Transcription
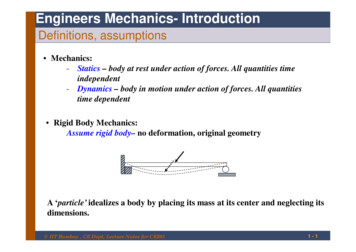
Engineers Mechanics- IntroductionDefinitions, assumptions Mechanics:- Statics – body at rest under action of forces. All quantities timeindependent- Dynamics – body in motion under action of forces. All quantitiestime dependent Rigid Body Mechanics:Assume rigid body– no deformation, original geometryA ‘particle’ idealizes a body by placing its mass at its center and neglecting itsdimensions. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011-1
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesIntroduction For a rigid body in static equilibrium, external forces and momentsare balanced and will impart no translational or rotational motionto body. Condition for static equilibrium of a body is that resultant force andresultant couple due to all external forces are zero, R 0 ; MO r F 0 Resolving into rectangular Cartesian components leads to 6 scalarequations for static equilibrium, Fx 0 Fy 0 Fz 0 Mx 0 My 0 Mz 0 IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011-2
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesFree-Body Diagram (Most Important Step)Show all forces acting on the body in a free-bodydiagram. Select entire body, isolate it from ground andfrom other bodies. Show applied external forces/moments (magn.& dir.) at their points of application (includeself weight of body). Show unknown forces/moments (with assumeddirection) at their points of application. Theseusually consist of reactions by which theground and other bodies oppose the possiblemotion of the body. Show dimensions necessary to computemoments due to forces. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011-3
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesReactions from supports and connectionsSupports and connections hold body in position (equilibrium) under actionof externally applied forcesBody exerts force on support / connection. From Newton’s third law,support / connection exerts equal and opposite reaction force on bodyThe reaction force on body opposes the motion of the body.For a 2D body, 2 translational motions and 1 rotational motion possibleFor a 3D body, 3 translational motions and 3 rotational motions possible IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011-4
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesReactions at Supports / Connections for 2-D Structure Reactions equivalent to aforce with knowndirection.In case of a guideroller, short link,collar and frictionlesspin in slot, motionopposable in bothvertical directions. Sono need to judge apriori the correctdirection, will comeout thru sign. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011-5
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesReactions at Supports / Connections for 2-D StructureHinge support opposes movement in vertical and horizontal direction Reactions equivalent to aforce of unknown directionand magnitude, which iseqvt. to two forces ofunknown magnitude.Fixed support opposes movement in vertical and horizontal directionas well as rotation Reactions equivalent to aforce of unknowndirection and magnitudeand a couple.of unknownmagnitudeFor pin or fixed support, no need to a-priori judge the correct direction (i.e., or -). It will come out thru the sign in the result. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011-6
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies2-D Equilibrium For 2-D structure in x-y plane, with appliedforces/moments in in x-y plane, followingidentically satisfiedFz 0 M x M y 0 Useful equations of equilibrium are Fx 0 Fy 0 (M z ) A 0where A is any point in plane of structure. The 3 equations can be solved for at most 3unknowns. Concept of Static Determinacy. Due to linear dependence, the 3 equations cannot be augmented with additional equations,but can be replaced F 0 (M )x IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE201z A 0 (M )z B 01-7
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesStatically Indeterminate Reactions More unknownsthan equations Fewer unknowns than Equal number unknownsand equations butequations, partiallyimproperly constrainedconstrained IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011-8
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies3-D Equilibrium For general 3-D body, six scalar equations required toexpress equilibrium. F 0 F 0 F 0 M 0 M 0 M 0xyxzyz Equations can be solved for at most 6 unknowns whichgenerally are reactions. Scalar equations conveniently obtained from vector equations ofequilibrium, F 0 MO r F 0 IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE201 1-9
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesReactions at Supports / Connections for 3-D Structure IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 10
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesReactions at Supports / Connections for 3-D Structure IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 11
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies3-D Equilibrium exampleSOLUTION: Create a free-body diagram for the sign.Signpost of uniform density weighs270 N, supported by ball-and-socketjoint at A and by two cables.Determine tension in each cable and Apply scalar or vector eqns ofreaction at A.equil. to find 5 reactions/unknons. But 6 equil eqns? IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE201 Mx 0 ?1 - 12
