Transcription
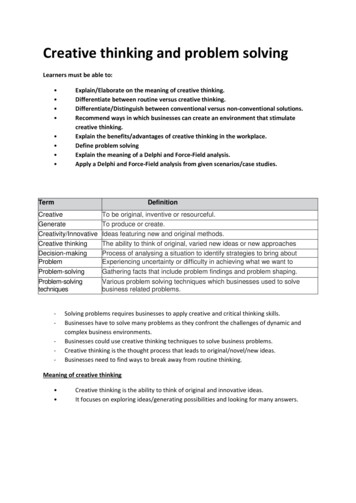
Creative thinking and problem solvingLearners must be able to: Explain/Elaborate on the meaning of creative thinking.Differentiate between routine versus creative thinking.Differentiate/Distinguish between conventional versus non-conventional solutions.Recommend ways in which businesses can create an environment that stimulatecreative thinking.Explain the benefits/advantages of creative thinking in the workplace.Define problem solvingExplain the meaning of a Delphi and Force-Field analysis.Apply a Delphi and Force-Field analysis from given scenarios/case nnovativeCreative thinkingDecision-makingProblemProblem-solvingTo be original, inventive or resourceful.To produce or create.Ideas featuring new and original methods.The ability to think of original, varied new ideas or new approachesProcess of analysing a situation to identify strategies to bring aboutchange.Experiencing uncertainty or difficulty in achieving what we want toachieve.Gathering facts that include problem findings and problem shaping.Problem-solvingtechniquesVarious problem solving techniques which businesses used to solvebusiness related problems.-Solving problems requires businesses to apply creative and critical thinking skills.Businesses have to solve many problems as they confront the challenges of dynamic andcomplex business environments.Businesses could use creative thinking techniques to solve business problems.Creative thinking is the thought process that leads to original/novel/new ideas.Businesses need to find ways to break away from routine thinking.Meaning of creative thinking Creative thinking is the ability to think of original and innovative ideas.It focuses on exploring ideas/generating possibilities and looking for many answers.
Differentiate between routine thinking and creative thinkingROUTINE THINKINGCREATIVE THINKING- Doing the same thing and expectingdifferent results.- The process used to come up withnew ideas to solve problems.- Using past decisions as a guidanceto solve current problems.- Exploring new and different ways todo things to obtain better results.Ways in which a business can create an environment that stimulates/promote creative thinking Encourage alternative ways of working/doing things.Encourage staff to come up with new ideas/opinions/solutions.Respond enthusiastically to all ideas and never let anyone feel less important.Place suggestion boxes around the workplace and keep communication channels openfor new ideasEmphasise the importance of creative thinking to ensure that all staff know thatmanagement want to hear their ideas.Make time for brainstorming sessions to generate new ideas, e.g. regular workshops/generate more ideas/build on one another's ideas.Train staff in innovative techniques/creative problem solving skills/mind-mapping/lateral thinking.Encourage job swops within the organisation/studying how other businesses are doingthings.Advantages/Benefits of creative thinking in the workplace Better/Unique/Unconventional ideas/solutions are generated.Complex business problems may be solved.Improves motivation amongst staff members.Management/employees may keep up with fast changing technology.Creativity may lead to new inventions which improves the general standard of living.May give the business a competitive advantage if unusual/unique solutions/ideas/strategies are implemented.Productivity increases as management/employees may quickly generate multiple ideaswhich utilises time and money more effectively.Managers/Employees have more confidence as they can live up to their full potential.Managers will be better leaders as they will be able to handle/manage change(s)positively and creatively.Managers/Employees can develop a completely new outlook, which may be applied toany task(s) they may do.Leads to more positive attitudes as managers/employees feel that they have contributedtowards problem solving.
