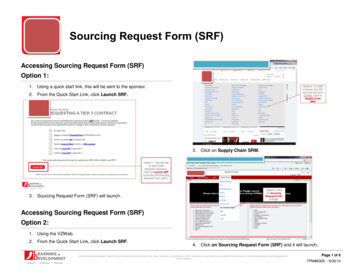
Transcription
Strategic Sourcing in theNew Economy:Harnessing Sourcing Business Models inModern ProcurementUniversity of TennesseeKate Vitasekwww.sig.org/eval
Sourcing Business Model Theoryand Decision Tree(Practitioner Deck)
Are We at the Dawn of a New Era?There is anold sayingthat the firstone to knowThanksgivingis gettingclose is theturkey3
The Sacred Cows of Procurement Porter’s FiveForces Kraljic Matrix Multi-StepSourcing Models ATK’s PurchasingChessboard4
Porter’s Five Forces - 1979 Born out of Michael Porter’s1979 best selling bookCompetitive Strategy:Techniques for AnalyzingIndustries and CompetitorsThreat ofNewEntrantsBargainingPower ofSuppliersRivalryAmongExistingCompetitorsThreat ofSubstituteProducts orServicesBargainingPower ofBuyers An organization’s barteringpower with it’s supplier isone of five key “competitiveforces” Companies should seekways to improve their powerover suppliers to gain acompetitive advantagePorter misses the power of creating highly strategiccollaborative supplier relationships.5
The Kraljic Matrix - 1983Profit ImpactHighLowLeverage ItemsStrategic ItemsGoal:Exploit powerfor leverageproductsGoal:Ensure long termavailability ofsupplyRoutine ItemsGoal:Ensure efficientprocessing fornoncriticalproductsBottleneckItemsGoal:Ensure supply andmaintain costsSupply RiskHigh Logical and easy to use way tosegment suppliers in a 2 x 2matrix Suggested three “strategies” forworking with suppliers– Leverage/exploit (preferredstrategy)– Diversify– Balance (only use if you areunable to leverage ordiversify)Kraljic misses the power of creating highly strategiccollaborative supplier relationships.6
The Achilles Heel of the Kraljic Matrix Kraljic was asked “If you hadthe chance to rewrite the 1983article with the benefit of 25years’ hindsight, would therebe anything to add? Kraljic replied, “Theimportance of trust in longterm relationships withsuppliers. You need [trust] tocreate win-win.7
Multi-Step Sourcing Processes – Beginning oSelectImplementationPathNegotiate andSelect ile successful, multi-step processes fall short Sourcing is not a destination, it is continuous process Best practice vs. best fit mentality Limited emphasis on end-to-end category managementphilosophies Failure to incorporate the concept of Sourcing BusinessModelsToday’s models miss several key concepts.8
ATK Purchasing Chessboard– 2000s4 PurchasingStrategies16 Levers64 Methods Born out of consulting firm A.T.Kearney A chessboard of 64 procurementstrategies to help organizations“win” the procurement game Three quadrants are based onasserting market power Fourth quadrant seeks jointadvantage with suppliers(occurs when buyers andsuppliers “have equal marketpower”)Sending the message to only be collaborative when youdon’t have the muscle to win outright is myopic.9
Oliver Williamson – Style Matters“Muscular buyers not onlyuse their suppliers, but theyoften ‘use up’ their suppliersand discard them.Oliver WilliamsonProfessorUC BerkeleyThe muscular approach tooutsourcing of goods andservices is myopic andinefficient.”Williamson won a Nobel Prize in Economics in 2009.10
Power Based Approaches are MyopicJeffery DyerBrigham Young University,Marriot School Studied trust in serviceprovider – automakerrelationships General Motors was theleast trusted automakerand Toyota the mosttrusted General Motors incurredsix times highertransaction costs(procurement costs) thanToyota11
Companies Are at an Inflection Point12
Transactional Models Have Inherent Weaknesses
The Conventional Approach: Make vs. BuyBuyUse“The Market”MakeCreate“CorporateHierarchy”14
A New View: A “Hybrid” ApproachBuyUse“The Market”There is awholeplaygroundin the ierarchy”15
What Game Are You Playing?Image source: /photostream/Article: utsourcing-agreement-71332152.html16
