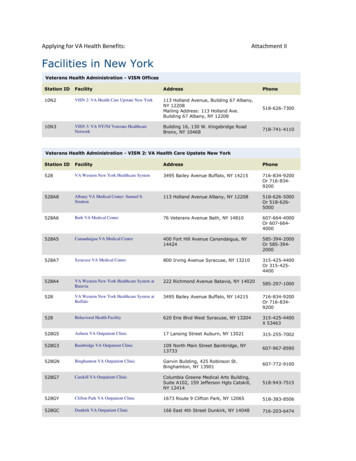
Transcription
CLEAREDFor Open PublicationDec 11, 2020Department of DefenseOFFICE OF PREPUBLICATION AND SECURITY REVIEWCAREER PATHWAYINFORMATION SYSTEMSSECURITY MANAGER (722)Developed By:The InteragencyFederal Cyber CareerPathways WorkingGroupEndorsed By:November 20201
Table of ContentsCAREER PATHWAY INFORMATION SYSTEMS SECURITY MANAGER (722) . 11722-INFORMATION SYSTEMS SECURITY MANAGER . 31.1Work Role Overview . 31.2Core Tasks. 61.3Core Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities . 91.4Core Competencies. 131.5Suggested Qualifications / Capability Indicators . 162 APPENDIX: 722-INFORMATION SYSTEMS SECURITY MANAGER TASK ANALYSIS AND KSAMAPPING .172.1Key to Reading the Task Analysis and KSA Mapping . 172.2722-Information Systems Security Manager Task Analysis and KSA Mapping . 182
1 722-INFORMATION SYSTEMS SECURITY MANAGER1.1 WORK ROLE OVERVIEWThe table below provides an overview of various role-specific elements related to 722-InformationSystems Security Manager.Disclaimer: The 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role contains tasks and knowledge,skills, and abilities that may be shared amongst Information Systems Security Officers (ISSOs) as wellas Information Systems Security Managers (ISSMs).Table 1. 722-Information Systems Security Manager Work Role OverviewNICE Role DescriptionResponsible for the cybersecurity of a program, organization, system, or enclave.Personnel performing the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role are most commonlyaligned to the following Occupational Series (Top 5 shown):OPM OccupationalSeries-2210-Information Technology – 83%0080-Security Administration – 4%1550-Computer Science – 3%0301-Miscellaneous Administration and Program – 2%0343-Management and Program Analysis – 2%Personnel performing the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role are most commonlypaired with the following complimentary Work Roles (Top 5 shown):Work Role Pairings-612-Security Control Assessor – 19%541-Vulnerability Assessment Analyst – 10%752-Cyber Policy and Strategy Planner – 10%461-Systems Security Analyst – 7%723-COMSEC Manager – 6%Personnel performing the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role may unofficially oralternatively be called:Functional TitlesDistribution of GSLevels-Common Control ProviderCybersecurity OfficerEnterprise Security OfficerInformation Assurance AnalystInformation Assurance Security ManagerInformation Assurance Security OfficerInformation Security Program ManagerInformation Systems Security Officer (ISSO)Information Systems Security SpecialistSecurity Domain SpecialistPersonnel performing the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role are most commonlyfound within the following grades on the General Schedule*.3
- GS-6 – redacted** GS-7 – redacted** GS-9 – redacted** GS-10 – redacted** GS-11 – 9% GS-12 – 25% GS-13 – 26% GS-14 – 16% GS-15 – 5%*19% of all personnel performing the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role are in nonGS pay plans and are excluded from this section.**Percentages less than 3% have been redactedThe following work roles are examples of possible roles an individual may perform prior totransitioning into the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role:On Ramps-441-Network Operations Specialist671-System Testing and Evaluation Specialist461-Systems Security Analyst511-Cyber Defense Analyst521-Cyber Defense Infrastructure Support Specialist531-Cyber Defense Incident Responder541-Vulnerability Assessment Analyst612-Security Control Assessor622-Secure Software Assessor723-Communications Security (COMSEC) Manager732-Privacy Compliance ManagerThe following work roles are examples of common transitions an individual may pursue after havingperformed the 722-Information Systems Security Manager. This is not an exhaustive list, nor does itconsider learning and development opportunities an individual may pursue to prepare themselves forperforming alternate work roles:-Off Ramps612-Security Control Assessor723-Communications Security (COMSEC) Manager*Note: Leveraging the knowledge, skills, abilities, and tasks of the 722-Information Systems SecurityManager work role, individuals may prepare themselves to transition into one or more of thefollowing cross-functional work roles:-711- Cyber Instructional Curriculum Developer712-Cyber Instructor732-Privacy Compliance Manager / Officer751-Cyber Workforce Developer and Manager752-Cyber Policy and Strategy Planner802-IT Project Manager901-Executive Cyber Leadership4
5