Managers/Employees have a feeling of great accomplishment and they will notresist/obstruct the process once they solved a problem/contributed towards the successof the business.Stimulates initiative from employees/managers, as they are continuously pushed out oftheir comfort zone.PROBLEM SOLVINGMeaning of problem solving It is the process of analysing a situation to identify strategies that can be used to changethe situation. Problem solving requires creative thinking.Problem solving is a mental process that involves problem finding, which is the ability toidentify the problem.It also involves problem shaping, which is the ability to break-down the problem in sucha way that a clear solution can be found.Problem solving steps Identify the problem. Define the problem. Identify possible solutions to the problem. Select the most appropriate alternative. Develop an action plan. Implement the suggested solution/action plan. Monitor the implementation of the solution/action plan. Evaluate the implemented solution. Formulate strategy Implement strategy Evaluate strategyApplication/Discussion of problem solving stepsIdentify the problem Acknowledge that there is a problem Identify the exact problem Break down the problem into smaller parts that are easier solve separately
Define the problem Name the problem by stating exactly what the problem is. Find different ways of defining the problem. Define the possible causes of the problem The nature of the problem must be precise. Gather as much information as possible to establish the cause of the problem.Identify alternative solutions Identify all different possible solutions Use creative thinking strategies to generate a wide range of solutions Focus on generating as many ways as possible through using creative thinking. Collect as many ideas as possible and find the best idea/decide on one strategy to follow.Evaluate alternative solutions Use critical evaluation and analytical skills to evaluate each solution. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative solution.Choose the best solution Set criteria for the best solution, in terms of aspects such as time/cost/risk involved Identify which solution will be used The best solution should match the size and the resources of the business. If the solution is not appropriate, the business should go back to defining the problem.Formulate/Develop an action plan/strategy Arrange the necessary resources and delegate tasks. Establish a time line for implementation and set deadlines
Implement the action plan Carry out the planned actions/solution. Communicate delegated tasks/deadlines to employees.Evaluate the solution/action plan Assess whether the problem has been solved partially or entirely Monitor/test the solution/action plan/strategy continuously. If problems emerge, they must recognise and re-formulate the problem for improvedsolutions in the future.Problem solving techniques Delphi technique Force field analysisNOTE: You only need to focus on the above mentioned problem solving techniquesApplication of the problem solving techniquesApplication of the Delphi technique Businesses must invite a panel of experts to research the complaints from customers.Experts do not have to be in one place and will be contacted individually.Design a questionnaire consisting of questions on how to improve the quality of theirproducts and distribute it to the panel members/experts.Request the panel to individually respond to the questionnaire/suggest improve-mentsto the products and return it to the businessSummarise the responses from the experts in a feedback report.Send the feedback report and a second set of questions/questionnaire based on thefeedback report to the panel members.Request panel members to provide further input/ideas on how to improve the quality ofproducts after they have studied the results/documentation.Distribute a third questionnaire based on previous feedback from the second round.Prepare a final summary/feedback report with all the methods to improve the quality ofthe business’s productsThe business should choose the best solution/proposal after reaching consensus.
Impact of Delphi techniquePositives/Advantages Businesses may use a group of experts without bringing them together.The experts will give the business clear ideas/solutions on how to improve onproductivity/profitability.Information received from experts can be used to solve complex business problems.Experts may give honest/credible opinions as they do not have a direct/personal interest inthe business.Conflict may be avoided especially if all employees are knowledgeable and well qualified.Dominating employees may not take over the process as they do not form part of theproblem solving process.It reduces noise levels in an office environment since there is no group discussion.Negatives/Disadvantages It is an expensive technique to use due to high administrative costs.May be time consuming/complicated to analyse data received from experts.Not all experts are willing/interested to give feedback/complete questionnaires.Some experts might not have an in-depth knowledge of certain topics.Experts' suggestions may not be considered by some employees so consensus may notbe reached.Application of Force-Field Analysis Describe the current situation/problem and the desired situation.List all driving/pros and restraining/cons forces that will support and resist change.Allocate a score to each force using a numerical scale, where 1 is weak and 5 is strong.Weigh up the positives and negatives then decide if the project is viable.Choose the force with the highest score as the solution.If the project is viable, find ways to increase the forces for change.Identify priorities and develop an action plan.Impact of the Force-Field AnalysisPositives/Advantages It provides a visual summary of all the various factors supporting and opposing aparticular ideaEmployees feel included and understood.Employees develop and grow with the business.Informed decisions can be made as forces for and against are critically evaluated.
