Transcription
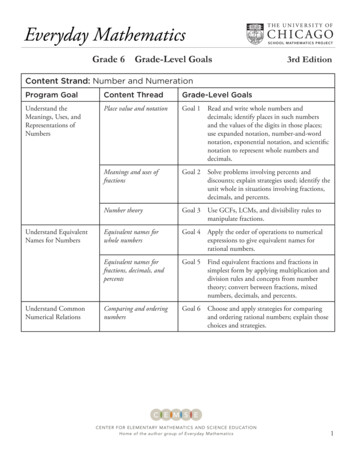
Everyday MathematicsGrade 6S C H O O L M AT H E M AT I C S P R O J E C TGrade-Level Goals3rd EditionContent Strand: Number and NumerationProgram GoalContent ThreadGrade-Level GoalsUnderstand theMeanings, Uses, andRepresentations ofNumbersPlace value and notationGoal 1 ead and write whole numbers andRdecimals; identify places in such numbersand the values of the digits in those places;use expanded notation, number-and-wordnotation, exponential notation, and scientificnotation to represent whole numbers anddecimals.Meanings and uses offractionsGoal 2S olve problems involving percents anddiscounts; explain strategies used; identify theunit whole in situations involving fractions,decimals, and percents.Number theoryGoal 3 Use GCFs, LCMs, and divisibility rules tomanipulate fractions.Equivalent names forwhole numbersGoal 4 pply the order of operations to numericalAexpressions to give equivalent names forrational numbers.Equivalent names forfractions, decimals, andpercentsGoal 5 Find equivalent fractions and fractions insimplest form by applying multiplication anddivision rules and concepts from numbertheory; convert between fractions, mixednumbers, decimals, and percents.Comparing and orderingnumbersGoal 6 hoose and apply strategies for comparingCand ordering rational numbers; explain thosechoices and strategies.Understand EquivalentNames for NumbersUnderstand CommonNumerical RelationsCENTER FOR ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCE EDUCATIONHome of the author group of Everyday Mathematics1
Everyday MathematicsGrade 6S C H O O L M AT H E M AT I C S P R O J E C TGrade-Level Goals3rd EditionContent Strand: Operations and ComputationProgram GoalContent ThreadGrade-Level GoalsComputes AccuratelyAddition and subtractionproceduresGoal 1 se mental arithmetic, paper-and-pencilUalgorithms, and calculators to solve problemsinvolving the addition and subtractionof whole numbers, decimals, and signednumbers; describe the strategies used andexplain how they work.Multiplication anddivision proceduresGoal 2 Use mental arithmetic, paper-and-pencilalgorithms, and calculators to solve problemsinvolving the multiplication and divisionof whole numbers, decimals, and signednumbers; describe the strategies used andexplain how they work.Procedures for additionand subtraction of fractionsGoal 3 se mental arithmetic, paper-and-pencilUalgorithms, and calculators to solve problemsinvolving the addition and subtraction offractions and mixed numbers; describe thestrategies used and explain how they work.Procedures formultiplication and divisionof fractionsGoal 4 se mental arithmetic, paper-and-pencilUalgorithms, and calculators to solve problemsinvolving the multiplication and division offractions and mixed numbers; describe thestrategies used and explain how they work.Computational estimationGoal 5 ake reasonable estimates for whole number,Mdecimal, fraction, and mixed numberaddition, subtraction, multiplication, anddivision problems; explain how the estimateswere obtained.Make ReasonableEstimatesCENTER FOR ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCE EDUCATIONHome of the author group of Everyday Mathematics2
Everyday MathematicsGrade 6S C H O O L M AT H E M AT I C S P R O J E C TGrade-Level Goals3rd EditionContent Strand: Operations and Computation (continued)Program GoalContent ThreadGrade-Level GoalsUnderstand Meanings ofOperationsModels for the operationsGoal 6 se ratios and scaling to model size changesUand to solve size-change problems; representratios as fractions, percents, and decimals,and using a colon; model and solve problemsinvolving part-to-whole and part-to-partratios; model rate and ratio number storieswith proportions; use and explain crossmultiplication and other strategies to solveproportions.Content Strand: Data and ChanceProgram GoalContent ThreadGrade-Level GoalsSelect and CreateAppropriate GraphicalRepresentations ofCollected or Given DataData collection andrepresentationGoal 1 ollect and organize data or use given dataCto create bar, line, circle, and stem-and-leafgraphs with reasonable titles, labels, keys, andintervals.Analyze and InterpretDataData analysisGoal 2 se the minimum, range, median, mode,Uand mean and graphs to ask and answerquestions, draw conclusions, and makepredictions; compare and contrast themedian and mean of a data set.Understand and ApplyBasic Concepts ofProbabilityQuantitative probabilityGoal 3 se the Multiplication Counting Principle,Utree diagrams, and other counting strategiesto identify all possible outcomes for asituation; predict results of experiments,test the predictions using manipulatives,and summarize the findings; comparepredictions based theoretical probability withexperimental results; calculate probabilitiesand express them as fractions, decimals, andpercents; explain how sample size affectsresults; use the results to predict futureevents.CENTER FOR ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCE EDUCATIONHome of the author group of Everyday Mathematics3
Everyday MathematicsGrade 6S C H O O L M AT H E M AT I C S P R O J E C TGrade-Level Goals3rd EditionContent Strand: Measurement and Reference FramesProgram GoalContent ThreadGrade-Level GoalsUnderstand theSystems and Processesof Measurement; UseAppropriate Techniques,Tools, Units, andFormulas in MakingMeasurementsLength, weight, and anglesGoal 1 stimate length with and without tools;Emeasure length with tools to the nearest 1/16inch and millimeter; estimate the measure ofangles with and without tools; use tools todraw angles with given measures.Area, perimeter, volume,and capacityGoal 2 hoose and use appropriate formulas toCcalculate the circumference of circles and tosolve area, perimeter, and volume problems.Use and UnderstandReference FramesCoordinate systemsGoal 3 se ordered pairs of numbers to name,Ulocate, and plot points in all four quadrantsof a coordinate grid.Content Strand: GeometryProgram GoalContent ThreadGrade-Level GoalsInvestigate Characteristicsand Properties of Twoand Three-DimensionalGeometric ShapesLines and anglesGoal 1 Identify, describe, classify, name and drawangles; determine angle measures by applyingproperties of orientations of angles and ofsums of angle measures in triangles andquadrangles.Plane and solid figuresGoal 2 Identify and describe similar and congruentfigures and describe their properties;construct a figure that is congruent toanother figure using a compass andstraightedge.Transformations andsymmetryGoal 3 Identify, describe, and sketch (includingplotting on the coordinate plane) instances ofreflections, translations, and rotations.Apply Transformationsand Symmetry inGeometric SituationsCENTER FOR ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCE EDUCATIONHome of the author group of Everyday Mathematics4
Everyday MathematicsGrade 6S C H O O L M AT H E M AT I C S P R O J E C TGrade-Level Goals3rd EditionContent Strand: Patterns, Functions, and AlgebraProgram GoalContent ThreadGrade-Level GoalsUnderstand Patterns andFunctionsPatterns and functionsGoal 1 xtend, describe, and create numericEpatterns; describe rules for patterns anduse them to solve problems; representpatterns and rules using algebraic notation;represent functions using words, algebraicnotation, tables, and graphs; translate fromone representation to another and userepresentations to solve problems involvingfunctions.Use Algebraic Notationto Represent and AnalyzeSituations and StructuresAlgebraic notation andsolving number sentencesGoal 2 etermine whether equalities and inequalitiesDare true or false; solve open number sentencesand explain the solutions; use a pan-balancemodel to solve linear equations in one or twounknowns; use trial-and-error and equivalentequation strategies to solve linear equationsin one unknown.Order of operationsGoal 3 Describe and apply the conventional order ofoperations.Properties of the arithmeticoperationsGoal 4 escribe and apply properties of arithmeticDand multiplicative and additive inverses.CENTER FOR ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCE EDUCATIONHome of the author group of Everyday Mathematics5
Grade 6 Grade-Level Goals 3rd Edition Content Strand: Operations and Computation (continued) Program Goal Content Thread Grade-Level Goals Understand Meanings of Operations Models for the operations Goal 6 Use ratios and scaling to model size changes and to solve size-change problems; represent ratios as fractions, percents, and decimals,