1.2 CORE TASKSThe table below provides a list of tasks that represent the Core, or baseline, expectations forperformance in the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role, as well as additional tasksthat those in this role may be expected to perform.Table 2. 722-Information Systems Security Manager Core TasksTask ire and manage the necessary resources, including leadership support, financialresources, and key security personnel, to support information technology (IT) security goalsand objectives and reduce overall organizational risk.Advise senior management (e.g., Chief Information Officer [CIO]) on risk levels and securityposture.Advise appropriate senior leadership or Authorizing Official of changes affecting theorganization's cybersecurity posture.Core or AdditionalCoreCoreCoreCollect and maintain data needed to meet system cybersecurity reporting.Communicate the value of information technology (IT) security throughout all levels of theorganization stakeholders.Ensure that security improvement actions are evaluated, validated, and implemented asrequired.Ensure that cybersecurity inspections, tests, and reviews are coordinated for the networkenvironment.Ensure that cybersecurity requirements are integrated into the continuity planning for thatsystem and/or organization(s).Evaluate and approve development efforts to ensure that baseline security safeguards areappropriately installed.Identify alternative information security strategies to address organizational securityobjective.Identify information technology (IT) security program implications of new technologies ortechnology upgrades.Interpret patterns of noncompliance to determine their impact on levels of risk and/or overalleffectiveness of the enterprise’s cybersecurity program.Manage the monitoring of information security data sources to maintain organizationalsituational awareness.CoreOversee the information security training and awareness program.Participate in an information security risk assessment during the Security Assessment andAuthorization process.Participate in the development or modification of the computer environment cybersecurityprogram plans and requirements.Prepare, distribute, and maintain plans, instructions, guidance, and standard operatingprocedures concerning the security of network system(s) operations.Provide system-related input on cybersecurity requirements to be included in statements ofwork and other appropriate procurement CoreCoreCoreCore6
Task 34TaskRecognize a possible security violation and take appropriate action to report the incident, asrequired.Recommend resource allocations required to securely operate and maintain an organization’scybersecurity requirements.Supervise or manage protective or corrective measures when a cybersecurity incident orvulnerability is discovered.Track audit findings and recommendations to ensure that appropriate mitigation actions aretaken.Promote awareness of security issues among management and ensure sound securityprinciples are reflected in the organization's vision and goals.Oversee policy standards and implementation strategies to ensure procedures and guidelinescomply with cybersecurity policies.Identify security requirements specific to an information technology (IT) system in all phasesof the system life cycle.Ensure that plans of actions and milestones or remediation plans are in place forvulnerabilities identified during risk assessments, audits, inspections, etc.Assure successful implementation and functionality of security requirements and appropriateinformation technology (IT) policies and procedures that are consistent with the organization'smission and goals.Support necessary compliance activities (e.g., ensure that system security configurationguidelines are followed, compliance monitoring occurs).Continuously validate the organization laws to ensure compliance.Acquire necessary resources, including financial resources, to conduct an effective enterprisecontinuity of operations program.Advise senior management (e.g., CIO) on cost/benefit analysis of information securityprograms, policies, processes, systems, and elements.Collaborate with stakeholders to establish the enterprise continuity of operations program,strategy, and mission assurance.Ensure that protection and detection capabilities are acquired or developed using the ISsecurity engineering approach and are consistent with organization-level cybersecurityarchitecture.Establish overall enterprise information security architecture (EISA) with the organization’soverall security strategy.Evaluate cost/benefit, economic, and risk analysis in decision-making process.Interface with external organizations (e.g., public affairs, law enforcement, Command orComponent Inspector General) to ensure appropriate and accurate dissemination of incidentand other Computer Network Defense information.Interpret and/or approve security requirements relative to the capabilities of new informationtechnologies.Lead and align information technology (IT) security priorities with the security strategy.Core or onalAdditionalAdditionalAdditionalAdditional7