Enables businesses to strengthen the driving forces and weaken the restraining forces.Businesses are able to have an idea of the timeline required and the requirements ofadditional resources.Negatives/Disadvantages It is time consuming since the business must stabilise before more changes can be made.Requires the participation of all business unitsThe analysis developed is entirely dependent upon the skill level and knowledge of thegroup working on the analysis.DECISION MAKINGPROBLEM SOLVING-It is often done by one person/a member ofsenior management who makes it authoritarian.-Problems can be solved by a group/ teamor an individual team member.-Various alternatives are considered beforedeciding on the best one.-Alternative solutions are generated/identified and critically evaluated.-It is part of the problem solving cycle asdecisions need to be taken in each step.-Process of analysing a situation to identifystrategies to bring about change.
MARKETINGLearners must be able to: Define marketing. Briefly explain the role of marketing. Outline/Mention/Discuss/Explain the following marketing activities:oStandardisation and gradingoStorageoTransportoFinancingoRisk-bearing andoBuying & selling Identify the above mentioned marketing activities from given scenarios/case studies/statements.PRODUCT POLICY Outline/Mention/ Explain /Discuss the product policy with specific reference to types of product, productdevelopment, trademarks and packaging. Outline/Mention/Discuss categories of consumer goods/products. Explain/Discuss the importance of product development Outline/Mention/Discuss/Explain the steps/stages of product design. Mention/Explain/Discuss the purpose of packaging Outline/Mention/Discuss/Describe/Classify types/kindsof packaging. Elaborate on the meaning of trademarks Discuss/Explain/Describe the importance of trademarks to businesses and consumers. Outline/Mention/Explain the requirements of a good trade mark.PRICING POLICY Define/Explain the meaning of price
Discuss/Explain the importance of pricing. Outline/Mention/Explain/Discuss the following pricing techniques e.g.: oCost-based/orientated pricingoMark-up pricingoCustomer/target based pricingoCompetition based/orientation pricingoPromotional pricingoPenetration pricingoPsychological pricingoBait pricingoSkimming pricesIdentify the above mentioned pricing techniques from given scenarios/statements. Quote from thescenario to support your answer. Outline/Mention/Explain/Discuss factors that influence pricing. Identify the these factors from given scenarios/statements. Quote from the scenario to support your answer.DISTRIBUTION POLICY Define/Explain the meaning of distribution. Outline/Discuss/Explain the channels of distribution. Differentiate/Distinguish between direct and indirect channel of distribution. Explain the meaning of intermediaries Outline/Mention different types of intermediaries. Explain the role of intermediaries in the distribution process. Draw the channel of distribution. Briefly explain the reasons why manufactures may prefer to make use of direct or indirect distributionmethods.
COMMUNICATION POLICY Define/Explain the meaning of a marketing communication policy. Outline/Mention/Explain/Discuss/Describe the following components of the marketing communicationpolicy:oSales promotionoAdvertisingoPublicity andoPersonal selling Explain the purpose of sales promotion and give practical examples. Explain the purpose of advertising and give examples of advertising medium. Elaborate on the meaning of publicity. Explain the role of the public relations in publicity. Give examples of publicity e.g. press release to the media. Explain the meaning of personal selling Justify the effectiveness of personal selling in promoting a business product.ELECTRONIC MARKETING Define electronic marketing and give examples. Identify methods of electronic marketing from given scenarios/case studies/cartoons/pictures etc. Explain/Discuss the impact (advantages and disadvantages)of electronic marketing. Compare the marketing mix of the formal sector with the formal sector e.g. the product of the informalsector usually does not have a logo or trade mark as compared to the formal sector.FOREIGN MARKETING Define foreign marketing Outline/Mention/Explain/Discuss restrictions and regulations that control foreign marketing e.g.:oTariffs trade agreementoExport subsidiesoProtection policies etc.
