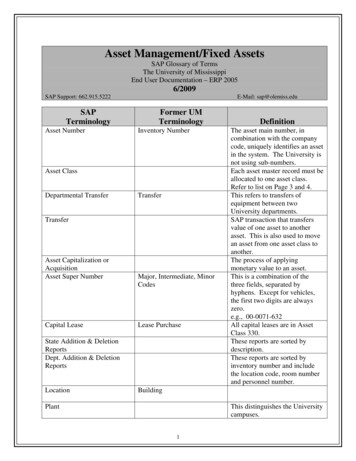
Transcription
Standard Operating Procedures for FixedAssets Management1
Purpose: This Policy document establishes policy & procedures for accounting of FixedAssets as per relevant Accounting Standards.It standardizes the procurement of Fixed Assets in accordance with the CapitalPurchase Budget.It emphasizes on the identification of Fixed Assets and its recording in FixedAssets Register & its periodical physical verification.SCOPE: This policy document will apply to the assets managed by the company at all itsunits.It would also emphasize on the additions and deletions made to the fixed assets.It also focuses on the proper documentation of these assets.2
Budget PlanningBudget:1.2.Cost Benefit tivity WiseBudget Approval by :Asset Classification:MD ED CFO Unit Head Technical Head Power Deptt. Head 1)2)3)4)5)6)7)8)LandBuildingPlant & MachineryFurniture & FixturesOffice EquipmentVehiclesOthersIntangiblesPost Budget Activity:Comparison with Actual3
Acquisition Process of Capital Assets:1.) Indenting :2.) Purchasing :3.) Receipt:Receipt at UnitUnitSpecific Deptt.Analysis of IndentInvite Quotations (at leastthree)Raises Indent to StoresAuthorized byrespective Deptt HeadStores check availability &ensures that indent iswithin capital budgetNett Req. sent toCentralized PurchaseDeptt.4Gate Officials verify Assetas per documents & makeEntry in Gate InwardRegisterPrepare ComparativeChartStores Receive Asset, verifiesBill & arrange for inspection ofAsset by the UserSelection of VendorInspection of Asset by the UserIn case of Single Quotationcheck reasonability of termsPreparation of MRNMRN along with PO &Invoice sent to AccountsRaise POPosting in Accounts Deptt.
Accounting Treatment :1.)AcquisitionDATEAsset does not requireInstallation/Inspection Capitalization &Accounting Entry onthe Date of Receipt ofAssetVALUEAsset requiresInstallation/Inspection Capitalization &Accounting Entry onthe Date of Receipt ofCommissioningCertificate from theTechnical Deptt. Till such date,asset shown asCapital Work InProgress (CWIP)51)2)3)4)5)6)7)8)9)Purchase PriceDuties & Taxes (non-recoverable)FreightBorrowing Cost (As per AS – 16)Installation ChargesInsurance Exp.Forex Fluctuations (As per AS – 11)Less Govt Grants (as per AS – 12)Less Trade Discounts & Rebate, ifany
2.) Depreciation Definition : As per AS-6,it is a measure of loss in value of an asset arising from use, passage of time,obsolescence due to change in technology & market conditions.Historical Value or Revalued Value Depreciation depends upon :Useful Life of the AssetEstimated Residual Value Depreciable Amount Historical Value or Revalued Value – Expected Residual Value Addition/Extension of Asset :Asset forms an integral part of the mainassetNoAddition/Extension to bedepreciated separatelyYesAddition/Extension to bedepreciated as per same rate &over same life Where the historical cost undergoes a change due to fluctuation in exchange rate, price adjustment etc.depreciation on the revised unamortized amount should be provided over the balance useful life of the asset. Useful life may be reviewed periodically after taking into consideration the expected physical wear and tear,obsolescence and legal or other limits on the use of the asset. In case of change in useful life, depreciationshould be provided taking into consideration the revised useful life over the remaining no. of years.6
As per Sec. 350 of the Companies Act,a company is required to provide depreciation as per ratesspecified in Sch. 14 given below. However in case the management expects the useful life of the asset to behigher, depreciation at lower rates can be provided with proper justification for the same. AlthoughHigher Rates can be provided.General RatesAsset BlockWDV RateSLM RateFactory Building10%3.34%Non Factory Buildings (Offices, Godowns, Employees Quarters Etc.)5%1.63%Plant & Machinery (continuous process plants)15.33%5.28%Motor-cars, motor cycles, scooters & other mopeds25.89%9.5%Motor Buses30%11.31%Data processing machines including computers40%16.21%18.1%6.33%Furniture & Fittings Notwithstanding anything mentioned in this Schedule depreciation on assets, whose actual cost does notexceed five thousand rupees, shall be provided depreciation at the rate of hundred per cent. However, if theaggregate value of assets purchased exceeds 10% of the existing value of its block than such assets shouldbe capitalized. Intangibles should be amortized as per AS – 26.7