Task 55T0256T0276T0277T0281T0282TaskLead and oversee information security budget, staffing, and contracting.Manage the publishing of Computer Network Defense guidance (e.g., TCNOs, Concept ofOperations, Net Analyst Reports, NTSM, MTOs) for the enterprise constituency.Manage threat or target analysis of cyber defense information and production of threatinformation within the enterprise.Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the enterprise's cybersecurity safeguards to ensurethat they provide the intended level of protection.Provide enterprise cybersecurity and supply chain risk management guidance fordevelopment of the Continuity of Operations Plans.Provide leadership and direction to information technology (IT) personnel by ensuring thatcybersecurity awareness, basics, literacy, and training are provided to operations personnelcommensurate with their responsibilities.Provide technical documents, incident reports, findings from computer examinations,summaries, and other situational awareness information to higher headquarters.Recommend policy and coordinate review and approval.Use federal and organization-specific published documents to manage operations of theircomputing environment system(s).Participate in Risk Governance process to provide security risks, mitigations, and input onother technical risk.Evaluate the effectiveness of procurement function in addressing information securityrequirements and supply chain risks through procurement activities and recommendimprovements.Participate in the acquisition process as necessary, following appropriate supply chain riskmanagement practices.Ensure that all acquisitions, procurements, and outsourcing efforts address informationsecurity requirements consistent with organization goals.Forecast ongoing service demands and ensure that security assumptions are reviewed asnecessary.Define and/or implement policies and procedures to ensure protection of criticalinfrastructure as appropriate.Core or Additional8
1.3 CORE KNOWLEDGE, SKILLS, AND ABILITIESThe table below provides a ranking of KSAs that represent the Core, or baseline, expectations forperformance in the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role, as well as additional KSAs thatthose in this role may be expected to demonstrate.Table 3. 722-Information Systems Security Manager Core Knowledge, Skills, and nowledge of data backup and recovery.Knowledge of business continuity and disaster recovery continuity ofoperations plans.Knowledge of intrusion detection methodologies and techniques fordetecting host and network-based intrusions.Knowledge of controls related to the use, processing, storage, andtransmission of data.Knowledge of encryption algorithmsKnowledge of the organization’s enterprise information technology (IT)goals and objectives.Knowledge of network security architecture concepts includingtopology, protocols, components, and principles (e.g., application ofdefense-in-depth).Knowledge of measures or indicators of system performance andavailability.Knowledge of applicable laws, statutes (e.g., in Titles 10, 18, 32, 50 inU.S. Code), Presidential Directives, executive branch guidelines, and/oradministrative/criminal legal guidelines and procedures.Business ContinuityBusiness ContinuityImportance toWork RoleFoundational toAll Work RolesFoundational toAll Work RolesFoundational toAll Work RolesFoundational toAll Work RolesFoundational toAll Work RolesCoreCoreComputer Network DefenseCoreDatabase AdministrationCoreEncryptionEnterprise ArchitectureCoreCoreInformationSystems/Network SecurityCoreInformation TechnologyAssessmentLegal, Government, andJurisprudenceCoreKnowledge of laws, policies, procedures, or governance relevant tocybersecurity for critical infrastructures.Knowledge of network traffic analysis methods.Knowledge of network systems management principles, models,methods (e.g., end-to-end systems performance monitoring), andtools.Legal, Government, andJurisprudenceNetwork ManagementNetwork ManagementCoreDescriptionCompetencyKnowledge of cybersecurity and privacy principles.InformationSystems/Network SecurityInfrastructure DesignKnowledge of computer networking concepts and protocols, andnetwork security methodologies.Knowledge of laws, regulations, policies, and ethics as they relate tocybersecurity and privacy.Knowledge of risk management processes (e.g., methods for assessingand mitigating risk).Knowledge of specific operational impacts of cybersecurity lapses.Legal, Government, andJurisprudenceRisk ManagementVulnerabilities AssessmentCoreCoreCore9