Suggest ways in which South African businesses can enter into a foreign market e.g. exports, licensing,joint ventures, direct investments etc.MARKETINGDefinition of marketing Marketing is used to deliver value to the customers and satisfying their needs. The aim is to link the business products and services with the customer needs andwants. Marketing also aims to get the right product or service to the right customer at theright place and at the right time. Businesses also establish a target market or maintain market share of a currentproduct and locate the most appropriate customers through marketing activities Role of the marketing function Support the overall objectives of a business, which is to maximise profits The marketing team needs to work closely with staff members from other businessfunctions. Gather information about customer needs, preferences and buying behaviour andshare information with other departments. Assist the development of the marketing strategy in collaboration with seniormanagement from other business functions. Develop a marketing plan using elements of the marketing mix. Develop sales forecasts and projections and provide this information to other businessfunctions. Decide which products or services the business will sell and how the products will bedistributed. Determine what prices (cash or credit) they are going to sell. Marketing activities1. Marketing research A business needs to have a target market in mind when it starts the business or developa new product.The business can identify the consumers through research and gain information on:The size of the marketConsumer IncomeConsumer willingness to spend moneyAge and culture
Location of existing and potential customers.2. Standardisation and Grading Standardisation means producing identical goods that meet specific standards.The South African Bureau of Standarsd (SABS) seal of approval ensures productsconform to a specific standard or quality.Grading means calssing products according to their characteristics of such as size andweight. It usually refers to agricultural products.3. Storage Storage means keeping goods safe and protected until consumers need them.Goods are stored to prevent them from spoilage and to balance demand and supply.Fruit grown in winter can be available all year due to cold storage.4. Transport There are five different forms of transport: rail, water, road, pipeline and air.Factors that will influence the form of transport include the following: Cost- The form of transport must be affordable.Type of product- Heavy or bulky products would need rail or road transport or evenwater transport. Products that are expensive, light or breakable might need airtransport.Travel Time- air transport is very fast, water transport is much slower.5. Financing Financing can be provided by the manufacturer, the wholesaler, the retailer or afinancial institution.Different forms of credit include:o Credit on open account- the bueyr gets the goods and is given a certain period oftime in which to pay the amount owed.o Installment sale- the buyer pays a deposit and the pays the balance off over aspecified period of time.o Lease- the consumer is allowed to use the goods but may never become theowner of the goods.
o The bueyr can get finance through a credit card or loan from a finacialinstituition.6. Risk bearing(Insurance) Insurance is a contract entered into by two parties, the insurer and the insured, to coveragainst certain risks.Human risks such as theft, bad debt, breakage and damages due to negligence andstrikes.Physical risks which can be the result of natural causes.Economic risks such as changes in demand and supply.7. Buying and selling The main aim of marketing is to sell goods and services to those individuals andhouseholds that will use them.Selling is influencing buyers to buy through effective sales promotionsThrough the marketing activity of selling, the buer takes possession of the goods.Forms of selling includes:o Personal selling: Direct selling between the manufacturer and the buyer.o Agency selling: someone who sells goods on commission for others.o Vending Machineso Online shopping.MARKETING MIX(POLICIES)1. PRODUCT POLICY Includes the choice of products, design of products, packaging and the use oftrademarks.The product must satisfy both the customners practical needs but also the customersemotional needs.Components of the product policy-Types of products/ categories of of consumer goods.Design of the productProduct developmentPackaging
-Trademark- A trademark is a symbol, word/s legally registered or established by use as representing acompany or productCategories of consumer goods A consumer product is a product bought by final consumers for personal consumption.But not every consumer product is the same.Consumer goods in businesses are categorised for marketing purposes.There arethree different types of consumer products. Marketers usually classifyconsumer products into these types of consumer products.These 3 types of consumer products all have different characteristics and involve adifferent consumer purchasing behaviour.Thus, the types of consumer products differ in the way consumers buy them and, forthat reason, in the way they should be marketed.Convenience products Among the three types of consumer products, the convenience product is bought mostfrequently.A convenience product is a consumer product or service that customers normally buyfrequently, immediately and without great comparison or buying effort.Examples include articles such as laundry detergents, fast food, sugar and magazines.As you can see, convenience products are those types of consumer products that areusually low-priced and placed in many locations to make them readily available whenconsumers need or want them.Select products Select products are a consumer product that the customer usually compares onattributes such as quality, price and style in the process of selecting and purchasing.Thus, a difference between the two types of consumer products presented so far is thatthe select product is usually less frequently purchased and more carefully compared.Therefore, consumers spend much more time and effort in gathering information andcomparing alternatives.Types of consumer products that fall within the category of select products are:furniture, clothing, used cars, airline services etc.