Sourcing Business Model ��SOURCING nessModelSharedServicesModelEquityPartnerships17
Systems Thinking is KeyA well designedsystem createsfeedback loopsand createsdesired results18
We Need “Rules” for Creating Each System!PerformanceManagementPricingApproachScope or WorkBusinessModelPURPOSEOFGovernance19
The Rules of the GameTransactional (Market)Investment(Hierarchy)Relational iderPerf.-Based /Managed ServicesVestedRelationshipInvestment (EquityPartner / Shared Services)EconomicModelTransaction-based (pertransaction, hour or unit)Transaction-based (pertransaction, hour or unit)Transaction-based (peractivity, hour or unit)Output-basedOutcome-basedTransactional, outputbased or outcome-basedRelationshipModelTransactional /no relationshipTransactional / suppliervetted on “Approved” listRelational contract /emerging collaborationRelational contract(collaborative)Relational contract(highly collaborative)Investment-basedVision& IntentSupply atlowest costRecurring commodities atfair or lowest costValue-added capabilitiesat best valuePerformance to SLA /process efficienciesShared Vision, DesiredOutcomes & Value CreationSustainable Value“Who” and / or “How”“Who” and / or “How”“Who” and / or “How”(jointly defined “How”)“What” and limitedemphasis on “How”“What”“What If”, “What For”and “When”BUSINESS MODELSCOPE OF WORKStatement of Work& ObjectivesPERFORMANCE MANAGEMENTPerformanceFocusSimple three-wayaccounting matchPOrequirementsActivity-basedservice level agreementsOutput-based servicelevel agreementsStrategicDesired OutcomesP&L-basedMeasuresPerformanceMeasuresRight quantity, right price,damage-freeBasic provider metrics increased quality emphasisOperational customer satisfactionOperational relational(Values & Behaviors)Ops transformational relational system-wide KPIsJoint Measuresof SuccessFixed price / typically noincentives / volume rebatesFixed price / low-noincentives / volume rebatesFixed price / low incentives /volume rebatesPrice with incentivesand / or penaltiesPricing Model with valuebased incentivesP&L-basedEquity SharingRelationshipManagementDelivery & pricing validation(3-way PO match)Some performance &pricing oversightLimited SupplierRelationship ManagementOversight emphasis:Supplier Relationship Mgmt.Insight emphasis: StrategicRelationship Mgmt.Shared control andmanagementImprove, Transform& InnovateNone /market-drivenLimited /market-drivenBeginning to focus onincremental improvementsSupplier-driven to meetSLAs / price glide pathJoint & proactiveTransformation Mgmt.Core innovationcapabilitiesExitManagementOne-way / limitedcommitment to buyOne-way / termination forcause & convenienceOne-way / termination forcause & conveniencePerf.-based termination forcause w/ safeguardsJoint ExitManagement PlanDivestitureCompliance &Special ConcernsCompliance-driven /survey-basedTypically compliance-driven/ survey-basedTypically market-based /minimum audit requirementsCorporate-basedaudit requirementsOutcome-basedjoint requirementsInvestment-basedjoint requirementsPRICINGPricing Model &IncentivesGOVERNANCE
Architecting the Right Agreement Matters!Are you buying acommodity or astrategicpartnership tocreate value?Matt McClishPurchasing Group ManagerProcter & Gamble21
“Cherry Picking” the Rules Creates Chaos Mix and matching “bestpractices” withoutunderstanding the systemimplications creates aBusiness Model mismatch Instead architect the “bestfit” solution for yoursolution using a wellstructured agreementfollowing the SourcingBusiness Model rules22
