiplyingdecimalsp.119Chapter 11pre-testMIF TextbookB p. ALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.5 Reasonabstractly andquantitativelyCC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.April(12 days)7/3/2018Big Idea: Area is measured in square units,CC.2.3.6.A.1 ApplyNet11
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)Chapter 12: Surfacearea and volume ofsolidsand the surface area of a prism or pyramid isthe sum of the areas of its faces. Volume ismeasured in cubic units, and the volume of aprism is the area of its base timesappropriate tools to solvereal-world and mathematicalproblems involving area,surface area, and volume.RPK: Findingvolumes ofvarious solidsp.16912.1 Nets of Solids Identify the net o a prism and apyramid Identify the solid formed by a givennet.12.2 Surface area of solids Find the surface area of a prism12.3 Volume of prisms Find the volume of a prism12.4 Real-world problems: Surface andvolume Solve problems involving surfacearea and volume of prismsCC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.Chapter 12pre-testMIF TextbookB p. 169-213CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.PyramidSurface areaCross sectionALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.5 Reasonabstractly andquantitativelyCC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.May(8 days)Chapter 13:Introduction toStatisticsBig Idea: Statistics summarize data so thatinformation can be gathered from the data.13.1 Collecting and tabulating data Collect, organize, and tabulate data.7/3/2018CC.2.4.6.B.1 Demonstratean understanding ofstatistical variability byRPK:Interpretingdata on a lineplot p. 215FrequencyDot plotSkewedSymmetrical12
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF)13.2 Dot plots Display and analyze data using a dotplot13.3 Histograms Display and analyze data using ahistogramdisplaying, analyzing, andsummarizing distributions.CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.Chapter13pre-testMIF TextbookB p. 217-241RangeHistogramOutlierALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.CC.K-12.MP.5 Reasonabstractly andquantitativelyCC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.May(13 days)Chapter 14: Measureof central tendencyBig Idea: Measures of central tendency canbe used to summarize data distributions, andhelp you make decisions in real-worldproblems.14.1 Mean Find the mean of a set of data Use the mean of a set of data tosolve problems14.2 Median7/3/2018CC.K-12.MP.1 Solveproblems and persevere insolving them.CC.K-12.MP.2 Reasonabstractly andquantitatively.RPK: Dividingdecimals andfindingaverages andmeans p.243MeanMedianModeChapter 14pre-test13
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF) Find the median of a set of dataUse the median of a set of data tosolve problems.14.3Mode Find the mode of a set of data Use the mode of a set of data tosolve problems.14.4 Real-world problems: Mean, Median,and Mode Solve the problems that are related tothe concepts of mean, median, andmode, including the selection of themeasure of central tendency to beused for problems.CC.K-12.MP.3 Constructarguments and critique thereasoning of others.CC.K-12.MP.4 Model withmathematics.MIF TextbookB p. 244-279ALEKS andQuick tablesCC.K-12.MP.5 Reasonabstractly andquantitativelyCC.K-12.MP.6 Attend toprecisionCC.K-12.MP.7 Look for anduse structure.CC.K-12.MP.8 Look for andexpress regularity inrepeated reasoning.7/3/201814
Grade 6 Curriculum Map 2018-19 Key: Math in Focus Course 1 (MIF) 5 7/3/2018 CC.K-12.MP.7 Look for and use structure. Chapter 4 Test - Math in Focus November (8 days) Chapter 5: Rates Big Idea: You can use a rate to compare one quantity to another quantity, and use rates to solve problems. ratio concepts and use ratio reasoning