As a matter of fact marketers usually distribute these types of consumer productsthrough fewer outlets, but provide deeper sales support in order to help customers inthe comparison effort.Speciality products Speciality products are consumer products and services with unique characteristics orbrand identification for which a significant group of consumers is willing to make aspecial purchase effort.As you can see, the types of consumer products involve different levels of effort in thepurchasing process: the speciality product requires a special purchase effort, but appliesonly to certain consumers.PRODUCT DESIGN-Product design is the process of creating a new product to be sold by a business to itscustomers.Steps involved in developing/designing a product Idea generation/ Design and development of product ideas Selecting and sifting of product ideas/ Idea screening Concept development and testing/ Design and testing of the product concept whichshould happen before a product is developed Analysis of the profitability of the product concept/Business analysis , will determinewhether money should be invested in the product. Consumer responses must be tested, using a small sample of the product. The importance of product design Product design needs to be designed to suit the needs of the customers If the product design does not suit the target market, there will be very little demandfor the product. Business need to develop new products in order to replace older products in stage 4when the sale declines. Businesses are able to remain competitive because they are always on a lookout forways to improve their products. Products become different from those of the competitors. PACKAGING
-Packaging occurs when a product is placed in a container or wrapping.Packaging refers to the container or wrapping that holds a product or group of products.- Packaging of a product can influence a customer to buy or not to buy the product.Purpose of packaging: Packaging is needed to contain the item / product, e.g. olive oil in a bottlePackaging indicates brand / trademark of the business and should have informationabout the productRequirements/Purpose of good packaging-Must be eye-catching and attract the immediate attention of the consumer.Suit the product.Suitably designed for the target market.Distinguish itself from its competitors.Support the image the business is trying to create.Right for display purposes and meet the requirements of retailers.Environmentally responsible.Protect the content.Easy to distribute, handle, transport and use.Types of packagingSpeciality packaging -packed in a certain way to create a certain image.Packaging for immediate use -Unit packaging /the package is effortless and easy to usethe content.Re-useable packaging -packaging can be used for the same purpose more than once.Packaging for double use -the packaging can be used for something else.Kaleidoscopic packaging -certain part of the packaging changes continuously.Combination packaging -Two related items are packaged together.Unique packaging -Consumer buy the product to obtain the container.Packaging for re-sale -buying products in bulk to sell them separately on in smallerquantities.TRADEMARKS-A trademark is a symbol, word/s legally registered or established by use as representinga company or productRequirements
Make it easy for consumers to recognise the productMust be easy to spell and read, e.g. NIKEEasy to recognise, remember and pronounceHelps build brand familiarityImportance of a trademark-Forms the starting point for advertising the business and its productsCan extend its product range, because it is easy to market products under a well-knownand popular trademark.Can speed up a purchase transaction and increase sales.Creates loyalty among consumers and makes it difficult for the consumer to choosesubstitutes.Creates a product image that can be trusted by consumers.2. PRICING POLICY A value that will purchase a finite quantity, weight, or other measure of a good orservice.As the consideration given in exchange for transfer of ownership, price forms theessential basis of commercial transactions. It may be fixed by a contract, left to bedetermined by an agreed upon formula at a future date, or discovered or negotiatedduring the course of dealings between the parties involved.Price is the money charged for a good or service. For example, an item of clothing costsa certain amount of money. Or a computer specialist charges a certain fee for fixing yourcomputer.Price is also what a consumer must pay in order to receive a product or service. Pricedoes not necessarily always mean money. Bartering is an exchange of goods or servicesin return for goods or servicesPrice is the easiest marketing variable to change and also the easiest to copy.In business, price is determined by whato (1) a buyer is willing to pay,o (2) a seller is willing to accept, ando (3) the competition is allowing to be charged.Pricing techniquesA business can adopt different pricing strategies for several reasons, such as: To try to break into a new market