PastRelationshipChanging the GameCurrentRelationshipTransactional (Market)Relational (Hybrid)Investment roviderPerf.-Based /Managed ServicesVestedRelationshipInvestment (EquityPartner / Shared Services)EconomicModelTransaction-based (pertransaction, hour or unit)Transaction-based (pertransaction, hour or unit)Transaction-basedTransaction-asked (peractivity, hour or unit)Output-basedOutcome-basedTransactional, outputbased or outcome-basedRelationshipModelTransactional /no relationshipTransactional / suppliervetted on “Approved” listRelational contract /emerging collaborationRelational contract(collaborative)Relational contract(highly collaborative)Investment-basedVision& IntentSupply atlowest costRecurring commodities atfair or lowest costValue-added capabilitiesat best valuePerformance to SLA /process efficienciesShared Vision, DesiredOutcomes & Value CreationSustainable Value“Who” and / or “How”“Who” and / or “How”“Who” and / or “How”(jointly defined “How”)“What” and limitedemphasis on “How”“What”“What If”, “What For”and “When”BUSINESS MODELSCOPE OF WORKStatement of Work& ObjectivesPERFORMANCE MANAGEMENTPerformanceFocusSimple three-wayaccounting matchPOrequirementsActivity-basedservice level agreementsOutput-based servicelevel agreementsStrategicDesired OutcomesP&L-basedMeasuresPerformanceMeasuresRight quantity, right price,damage-freeBasic provider metrics increased quality emphasisOperational customer satisfactionOperational relational(Values & Behaviors)Ops transformational relational system-wide KPIsJoint Measuresof SuccessFixed price / typically noincentives / volume rebatesFixed price / low-noincentives / volume rebatesFixed price / low incentives /volume rebatesPrice with incentivesand / or penaltiesPricing Model with valuebased incentivesP&L-basedEquity SharingRelationshipManagementDelivery & pricing validation(3-way PO match)Some performance &pricing oversightLimited SupplierRelationship ManagementOversight emphasis:Supplier Relationship Mgmt.Insight emphasis: StrategicRelationship Mgmt.Shared control andmanagementImprove, Transform& InnovateNone /market-drivenLimited /market-drivenBeginning to focus onincremental improvementsSupplier-drivenSupplier driven to meetSLAs / price glidepathSLAs/SavingsGlidepathJoint & proactiveTransformation Mgmt.Core innovationcapabilitiesExitManagementOne-way / limitedcommitment to buyOne-way / termination forcause & convenienceOne-way / termination forcause & conveniencePerf.-based termination forcause w/ safeguardsJoint ExitManagement PlanDivestitureCompliance &Special ConcernsCompliance-driven /survey-basedTypically compliance-driven/ survey-basedTypically market-based /minimum audit requirementsCorporate-basedaudit requirementsOutcome-basedjoint requirementsInvestment-basedjoint requirementsPRICINGPricing Model &IncentivesGOVERNANCE23
The Dell StoryProfiled in Chapter 12 in the Vested Outsourcing Book24
The SIG Sourcing WheelKey to sourcing strategysuccess is to integrateSourcing BusinessModel theory intopractice as youdevelop your sourcingsolution.This can be done byusing the SIG U“Sourcing Wheel.”25
Last Words of WisdomDon’t bedinner in thedawn of anew era ofprocurement!26
HUGE THANK YOU!Thank you toJLL forsponsoringthe books.Enjoy theread!27
Contact Me with Questions!kvitasek@utk.eduwww.vestedway.com28
Evaluation How-to:Why? Your feedback drivesSIG Event content By signing andsubmitting yourevaluation, you areautomatically enteredinto a prize drawingHow?Option 1: App1. Select Schedule2. Select Schedule by Day3. Select Day4. Select Session5. Scroll to Description6. Click on the Evaluation linkOption 2: Browser1. Go to www.sig.org/eval2. Select Session (GS TH PM)COMPLETE &SUBMIT EVAL
Session #GS TH PMwww.sig.org/evalStrategic Sourcing in the New Economy: HarnessingSourcing Business Models in Modern ad the App: bit.ly/SIGCAappTweet: #SIGfall15
1979 best selling book Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing . competitive advantage Porter’s Five Forces - 1979 Porter misses the power of creating highly strategic collaborative supplier relationships. Threat of New Entrants Bargaining Power of . Strategic Sourcing in the New