K0199DescriptionCompetencyKnowledge of server and client operating systems.Skill in creating policies that reflect system security objectives.Operating SystemsPolicy ManagementImportance toWork RoleCoreCoreKnowledge of information technology (IT) supply chain security andsupply chain risk management policies, requirements, and procedures.Knowledge of new and emerging information technology (IT) andcybersecurity technologies.Knowledge of current and emerging threats/threat vectors.Knowledge of vulnerability information dissemination sources (e.g.,alerts, advisories, errata, and bulletins).Knowledge of system and application security threats andvulnerabilities (e.g., buffer overflow, mobile code, cross-site scripting,Procedural Language/Structured Query Language [PL/SQL] andinjections, race conditions, covert channel, replay, return-orientedattacks, malicious code).Knowledge of what constitutes a network attack and a networkattack’s relationship to both threats and vulnerabilities.Knowledge of penetration testing principles, tools, and techniques.Risk ManagementCoreTechnology AwarenessCoreThreat AnalysisVulnerabilities AssessmentCoreCoreVulnerabilities AssessmentCoreVulnerabilities AssessmentCoreVulnerabilities AssessmentCoreEnterprise ArchitectureAdditionalIncident ManagementIncident ManagementAdditionalAdditionalInformation AssuranceAdditionalInformation AssuranceAdditionalInformationSystems/Network SecurityInformation TechnologyAssessmentAdditionalInformation TechnologyAssessmentAdditionalKnowledge of security architecture concepts and enterprisearchitecture reference models (e.g., Zachman, Federal EnterpriseArchitecture [FEA]).K0042 Knowledge of incident response and handling methodologies.K0150 Knowledge of enterprise incident response program, roles, andresponsibilities.K0038 Knowledge of cybersecurity and privacy principles used to manage risksrelated to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of informationor data.K0054 Knowledge of current industry methods for evaluating, implementing,and disseminating information technology (IT) security assessment,monitoring, detection, and remediation tools and procedures utilizingstandards-based concepts and capabilities.K0033 Knowledge of host/network access control mechanisms (e.g., accesscontrol list, capabilities lists).S0027 Skill in determining how a security system should work (including itsresilience and dependability capabilities) and how changes inconditions, operations, or the environment will affect these outcomes.A0170 Ability to identify critical infrastructure systems with informationcommunication technology that were designed without system securityconsiderations.Additional10
KSAIDK0061DescriptionCompetencyInfrastructure DesignInfrastructure DesignAdditionalInfrastructure DesignAdditionalProject ManagementProject ManagementAdditionalAdditionalRequirements AnalysisAdditionalRisk ManagementRisk ManagementAdditionalAdditionalSystem AdministrationAdditionalSystems IntegrationAdditionalSystems IntegrationAdditionalSystems IntegrationAdditionalK0092Knowledge of how traffic flows across the network (e.g., TransmissionControl Protocol [TCP] and Internet Protocol [IP], Open SystemInterconnection Model [OSI], Information Technology InfrastructureLibrary, current version [ITIL]).Knowledge of critical infrastructure systems with informationcommunication technology that were designed without system securityconsiderations.Knowledge of network protocols such as TCP/IP, Dynamic HostConfiguration, Domain Name System (DNS), and directory services.Knowledge of resource management principles and techniques.Knowledge of information security program management and projectmanagement principles and techniques.Knowledge of applicable business processes and operations ofcustomer organizations.Knowledge of Risk Management Framework (RMF) requirements.Knowledge of organization's risk tolerance and/or risk managementapproach.Knowledge of system administration, network, and operating systemhardening techniques.Knowledge of server administration and systems engineering theories,concepts, and methods.Knowledge of system software and organizational design standards,policies, and authorized approaches (e.g., International Organizationfor Standardization [ISO] guidelines) relating to system design.Knowledge of system life cycle management principles, includingsoftware security and usability.Knowledge of technology integration processes.Importance toWork RoleAdditionalSystems IntegrationAdditionalS0086Skill in evaluating the trustworthiness of the supplier and/or product.Third s AssessmentVulnerabilities AssessmentAdditionalComputer Network owledge of cyber threats and vulnerabilities.Knowledge of Application Security Risks (e.g. Open Web ApplicationSecurity Project Top 10 list)A0128 Ability to apply techniques for detecting host and network-basedintrusions using intrusion detection technologies.K0126 Knowledge of Supply Chain Risk Management Practices (NIST SP 800161)K0163 Knowledge of critical information technology (IT) procurementrequirements.AdditionalAdditional11