To try to increase its market sharesTo try to increase its profitsTo make sure all its costs are covered and a particular profit is earned.The techniques/strategies include Cost-based/orientated pricing is a technique of pricing that is aligned to the cost ofthe product. Mark-up pricing is calculated as a percentage from the cost per unit. Customer/target based pricing is a technique used by a business that has setcertain targets to achieve based on the large capital spent on machinery. Competition based/orientation pricing is when businesses set prices below thevalue of their competitors. Promotional pricing is a technique used by businesses who offer sales or specialoffers to attract customers. Penetration pricing is used when the business enters a new market by charginglow prices. Psychological pricing gives the customer an impression that an item is cheaperthan it really is. Bait pricing is a policy whereby products are advertised at prices that are usuallylower than the items cost price in order to attract them. Skimming prices are attached to a new innovative product that is consideredunique and prestigiousFactors influencing pricing Production costs: All input costs have to be added up and this is the basis of the price.This price changes as inputs increase or decrease. Nature of the product: Basic goods have lower prices, while luxury goods have higherprices. Prices of essential goods (petrol) can increase without greatly affecting demand. Demand and supply: Large demand and shortage of supply allows the producer toincrease prices. Low demand and increased supply forces producers to decrease price. Income levels of consumers: When the target market experiences a drop in income,the business have to react by reducing the price if they wish to maintain market share. Complements: A complementary product can have a high price if it is the only one thatcan be used. Substitutes: If a product has no substitute, then prices can increase without affectingthe market. Pricing Technique: Prices are influenced by the pricing technique used at the time. Competitor prices: Producers have to react when their competitors drop their prices. Economic conditions: In economic downturns, consumers have less money to spend.This also applies to times of high inflation.3. DISTRIBUTION POLICYoDistribution means the route that a productfollows from the time it wasmade/produced/manufatcured until it is sold to the final consumer.Channel of distributions
Manufacturer -consumero The manufacturer sells directly to the consumer without using the middlemen.o Manufactures using this channel have to advertise their products themselves.Manufacturer-Retailer-Consumero Goods move from the manufacturer to the retailer, where they are sold toconsumers.o The manufacturer sells its products to the consumer by using a retailer.Manufacturer-agent-retailer-consumero Goods move from the manufacturer to an agent. Goods are sold by an agent toretailers who will in turn sell to consumers.o Agents and retailers are responsible for adverting goods.Manufacturer-wholesaler-retailer-consumero This channel is known as the traditional channel of distribution.o Goods move from the manufacturer to the wholesaler and they are bought byretailers who sell them to onsumero Goods move from the manufacturer to an agent, who sells goods to wholesalers.o Small retailers then buy goods from the wholesaler and sell the products toconsumers.Intermediaries Individuals or businesses that link producers and consumers and make up thedistribution channel.Their purpose is to promote, sell or make available goods or services by buying andreselling, and each intermediary adds to the price of the item until it reaches the finalconsumer.Intermediaries
Meaning of creative thinking Creative thinking is the ability to think of original and innovative ideas. It focuses on exploring ideas/generating possibilities and looking for many answers. Term Definition Creative To be original,










