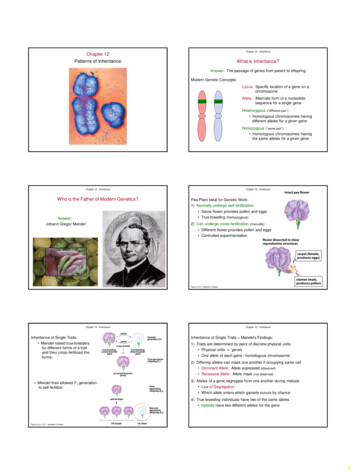
Transcription
Chapter 13beginning thesales processSection 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesSection 13.2First Steps of a Sale
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesCONSIDER Do you think everyone who buys anitem has the same reasons for buying it? Why orwhy not?Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary Activities Explain how salespeople get ready to sell. List sources of product information. Explain feature-benefit selling and how it creates selling points. Identify consumer buying motives. List prospecting methods and explain how prospects are qualified.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesGetting ready to sell involves preliminaryactivities that help salespeople with the salesprocess, such as learning about the product,industry, and customer, to develop effectiveselling points.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary Activities merchandising rational motives feature-benefit selling emotional motives product features patronage motives physical features prospect extended product features referrals customer benefits endless-chain method selling points cold canvassing buying motivesCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesOutline of thePreliminaryActivitiesAssociated withthe Sales ProcessCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesOutline of thePreliminaryActivitiesAssociated withthe Sales ProcessCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesGetting Ready to SellProduct KnowledgeExperiencePublishedMaterials andWeb SitesTrainingCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesGetting Ready to SellIndustry Trends and CompetitionTradePeriodicalsStandard &Poor’sResearchCompetitionCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesGetting Ready to SellMerchandisingGive-AwaysSigns andDisplaysLocationmerchandisingCoordinating sales and promotionalplans with buying and pricing.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingWhat is feature-benefit selling?feature-benefit sellingMatching the characteristics of a productto a customer’s needs and wants.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingProduct tFeaturesproduct featureBasic, physical, or extended attribute of a product or purchase.physical featureTangible attribute that helps explain how a product is constructed.extended product featureIntangible attribute related to the sale of a product thatcustomers find important.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingProduct Feature ExamplesCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingProduct Feature ExamplesCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingIt is the salesperson’s job toanalyze a product and determinecustomer benefits.customer benefitAdvantage or personal satisfaction acustomer will get from a good or service.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingA well-designed catalog willidentify important selling points.selling pointThe function of a product feature and itsbenefit to a customer.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingCustomerBuying MotivesRational MotivesEmotional MotivesPatronage MotivesMultiple Motivesbuying motiveA reason a customer buys a product.rational motiveA conscious, logical reason for a purchase.emotional motiveA feeling expressed by a customer throughassociation with a product.patronage motiveA reason for remaining a loyal customer ofa company.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingFill in this diagram. The product is a car.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingFill in this diagram. The product is a car.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingWhat is prospecting?What is a prospect?prospectingLooking for new customers.prospectA sales lead; a potential customer.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingProspecting ales Leadsendless-chain methodreferralA recommendation of another person who might buy the product being sold.endless-chain methodWhen salespeople ask previous customers for names of potential customers.cold canvassingThe process of locating as many potential customers as possible withoutchecking leads beforehand.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingProspecting TechniquesCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesFeature-Benefit SellingProspecting TechniquesCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesSection 13.11.List three things that salespeople do to get ready to sell.To get ready to sell, salespeople must gatherinformation about their products, industry trends, and the competition.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesSection 13.12.Explain how a customer might use a combination of rational,emotional, and patronage buying motives when purchasing ahybrid automobile.A sample explanation: rational motive–buying a hybrid automobile willhelp save on gas consumption and cost less money to operate;emotional motive–buying a hybrid automobile will help save theenvironment for my children and grandchildren; patronage motive–I’vebeen very satisfied buying cars from this manufacturer for years; Iexpect their hybrid will be good quality.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesSection 13.13.Identify three prospecting techniques.Prospecting techniques include customer referrals, cold canvassing,and employer sales leads.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SalePREDICT Why is asking a customer “May I helpyou?” not an effective way to begin in a retailenvironment?Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a Sale Demonstrate how to properly approach a customer to open a sale. Differentiate between organizational and retail approaches. List three retail approach methods. Discuss when and how to determine customer needs.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleThe actual sales presentation begins when youapproach customers to open the sale anddetermine their needs.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a Sale greeting approach service approach merchandise approach nonverbal communication open-ended questionCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleOutline This Section’s ContentCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleOutline This Section’s ContentCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleThe ApproachThe Effective Sales OpeningTreat customers as individuals.Be aware of the customer’s personality and buying style.Show interest in customer with eye contact and friendliness.Learn the customer’s name.Incorporate a theme in the approach.Know that approaches differ in organizational selling and retail selling.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleThe ApproachOrganizational SellingArrive early.Be aware that first impressions count.Be conversational to put the customer at ease.Use information you gathered during prospecting.Explain how you can reduce costs, increase productivity,or improve profits.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleThe ApproachRetail Selling seApproachgreeting approachA retail approach method in which the salesperson welcomes the customer tothe store.service approachA retail-selling method in which salespeople ask customers if they need assistance.merchandise approachA retail-sales method, also called the theme approach, in which the salespersonmakes a comment or asks a question about a product in which the customer showsan interest.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleThe ApproachFacts About the Three Retail ApproachesCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleThe ApproachFacts About the Three Retail ApproachesCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleDetermining NeedsA good salesperson can readnonverbal communication.nonverbal communicationExpressing oneself without the use ofwords, such as with facial expressions,eye movement, and hand motions.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleDetermining NeedsFacts About the Three Methodsof Determining NeedsCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleDetermining NeedsFacts About the Three Methodsof Determining NeedsCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleDetermining NeedsQuestions to Ask andQuestions Not to AskWhen the Customer isShopping for aMicrowave OvenCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleDetermining NeedsQuestions to Ask andQuestions Not to AskWhen the Customer isShopping for aMicrowave OvenCopyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleSection 13.21.Discuss the importance of knowing how to ask the right questions.Asking the right questions gets the customer talking and allows thesalesperson to zero in on the customer’s needs and wants.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleSection 13.22.List three retail approach methods.Retail approach methods include the greeting approach, the serviceapproach, and the merchandise or theme approach.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
Section 13.2First Steps of a SaleSection 13.23.Identify when salespeople should determine customers’ needs.In organizational sales, the needs should be determined whenqualifying a prospect. In retail sales, the needs should be determinedduring or immediately after the approach.Copyright by McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
End ofChapter 13beginning thesales processSection 13.1Preliminary ActivitiesSection 13.2First Steps of a Sale
MARKETING ESSENTIALS Author: GLENCOE