KSADescriptionIDA0161 Ability to integrate information security requirements into theacquisition process; using applicable baseline security controls as oneof the sources for security requirements; ensuring a robust softwarequality control process; and establishing multiple sources (e.g., deliveryroutes, for critical system elements).K0043 Knowledge of industry-standard and organizationally accepted analysisprinciples and methods.K0260 Knowledge of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) data securitystandards.K0261 Knowledge of Payment Card Industry (PCI) data security standards.K0262K0287Knowledge of Personal Health Information (PHI) data securitystandards.Knowledge of an organization's information classification program andprocedures for information compromise.Contracting/ProcurementImportance toWork RoleAdditionalData AnalysisAdditionalData Privacy and ProtectionAdditionalData Privacy and ProtectionAdditionalData Privacy and ProtectionAdditionalInformation ManagementAdditionalCompetency12
1.4 CORE COMPETENCIESThe table below is a compilation of competencies aligned to the 722-Information Systems SecurityManager work role, and their associated importance. Listed competencies are collections of three ormore similar Knowledge, Skills, or Abilities aligned to the Work Role. These competencies originate fromthe NICE Framework Competency Pivot Tool.Table 4. 722-Information Systems Security Manager Core k Role Related KSAs-Contracting /ProcurementData Privacy andProtectionC010KSAs that relate to the varioustypes of contracts, techniquesfor contracting orprocurement, and contractnegotiation andadministration.C014KSAs that relate to therelationship between thecollection and disseminationof data, technology, the publicexpectation of privacy, legaland political issuessurrounding them---InformationTechnologyAssessmentC025KSAs that relate to theprinciples, methods, and tools(for example, surveys, systemperformance measures) toassess the effectiveness andpracticality of informationtechnology systems.---LegalGovernment andJurisprudenceC030KSAs that relate to laws,regulations, policies, andethics that can impactorganizational activities.--ImportanceKnowledge of Supply Chain Risk ManagementPractices (NIST SP 800-161)Knowledge of critical information technology (IT)procurement requirements.Ability to integrate information security requirementsinto the acquisition process; using applicable baselinesecurity controls as one of the sources for securityrequirements; ensuring a robust software qualitycontrol process; and establishing multiple sources(e.g., delivery routes, for critical system elements).CoreKnowledge of Personally Identifiable Information (PII)data security standards.Knowledge of Payment Card Industry (PCI) datasecurity standards.Knowledge of Personal Health Information (PHI) datasecurity standards.CoreKnowledge of measures or indicators of systemperformance and availability.Skill in determining how a security system shouldwork (including its resilience and dependabilitycapabilities) and how changes in conditions,operations, or the environment will affect theseoutcomes.Ability to identify critical infrastructure systems withinformation communication technology that weredesigned without system security considerations.Knowledge of laws, regulations, policies, and ethicsas they relate to cybersecurity and privacy.Knowledge of applicable laws, statutes (e.g., in Titles10, 18, 32, 50 in U.S. Code), Presidential Directives,executive branch guidelines, and/oradministrative/criminal legal guidelines andprocedures.Knowledge of laws, policies, procedures, orgovernance relevant to cybersecurity for criticalinfrastructures.CoreCore13