3.) Sale & Discard of Fixed Asset :DiscardSALEDateDate on which theright over the asset issacrificed i.e. InvoiceDateDateValueDate on whichthe asset isretired from itsactive useInvoice ValueProfit & Loss tobe routedthrough P/LValueAsset to bevalued at lesserof Net BookValue or NetRealizable ValueProfit & Loss tobe routedthrough P/L4.) Capital Work In Progress (CWIP) : It is an asset which is not completed to be used. All expenses in relation to the CWIP should be debitedto CWIP A/c. When the asset is completed & ready to be used then Amount should be transferred to theRespective Asset A/c. Quarterly review should be done in order to ensure that expense in relation to CWIPis debited to CWIP A/c & not in the respective expense A/c.8
5.) Revaluation of an Asset : Assets are valued at Historical Cost in the books of accounts. In the subsequent yearsthe value of asset could be higher or lower than its present book value due to the inflationary conditionsof the economy.Net Book ValueUPWARDRelated to previousdecreaseYESDOWNWARDRelated to previous increaseCredit to P/L A/c tothe extent alreadycharged to P/L A/c &the excess if any, toRevaluation ReserveNOYESDebit to RevaluationReserve to the extentavailable & charge thebalance to P/L A/cNOCharge the differenceto P/L A/cCredit the difference toRevaluation ReserveNote: “No” means first time revaluation. “Yes” means second and subsequent revaluations9
6.) Impairment of an Asset : As per AS – 28 , an organization should make an assessment of the recoverable value of all its fixed assetsat every balance sheet date to find whether an asset needs to be impaired based on the factors given below :Factors causing ImpairmentExternalInternalPhysicalDamage to anAssetEarlier Disposalof an AssetCarrying Amt ofAssets MarketCapitalization ofOrganizationSignificantDecline inMarket ValueDecline in theEconomicPerformance ofAssetChange inMarket InterestRate As per AS - 28, if the Recoverable Value of an Asset is less than its Carrying Value than the asset should berevalued at the Recoverable amount by charging the difference to P & L Account known as Impairment Loss.Carrying Amount :Net Book Value ofan AssetRecoverableAmount :LESSHigher ofNet Selling PriceorValue in Use10 Impairment Loss :To be debited toP & L A/c
Fixed Assets Tagging & Coding Process:The process of scientifically numbering fixed assets is called tagging. The purpose of Taggingassets is to track the movement of assets from one place to another place. A tag (bar code orunique number) helps in verification of the existence of assets and their location, aids inmaintenance, provides a common ground for communication between the AccountsDepartment and the end-users and recording the net book value of asset in case of sale /scrapping. All fixed assets must be tagged except land, building etc.Fixed AssetReceiptInspectionAccountingCode generated eitherthrough system ormanuallyTagging of such code onFixed Asset11Recording the Codein FAR if generatedmanually
Fixed Assets Register (FAR) :What is FAR ?It is a register showing all the permanent assets owned by the company. It shows the qty, value &location of these assets. Any deletion and addition to/of assets are also recorded in this register.FAR V/s Stock RegisterStock RegisterFARTo keep record of goods received & issuedTo exercise effective control over the FixedAssets held by the companyUsed for items which are not permanentUsed for assets which are permanent innatureContains low value itemsContains relatively high value itemsSignificance :Effective ControlCARO Compliance12Provides final Value of FAfor financial statements
Contents of ategoryCostBasicValueDuties& erestCost