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesEquilibrium of Two-Force Body Applied forces only F1 and F2 . No momentsapplied. For equilibrium, moment of F2 about A must bezero. Thus line of action of F2 must pass through A. Similarly, line of action of F1 must pass through Bfor sum of moments about B to be zero. From above, and from sum of forces in anydirection being zero, we conclude that F1 and F2must have equal magnitude and opposite sense, andbe directed along line joining their points ofapplication. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 13
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesEquilibrium of Three-Force Body Forces acting at only 3 points. Assume their lines of action intersect. Moment of F1and F2 about intersection D is zero. But, for equilibrium, sum of moments of F1, F2, F3 ,about any point is zero. Thus moment of F3 about D iszero, i.e., line of action of F3 must pass through D. The lines of action of the three forces must beconcurrent. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 14
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesThree-Force Body exampleMan raises 10 kg joist, of length4 m, by pulling rope.Find tension in rope andreaction at A.Free body diagram IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 15
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesUsing Symmetry to convert 3D problems to 2D Box has 3-planes of symmetry. Loading had only one plane of symmetry Using symmetry and static equivalence, the problem can be converted into a 2Dproblem IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE201
Engineers Mechanics- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesExample: 3D problem as 2D problem IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE201
Engineers Mechanics- TrussTruss - Method of Joints Loading at joints only and joints are pins. Somember are two force members, i.e., theypossess equal and opp. forces, directed alongmember, at each end. Create FBD for each (member and) pin joint. So forces exerted by member on the pin joints atits ends are directed along member (equal andopposite to coresponding member force). Equilibrium of pins provide 2n equations for 2nunknowns for plane truss. For simple truss, 2n m r. Solve m member forces and r reactions.r 3 for a simple truss. Simple truss isstatically determinate. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 18
Engineers Mechanics- TrussSpecial cases – zero force members, etc. Only four members intersect at joint as twostr. lines, forces in colinear. mem’s equal. Only 3 mem’s intersect, two of themcolinear, force in two col. mem’s equal ifload aligned with third mem. Third mem.force equals load (including zero load). Only two members connected at unloadedjoint. Forces in mem’s equal if mem’scolinear, else zero. Recognizing these simplifies trussanalysis. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 19
Engineers Mechanics- TrussTruss - Method of Sections When forces in few members are required. To find force in BD, pass section n-n, createFBD for left side. Apply equilibrium to FBD. Only threeunknowns (exposed member forces), so cansolve for them. Choose section so that at most threeunknown member forces get exposed. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 20
Engineers Mechanics- FramesAnalysis of Frames Joints may not be only pins, loading may not be only atjoints. At least one member multiforce member.This is Rigid Frame , i.e., its internal members do notcollapse if supports are removed FBD of complete frame used to determine unknownexternal forces coming from supports or connectedbodies). This is external equilibrium analysis. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 21
Engineers Mechanics- FramesAnalysis of Frames Forces on two force members haveknown lines of action but unknownmagnitude and sense. Forces on multiforce members haveunknown magnitude and line of action.They must be represented with twounknown components. Forces between connected componentsare equal and opposite. 2 planar FBD’s give 2*3 6 equilibriumequations. We have 3 unknowns, aftersolving reactions from externalequilibrium. FBD of BE useless sincetwo force member concept used, soequilibrium identically satisfied for BE. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 22
Engineers Mechanics- FramesNon-rigid frames Some frames collapse if removed from supports.Such frames can not be treated as rigid bodies. External FBD shows 4 reaction components.Cannot be determined from 3 external equilibriumequations. Must dismember frame. Draw component FBD’s. 2 FBD’s, 2*3 6 equil. eqns., 6 unknown forces. Nothing special about this method. Can use it forrigid frames also. In previous example of rigid frame, we have 2planar FBD’s give 2*3 6 equilibrium equations.We have 6 unknowns. FBD of BE useless sincetwo force member concept used, so equilibriumidentically satisfied for BE. IIT Bombay , CE Dept, Lecture Notes for CE2011 - 23
Mechanics:-Statics - body at rest under action of forces. All quantities time independent-Dynamics - body in motion under action of forces. All quantities time dependent Engineers Mechanics- Introduction A 'particle' idealizes a body by placing its mass at its center and neglecting its dimensions. Rigid Body Mechanics: