Transcription
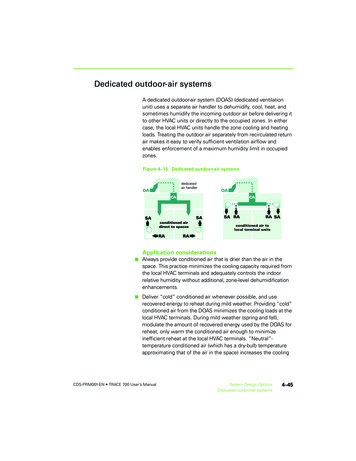
AppendixHow to Measure a Bulb DIA.DIA. DIA: The diameter of a bulb at its widest point,measured in eighths of an inch. MOLMOLLCL MOL: Maximum Overall Length from the top ofthe bulb to the bottom of the base, measuredin inches.LCL: Distance from the center of the lightsource to the bottom of the base, measured ininches.Lamp ConstructionSpecial chemicals are appliedinside lamp and on the filamentto protect against prematurefailure.HG Long life lamps utilize long,Long life lamps utilize five Ffilament supports to enhancelongevity and guard againstfilament sagging andbreakage.thick coiled filaments.C Stem type is matched to lampArgon and Nitrogen gases areused for washing and fillinglamps.Dtype to enable exact positioningof filament.B Tempered glass stem providesstrength and durability.Lamp bases made with brass Aor nickel-plated brass do notfreeze or corrode in the socket.E Fused lead - wire carrieselectricity from the base to thefilament and guards againstpotential fire hazards.Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com137
AppendixGlossary of Terms2-Tap: HID ballast that operates at two inputvoltages: 120, 277.4-Tap: HID ballast that operates at four inputvoltages: 120, 208, 240, 277.5-Tap: HID ballast that operates at five inputvoltages: 120, 208, 240, 277, 480.Accent Lighting: Directional lighting used tohighlight a particular object or area.Alternating Current (AC): Electron flow thatperiodically reverses polarity and direction of travelthrough a circuit.Ambient Lighting: The overall general lighting in anarea or room.Ambient Temperature: Refers to the temperature ofthe air around the device specified.Ampere (amp): A standard unit of measurement ofelectrical current. Amps Watts / VoltageANSI (American National Standards Institute):The organization that develops voluntary guidelinesand product performance standards for the electricaland other industries.ANSI Ballast Type: A reference to the ANSIdocument which describes the lamp and lists thecharacteristics of the ballast required to operate thelamp. For HID lamps this is a code with a letter prefixfollowed by numbers. The following naming systemis used: H – mercury lamps; M – metal halide lamps;S – high pressure sodium lamps; L – low pressuresodium lamps. ANSI codes must match for a lampand ballast to be compatible.ANSI Lamp Codes: These are 3-letter codesassigned by the American National StandardsInstitute. They provide a system of assuringmechanical and electrical interchangeability amongsimilarly coded lamps from various manufacturers.Often found in halogen lamps.138Arc Tube: A completely sealed quartz or ceramictube where an electrical arc occurs and generateslight.Argon: Inert gas used in incandescent andfluorescent lamp types. In incandescent light sources,argon retards evaporation of the filament.Auto-Transformer: A type of transformer thatelectrically connects the primary and secondary coils.This type of circuit is used to make many ballastssmaller and more efficient.Average Rated Life: An average rating, in hours,indicating when 50% of a large group of lamps havefailed, when operated at nominal lamp voltage andcurrent. Manufacturers use 3 hours per start forfluorescent lamps and 10 hours per start for HIDlamps when performing lamp life testing procedures.Every lamp type has a unique mortality curve thatdepicts its average rated life.Ballast: A device used to obtain the necessarycircuit conditions (voltage, current and waveform) forstarting and operating an electric-discharge lamp. Allfluorescent and HID light sources require a ballast forproper operation.Ballast Efficacy Factor (BEF): The ratio of aballasts’ light output to input power. Useful forcomparing the efficiency of two different ballasts on alight output to power consumption basis.BEF % Ballast Factor/Input Power (Watts)Ballast Factor (BF): The measured ability of aparticular ballast to produce light from the lamp(s) itpowers. Ballast factor is derived by dividing the lumenoutput of a particular lamp/ballast combination bythe lumen output of the same lamp(s) on a referenceballast.Ballast Kit: A kit developed to include all necessaryparts for the installation of a new ballast. For HIDballast kits this includes: ballast, capacitor, ignitor (ifused) and all necessary mounting hardware. For CFLkits this includes: ballast, mounting plate, lead wireset, wire-removal tool and mounting hardware.Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com
AppendixGlossary of TermsBallast Loss: The total power lost in the operationof the ballast measured in watts. This power is givenoff as heat energy. It is equivalent to the differencebetween the input power and the lamp wattage.Base: The base holds the lamp in place in the fixtureand conducts electricity from the circuit to the lamp. Itcan be designed to dissipate heat.Beam Angle: The angle of the cone of light emittedfrom a light source or luminaire. This is often used todescribe the light distribution of a reflectorized lamp(such as R and PAR types) or an LED replacementproduct and encompasses the central part of thebeam out to the angle where the intensity is 50%of the maximum. This is referred to in degrees. Thebeam angle (sometimes called “beam spread”) isoften part of the ordering code for reflectorized lamps.See also field angle.Beam Spread: See Beam Angle.BR Lamp: BR is a term for Bulged Reflector, andrefers to a shape of blown glass reflector lamps with a“stepped” reflector for better light extraction.Canadian Energy Standards: Note on label thatindicates that the ballast complies with the CanadianEnergy Standards and meets the requirements ofCAN/CSA-C654-M91.Canadian Standards Association (CSA): Anassociation that generates product performance andsafety standards for many Canadian industries.Candela: The measure of luminous intensity ofa source in a given direction. The term has beenretained from early lighting sciences when a standardcandle of a fixed size and composition was definedas producing one candela in every direction. A plotof intensity versus direction is called a candeladistribution curve and is often provided for directionallamps and luminaires with a lamp operating in them.Binning: A systematic process of dividing LEDsinto smaller subgroups with a similar brightness andchromaticity distributions. Halco minimizes colorvariation by utilizing binning for LEDs used in ProLEDlamps at /- 200K.Candelabra base: Small screw base for lamps, alsoknown as an E12 base.Bi-Pin – Fluorescent: A lamp design utilizing twopins on each end of a fluorescent lamp tube. This iscrucial to provide cathode heating voltage betweenthe two pins for rapid start and programmed startoperations. These lamp can also be used on instantstart ballasts that are rated to run them.Candlepower Distribution: The candlepowerat various angles from a light source show in anumerical table and in a graph known as the luminousintensity distribution curve. This data can be found inphotometric reports and is used to understand howthe light source will illuminate the area being lit.Bi-Pin – Halogen or Incandescent: A lamp designusing two pins rather than a screw in or twist lockbase to provide power to heat the filament. Most oftenused in low voltage lighting for JC halogen capsulesand MR-type lamps, there are line voltage versions.Black Body (Planckian radiator) – A theoretical idealthermal radiator whose SPD curve is defined by itstemperature in Kelvin and whose color coordinates lieexactly on the Planckian curve. Tungsten lamps (bothincandescent and halogen) are close enough to beconsidered blackbodies for the purpose of SPD.Capacitor: A device that can be used to store energyin an electric circuit. This is done via an electric fieldbetween two closely spaced conductors.Candlepower: Obsolete term for luminous intensity,see Candela.Cathode: Tungsten filaments that emit electrons in afluorescent lamp, and are often coated in an emissivematerial to assist in starting. Negatively charged freeelectrons emitted by the cathode are attracted to thepositive electrode (anode), creating an electric currentbetween the two electrodes, generating the UV that isconverted into visible light by the phosphor.Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com139
AppendixGlossary of TermsCathode Guard: Metal band encircling the cathodeof a fluorescent lamp, used to collect the evaporatingparticles from the cathode, greatly reducing endblackening.CDM: See Ceramic Discharge Metal Halide.CDMH: See Ceramic Discharge Metal Halide.Center Beam Candlepower (CBCP): Refers to theluminous intensity at the center of the beam of areflector lamp; measured in candelas.Class P: A classification for thermally protectedballasts established by Underwriters Laboratories. InClass P ballasts, internal thermal cutoff removes theinput power when the specified temperature limits areexceeded.CMH: See Ceramic Discharge Metal Halide.Coefficient of Utilization (CU): The fraction of initiallamp lumens that reach the work plane. It is a functionof luminaire efficiency, room surface reflectance, androom shape.Ceramic Discharge Metal Halide: A type of metalhalide discharge lamp that uses a translucentalumina (ceramic) material for the arc tube instead ofglass quartz. This material is stronger and has higherheat and chemical tolerances than quartz, allowinga different chemical mix to be used which resultsin better color rendering ( 80 CRI) and improvedlumen maintenance without sacrificing efficacy.Halco ceramic discharge metal halide lamps featurea 1-piece arc tube design that delivers excellentcolor consistency and lamp reliability. Also known asCeramic Metal Halide, CDM, CMH or CDMH.Coil: Windings of copper or aluminum wire aroundthe core in electromagnetic ballast that transforms thevoltage from input to output.Ceramic Metal Halide: See Ceramic DischargeMetal Halide.Color Spectrum: The visible light spectrum, rangingbetween 380 (violet) and 770 (red) nanometers in theelectromagnetic spectrum.Chip: A very small square of semi-conductingmaterial that is the active light-emitting component ofan LED. Also known as a die.Chromaticity: The aspect of color that includesconsideration of its dominant wavelength and purityand is typically described as a pair of coordinates ona color space.CIE: Commission Internationale De L’Eclairage(International Commission on Illumination):abbreviated as CIE from its French title, is anorganization devoted to international all mattersrelating to the science and art of lighting.Color Corrected: Refers to a lamp with a specialphosphor or coating to give it a color rendering profilesimilar to natural daylight.Color Rendering Index (CRI): A measurement to ratea lamp’s ability to render an object’s color on a scaleof 0-100, the higher the CRI, the more true to lifecolors appear, as they would in natural daylight.Color Temperature: The actual color of a lightsource, also referred to as Correlated ColorTemperature (CCT), measured in degrees Kelvin (K).Typical color temperature is:2700K Incandescent/Fluorescent - Warm White3000K Halogen/Fluorescent - Soft White3500K Fluorescent - White4100K Fluorescent - Cool White5000K Fluorescent - Natural White6500K Fluorescent - DaylightClass H: An operating temperature classification forelectrical components established by UnderwritersLaboratories. Allows operation up to 180 C.140Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com
AppendixGlossary of TermsCompact Fluorescent Lamp: A small, fluorescentlamp, often used as an alternative to incandescentlighting, that utilizes small diameter tubes that arebent so that they begin and end in a single base. Thelamp life is about 10 times longer than incandescentlamps and is 3-4 times more efficacious.Core and Coil Ballast: Another term for anelectromagnetic ballast.Consortium for Energy Efficiency (CEE): Anorganization that qualifies and promotes energyefficiency products including high performanceand reduced wattage linear fluorescent lamps andballasts. A growing number of utility programs acrossthe U.S. offer rebates for commercial and industrialcustomers that purchase and install CEE listed T8lamps and ballasts in new construction, replacementand retrofit projects.CoverShield: A safety coated Halco lamp that isprotected against rupture if it is dropped, struck orexperiences thermal shock. Often used for foodservice, daycare and medical facilities.Constant Current Driver: A current and voltageregulating power supply often used to power LEDs.This methodology produces more consistent colorand helps maintain the life and light of LEDs whenused in a lighting device.Constant Voltage Driver: A power supply thatprovides a constant voltage (usually DC) to a device,and is often used to power LED devices. This is morecommonly used in LED string or strip type devices.Constant Wattage Auto-Transformer (CWA):A type of HID ballast reactor that applies a constantwattage to the lamp and uses an auto-transformer tostep-up the voltage.Cool White: A term commercially used to describea color temperature of around 4100K generated bya halophosphor type fluorescent lamp. The CoolWhite(CW) designation is used most often for T12lamps but also for other fluorescent lamps usinghalophosphors and having a CRI of approximately62. These types of lamp are falling out of favor formore efficient Tri-Phosphor lamps. Cool White is alsoused to describe self-ballasted CFLs with a colortemperature of 4100K.Cove Lighting: Refers to light sources mountedabove a ledge or in a recess that distribute lightupward for ambient lighting.Crest Factor (Lamp Current Crest Factor): Theratio of the peak lamp current to RMS or averagelamp operating current. High current crest factorsare detrimental to lamp life and performance. ANSIstandard for lamp current crest factor is 1.7.CSA: Canadian Standards Association. Anassociation that generates product performance andsafety standards for many Canadian industries.cUL: Approval from Underwriters Laboratories for usein Canada.Current: A measure of the rate of flow of electricity,expressed in amperes (A).Daylight: A term used to describe a high correlatedcolor temperature light that has an appearanceroughly equal to that of midday sun, having a CCTof approximately 6500K. This type of light typicallyprovides very good contrast, but is considered tohave a “cold” and sometimes “harsh” feel.Dedicated Voltage: A ballast designed to work onone specific input voltage.Design Amperes: The approximate current that thelamp will draw at design voltage.Design Lumens: Lumen value at 40% of ratedaverage life. Also called Mean Lumens.Core: A component of an electromagnetic ballast,which is surrounded by the coil. Core is composed ofsteel laminations or a solid ferrite material.Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com141
AppendixGlossary of TermsDichroic: A type of reflector that is designed to allowinfrared waves to pass but reflect the visible spectrumof light. Often used on MR lamps, this is designed toprovide a “cooler” beam and have less direct infraredhitting the illuminated surface.Die: See Chip.Diffusion: The even redirection or spreading of lightby a lens or diffuser.Diode: Typically a semiconductor that is a twoelectrode device with an anode and a cathodethat passes current in only one direction. It may bedesigned as an electron tube.Directional Lighting: Illumination on the workplaneor on an object predominantly from a single direction.Discharge Lamp: A light source that produces lightby passing a current between electrodes through avapor or gas. Includes fluorescent and high intensitydischarge lamps.Double-Ended Lamp: Lamps that have two basesor points of electrical connection that provide extrastability in rough service applications.Down Lighting: A direct lighting unit, usually small,that aims the light downward. Can be recessed,surface mounted or suspended.Driver: A power supply that is used to power LEDs ina device. Essentially serves the same purpose as aballast, but for LEDs.Dual Connection: A CFL ballast with both sideand bottom exits for the lead wires, allowing use formultiple applications.Dual Inline Package: Also known as DIP, this is apackaging method for LEDs that the LED is locatedin a small reflector, and then totally encased in atransparent or colored plastic. The heat is dissipatedthrough the electrical pins, but is far less effective atheat dissipation than an SMD package, limiting totalpower dissipation potential and increasing lumendepreciation rates significantly.142Eco-Shield: Halco brand linear fluorescent lampsthat are TCLP compliant due to their low mercurycontent and other design features intended to preventmercury from escaping disposed of lamps.Efficacy: The measure of lumen output perunit power supplied to the product. Useful as ameasurement of how effective the light source is inconverting electrical energy to lumens of visible light.Expressed in lumens-per-watt (LPW), this measuregives more weight to the yellow region of thespectrum and less weight to the blue and red regionswhere the eye is not as sensitive (also known as thephotopic response curve).Efficiency: The efficiency of a light source issimply the fraction of electrical energy convertedto light, i.e. watts of visible light produced for eachwatt of electrical power with no concern about thewavelength where the energy is being radiated. Forexample, a 100-watt incandescent lamp converts7% of the electrical energy into light; dischargelamps convert 25% to 40% into light. The efficiencyof a luminaire or fixture is the percentage of thelamp lumens that actually comes out of the fixture.Efficiency can also refer to a ballast or driver, andrefers to the ratio of power supplied to the lamp orLED to the input power of the ballast or driver.Electrical Discharge: A gas electrically conductingand transmitting current, usually accompanied bythe emission of visible and other radiation. This is aprinciple behind many energy saving technologies.Electrode: An electrical conductor through whichcurrent enters or leaves a medium such as an arctube or gas filled lamp.Electromagnetic Ballast: A low-frequency ballastthat operates through the use of current carrying coilsassembled on a magnetic core.Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com
AppendixGlossary of TermsElectromagnetic Spectrum: A continuum of electricand magnetic radiation that can be characterizedby wavelength or frequency, encompassing a widerange of energies from infrared to visible to gammarays. Visible light encompasses a small part of theelectromagnetic spectrum in the region from about380 nanometers (violet) to 770 nanometers (red) bywavelength.Electronic Ballast: A ballast that uses semiconductorcomponents to increase the frequency of fluorescentlamp operation (typically in the 20-40 kHz range).Smaller inductive components provide the lampcurrent control. Fluorescent system efficiency isincreased due to high frequency lamp operation.Results are increased lamp efficacy, reduced ballastlosses and lighter, smaller ballasts compared toelectromagnetic ballasts. Electronic ballasts may alsobe used with HID (high intensity discharge) lamps.Electronic Component: A device or part employed inan electronic circuit to obtain some desired electronicaction.Electronic Transformer: A device for convertingelectricity from one voltage to another voltage thatis comprised of electrical components. This typeof transformer changes the frequency of power tothe lamp, and often operates at over 20kHz. Thesedevices tend to be smaller and more efficient thanmagnetic transformers but often have minimum loadratings that must be met for use. These can havecompatibility issues with other electrical devices suchas LED lamps.Elliptical Reflector: Incandescent lamp with areflector shell that is elliptically shaped. Focuseslight immediately in front of the lamp, which reducesabsorption and increases efficiency.End Blackening: Darkening around the ends of afluorescent tube caused by particles evaporating fromthe cathode and adhering to the glass. Lamps madewith cathode guards greatly reduce this occurrence.End-of-Life (EOL) Protection: Circuit in a compactfluorescent ballast that removes power supply to thelamp during abnormal lamp end-of-life. Ballast willreset when a new lamp is installed.Energy: A measure of work done by an electricalsystem over a given period of time; measured inkilowatt-hours (kWh).Energy Policy Act (EPACT): Energy legislationoriginally passed by Congress in 1992, and updatedperiodically, mandating labeling and minimum energyefficiency requirements for many commonly usedincandescent and fluorescent lamps.Energy Star : U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) andEnvironmental Protection Agency (EPA) administeredprogram that provides designation for certainproducts meeting energy efficiency and performancestandards.Energy Survey: Systematic cost comparison of anexisting system to a proposed system, accounting forelectrical, material, maintenance and labor costs.EOL Protection Circuit: For all T5 and smallerlamps, there is a circuit that monitors the operatingparameters within the ballast that, when normaloperations are exceeded, will shutdown the ballast.Etch: Markings on the glass envelope or shell of alamp designating product description, logo and/orbrand name.EMI/RFI: Electromagnetic Interference or RadioFrequency Interference. Unintentionally generatedpower during the operation of a ballast that is capableof interfering with other electrical devices operating athigh frequencies.Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com143
AppendixGlossary of TermsExclusionary Mogul Base: A variant of a mogulbase designed to prevent enclosed rated lamps frombeing used in an open rated fixture, which is alsoknown as an EX39 base. This base is only used inopen-rated metal halide lamps and has the bottomelectrical contact protruding that allows the lamp tomake contact with the recessed electrical contactwithin the exclusionary socket. The socket is pinkin color to denote the difference and help preventconfusion, as enclosed rated metal halide lamps willnot operate in this socket.Exitance: The total light that comes off of a surface.Exitance is dependent upon the illuminance on andreflectance off the surface.Extended Life (XL): Suffix for ProLume T5 and T8lamps with special cathode design and phosphorsthat provide 40,000 hours average rated life whenoperated with an instant start ballast and up-to 46,000hours when operated with a programmed start ballast.Eyeball: Fixture, usually recessed, which can berotated to point in a desired direction.Field Angle: The light distribution cone fromdirectional light sources encompassing the centralpart of the beam out to the angle where the intensityis 10% of maximum. See also Beam Angle.Filament: Wire used in incandescent lamps, usuallymade of tungsten and often coiled, that emits lightwhen heated by an electrical current.Fixture: Luminaire without lamps.Floodlight: A reflector lamp designed to produce abroad, relatively diffused beam of light.Fluorescence: The emission of electromagneticradiation light by a substance that has absorbedradiation of a different wavelength. In most cases,absorption of light of a certain wavelength inducesthe emission of light with a larger wavelength(and lower energy). Fluorescence can be eitherwide-band (emitting a wide range of wavelengthssuch as halophosphors or LED phosphors) or verynarrow (such as those used in a tri-phosphor lamp).144Fluorescent Lamp: A glass tube coated on theinside with a fluorescent substance that gives off lightwhen a stream of electrons from the cathode excitesmercury vapor in the tube.Flux: The basic measure of light flow that includesonly visible light and is weighted to match theresponse of the human eye; measured in lumens.Footcandle (fc): A unit measurement of directillumination. One footcandle is equal to one lumen persquare foot.Frequency: A measurement of the number of cyclesper second; the SI base unit is Hertz (Hz).Full Spectrum: Broad spectrum light source capableof producing colors throughout the entire range of thevisible spectrum, simulating actual sunlight.General Lighting: Uniform light throughout an area,with no special provisions for task lighting or accentlighting.Glare: An interference with visual perception causedby an uncomfortably bright light source or reflectionwithin one’s field of view.Grounded Plane: Linear fluorescent lamps mustbe within a certain distance of a grounded metalplane with a width at least the diameter of the lampor 1 inch, whichever is greater. This plane acts as astarting aid to the lamps and is important to startingoperations. The maximum distance between thebulb wall and the starting aid (grounded plane) is asfollows per ANSI C78.81-2010:Type of Fluorescent LampMaximum DistanceInch MmT5 Linear Lamps¼ (0.25)6T8 Linear Lamps¾ (0.75)19Other 500mA or less½ (0.5)13Other greater than 500mAOrders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com125
AppendixGlossary of TermsGrounding: The connection of an electricalcomponent that is a conductor to “ground” or earth sothat the electrical current can pass off to it. A ballast orpower supply with a ground input or a metal housingshould always be grounded. The grounding helpsassure safety and acceptable EMI/RFI performance.High Lumen (HL): Suffix for ProLume F32T8 lampsthat produce more light than standard lamps withoutconsuming additional power through the use ofspecial phosphors. Often used in conjunction with alow ballast factor ballast to provide energy savingswith minimal light loss.Halogen Cycle: A regenerative cycle of tungstenand halogen atoms, which prevents blackening of thelamp envelope during the life of the lamp.High Output Fluorescent (HO): Fluorescent lampsdesigned to be used with an 800 milliampere ballast.Able to operate at low temperatures (down to 0 F)and still produce high light levels.Halogen Lamp: An incandescent lamp with afilament that is surrounded by halogen gases.Halogen gases allow the filaments to be operated athigher temperatures and higher efficacies.HaloXen: A Halco product line utilizing a halogen/xenon gas mixture and specially designed filamentsthat produces a higher degree of energy efficiencythan standard incandescent and halogen lamps.The heavier xenon gas reduces filament evaporationand increases light output, while the halogengas maintains a clear glass wall and redepositsevaporated tungsten back onto the filament,extending the lamp life and allowing greater energyefficiency.Harmonic Distortion: Distortion of an AC waveformcaused by multiples of the fundamental frequency.Head: Luminaire for a track-lighting system.Hertz: A unit of frequency denoted as Hz. One Hzis equivalent to one cycle per second. Can also bemeasured in kHz, or one thousand cycles per second.High Ballast Factor: Ballast with a nominalballast factor of above 1.0, and typically ends upapproximately 1.18 for T8 lamps.High Intensity Discharge (HID) Lamp: Metal Halide,High Pressure Sodium, Low Pressure Sodium andMercury Vapor lamp types.High Power Factor: A power factor above 0.90 or90%.High Power LED: Generally defined as a packagedlight emitting diode that consumes 1W or greater.See Light Emitting Diode.High Pressure Sodium (HPS) Lamp: High intensitydischarge light sources which produce light by anelectrical discharge through sodium vapor operatingat relatively high pressures and temperatures.High Voltage: Voltages of 208 or higher.High Wattage CFLs (or Spirals): Higher powercompact fluorescent lamps (65, 85, and 105 watts arecommon power levels) which are used to replace highwattage incandescent lamps or low wattage metalhalide lamps (by removing the ballast). These lampsare found in mogul and medium base and typicallyhave a long life.HO: High Output. A lamp or ballast that operates at800mA is considered high output.Hot Restrike Time: If there is a momentary powerinterruption or the lights are turned off causing theHID lamp goes out, there will be a delay of 3 to 15minutes (depending on lamp type) before the lamphas cooled down sufficiently to start again.HX-HPF: A high reactance auto-transformer thatoperates at a high power factor. A type of circuit usedin HID ballasts.Orders and Inquiries 800.677.3334 Fax 800.880.0822 www.halcolighting.com145
AppendixGlossary of TermsHX-NPF: A high reactance auto-transformer thatoperates at a normal power factor. A type of circuitused in HID ballasts.Ignitor: An electronic device providing a high voltagepulse from 3000V to 6000V (depending on theballast) to initiate an electrical discharge in a gas filledtube. Typically, the ignitor is paired with or is a part ofthe ballast. See also starter.Illuminance: Light arriving at a surface, expressed inlumens per unit area; 1 lumen per square foot equals1 footcandle, while 1 lumen per square meter equals1 lux.Illumination: The result of the use of light.Incandescent Lamp: A light source that produceslight by the heating of a filament by an electriccurrent.Inches to Millimeters Conversion: To calculatethe metric equivalent of inches in millimeters (mm),multiply inches by 25.4.Indirect Lighting: Luminaires that distribute 90 - 100percent of their light upward to be reflected by theceiling.Induction Lighting: A means of lighting, whichuses RF induction of radio waves or microwavesto produce luminescence. Induction lamps haveno electrodes inside the chamber and generally,therefore, have longer life than standard incandescentlamps.Infrared: Radiant energy in the wavelength rangeof about 770 to 1100 nanometers (nm). Energy inthis range is not visible to the naked eye, but can besensed by the skin. Applications include heat lamps,photography, medical therapy and industry.InGaN: The main LED sem
Argon: Inert gas used in incandescent and fluorescent lamp types. In incandescent light sources, . The base holds the lamp in place in the fixture and conducts electricity from the circuit to the lamp. It . electrical components established by Underwri