FAR AlterationFAR will be updated once in a quarter or six months if it is maintained manually orsimultaneously if it is system generated. It will be updated for the following reasons :Addition ofan Asset : All FieldsSale , Discarding ,Demolition of Asset All FieldsProvidingDepreciation : Depreciation Rate Depreciation Amt.Inter Unit AssetTransfer : Location Additional duty& taxes FAR must be Yearly reviewed for ensuring its accuracy by an appropriate authority in theFinance Deptt.14
Physical Verification : Objective: To verify the actual existence of the book assets, check theircondition & provide for adjustments (short/excess, if any) of fixed assetsfound during physical.PhysicalVerification PolicyTeam Members: Stores Personnel Expert from Technical Deptt Personnel from User Deptt Personnel from Accounts Deptt Finance Personnel from HO Internal AuditorTenure:Once in threeyears15PhysicalVerificationReport signedby TeamMembers &Unit HeadAdjustmentsrelating toExcess/Shortageby the FinanceHead
Physical VerificationProcessIntimation by HO personnel to unit head via mail regarding Phy.Verification Program showing its date, team members, procedure etc.GM forwards the mail to stores & engg deptt.Physical Verification conducted on the decided date by the respective teamBased on the Physical, a Taking Report must be prepared signed by the team members and unit headSuch Report must be compared with the FAR and differences noted along with reasonsBased on differences a Reconciliation Statement must be preparedSuch Statement must be presented before higher authority like CFO & EDAfter their approval necessary actions to be taken & adjustments to be made in books16
PhysicalReportV/sFARDifferences in FAR & Physical Verification :Found inFAR but notin PhysicalMisappropriation of AssetWrong Entryor DoubleEntry In FARAsset has beenScrappedFound inPhysical butnot in FARAsset sent outon returnablebasisSale/ Transferentry omittedin FAR17Acquisitionentry not donein FARAsset pectionPendingAsset recd viainter unit transfer
AS 6 – Accounting forDepreciationAS 10 – Accounting for FixedAssetsAS 11 – Accounting for effects ofchange in Foreign Exchange RatesAccountingStandards relatedto Fixed AssetsAS 16 – Borrowing CostAS 26 – Intangible AssetsAS 28 – Impairment of Assets18
Companies (Auditor’s Report) Order (CARO), 2003As per paragraph 4(I) of this order, an auditor is required to comment on propermaintenance, physical verification and major disposal in relation to fixed assets during thefinancial year. Therefore CARO 2003, requires a Company to :Maintenance of properrecords showing: Description of Asset1. Categorization & Location of Asset Purchase Details2. Depreciation Details Revaluation/Impairment Details Details regards Sale, Discarding &Destruction of AssetMajor Disposal ofFixed AssetsPhysical verification3.At Regular Intervals(at least once in threeyears)Report preparationshowing materialdiscrepanciesProper adjustment ofthese in the books191.2.Proper AccountingAs per AS – 1, if thisaffects going concernthen its properexpression in financialstatements isnecessary.
What ?How ?Who ?Authorized By ?Reviewed By?Review Period ?BudgetPreparationRefer SlideNo. 4FinanceDepttChief FinancialOfficer (CFO)ExecutiveDirectorOnce in ThreeYearsBudget v/sActualComparisonRefer SlideNo. 4FinanceDepttChief FinancialOfficer (CFO)ExecutiveDirectorAt the end ofyearAcquisitionRefer SlideNo. 5PurchaseDeptt.Chief FinancialOfficer (CFO)ExecutiveDirectorYearlyAccountingRefer Slides6 –11UnitAccountsDepttDeptt. HeadUnit Head (GM)QuarterlyAssetTagging &CodingRefer SlideNo. 12UnitAccountsDepttDeptt. HeadUnit Head (GM)YearlyFARUpdatingRefer Slides13-15UnitAccountsDepttDeptt. HeadFinanceManagerYearlyPhysicalVerificationRefer Slides16-18PhysicalVerificationTeamUnit HeadChief FinancialOfficer (CFO)Once in ThreeYearsCARO & ASComplianceRefer Slide19 & 20AccountsDeptt.HO AccountsDeptt.Chief FinancialOfficer (CFO)Yearly20
Fixed Asset Code generated either through system or manually Recording the Code in FAR if generated manually The process of scientifically numbering fixed assets is called tagging. The purpose of Tagging assets is to track the movement of assets from one place to another place. A tag (bar code or unique number) helps in verification of the existence of assets and their location, aids in .File Size: 2MBPage Count: 20