TechnicalCompetencyCompIDDefinitionWork Role Related KSAs-RiskManagementC044KSAs that relate to themethods and tools used forrisk assessment andmitigation of risk.--SystemsIntegrationC049KSAs that relate to theprinciples, methods, andprocedures for installing,integrating, and optimizinginformation SAs that relate to theprinciples, methods, and toolsfor assessing vulnerabilitiesand developing orrecommending appropriatemitigation countermeasures.---ImportanceKnowledge of risk management processes (e.g.,methods for assessing and mitigating risk).Knowledge of Risk Management Framework (RMF)requirements.Knowledge of organization's risk tolerance and/orrisk management approach.Knowledge of information technology (IT) supplychain security and supply chain risk managementpolicies, requirements, and procedures.Knowledge of server administration and systemsengineering theories, concepts, and methods.Knowledge of system software and organizationaldesign standards, policies, and authorizedapproaches (e.g., International Organization forStandardization [ISO] guidelines) relating to systemdesign.Knowledge of system life cycle managementprinciples, including software security and usability.Knowledge of technology integration processes.Knowledge of cyber threats and vulnerabilities.Knowledge of specific operational impacts ofcybersecurity lapses.Knowledge of vulnerability information disseminationsources (e.g., alerts, advisories, errata, and bulletins).Knowledge of system and application security threatsand vulnerabilities (e.g., buffer overflow, mobilecode, cross-site scripting, ProceduralLanguage/Structured Query Language [PL/SQL] andinjections, race conditions, covert channel, replay,return-oriented attacks, malicious code).Knowledge of what constitutes a network attack anda network attack’s relationship to both threats andvulnerabilities.Knowledge of penetration testing principles, tools,and techniques.Knowledge of Application Security Risks (e.g. OpenWeb Application Security Project Top 10 list)CoreCoreCore14
Systems /NetworkSecurityCompIDDefinitionC026KSAs that relate to thearchitecture and typology ofsoftware, hardware, andnetworks, including LANS,WANS, andtelecommunications systems,their components andassociated protocols andstandards, and how theyoperate and integrate withone another and withassociated controllingsoftware.C024KSAs that relate to themethods, tools, andprocedures, includingdevelopment of informationsecurity plans to preventinformation systemsvulnerabilities and to provideor restore security ofinformation systems andnetwork services.Work Role Related KSAs-----ImportanceKnowledge of computer networking concepts andprotocols, and network security methodologies.Knowledge of how traffic flows across the network(e.g., Transmission Control Protocol [TCP] andInternet Protocol [IP], Open System InterconnectionModel [OSI], Information Technology InfrastructureLibrary, current version [ITIL]).Knowledge of critical infrastructure systems withinformation communication technology that weredesigned without system security considerations.Knowledge of network protocols such as TCP/IP,Dynamic Host Configuration, Domain Name System(DNS), and directory services.AdditionalKnowledge of cybersecurity and privacy principles.Knowledge of host/network access controlmechanisms (e.g., access control list, capabilitieslists).Knowledge of network security architecture conceptsincluding topology, protocols, components, andprinciples (e.g., application of defense-in-depth).Additional15
1.5 SUGGESTED QUALIFICATIONS / CAPABILITY INDICATORSTable 5. 722-Information Systems Security Manager Suggested Qualifications / Capability IndicatorsFor indicators of capability for the 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role, please seeDraft NISTR 8193 - National Initiative for Cybersecurity Education (NICE) Framework Work RoleCapability Indicators.Section to be populated with updated DoD-8140 Qualification Matrix for 722-Information SystemsSecurity Manager.16
2 APPENDIX: 722-INFORMATION SYSTEMS SECURITYMANAGER TASK ANALYSIS AND KSA MAPPING2.1 KEY TO READING THE TASK ANALYSIS AND KSA MAPPINGTable 6. Key to Reading the Task Analysis and KSA MappingProficiencyAs WrittenEntryIntermediateAdvancedTask StatementTask as written within the NICE Cybersecurity Workforce Framework (NICE Framework).ImportanceOverall Importance to WorkRoleExample behavioral indicator / task permutation for performing this task at an Entry skills proficiency level.Example behavioral indicator / task permutation for performing this task at an Intermediate skills proficiency level.Example behavioral indicator / task permutation for performing this task at an Advanced skills proficiency level.Table 7. Primary Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities Required to Perform the above TaskKSA IDDescriptionCompetencyID of K, S, or AKnowledge, Skil
Disclaimer: The 722-Information Systems Security Manager work role contains tasks and knowledge, skills, and abilities that may be shared amongst Information Systems Security Officers (ISSOs) as well as Information Systems Security Managers (ISSMs). Table 1. 722-Information Sys