Transcription
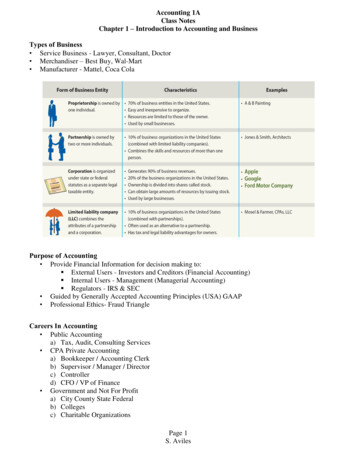
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessTypes of Business Service Business - Lawyer, Consultant, Doctor Merchandiser – Best Buy, Wal-Mart Manufacturer - Mattel, Coca ColaPurpose of Accounting Provide Financial Information for decision making to: External Users - Investors and Creditors (Financial Accounting) Internal Users - Management (Managerial Accounting) Regulators - IRS & SEC Guided by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (USA) GAAP Professional Ethics- Fraud TriangleCareers In Accounting Public Accountinga) Tax, Audit, Consulting Services CPA Private Accountinga) Bookkeeper / Accounting Clerkb) Supervisor / Manager / Directorc) Controllerd) CFO / VP of Finance Government and Not For Profita) City County State Federalb) Collegesc) Charitable OrganizationsPage 1S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessAll accounting is based on one simple formulaASSETS LIABILITIES OWNERS EQUITY(Owned)(owed)3 WAYS A COMPANY GETS ASSETS1. Contributed2. Borrowed3. EarnedAccounting keeps track of where your fundscame from(Contributed, Borrowed or Earned)AndWhere your funds went.(Asset Purchases, Expenses)ASSETS items OWNED by a business that will provide FUTURE BENEFITExamples: Money, merchandise, furniture, fixtures, machinery, buildings, landLIABILITIES DEBTS or obligations of a business OWED to others that can be paid with cash, goods,or services. Examples: Accounts Payable, Notes PayableOWNERS EQUITY (a.k.a. NET WORTH or CAPITAL) Represents the amount by which thebusinesses ASSETS EXCEED their LIABILITIES.It TRACKS that which was: CONTRIBUTED TO and DRAWN FROM the business by owners Added to or subtracted from the business through historical EARNINGS/LOSS ACTIVITYIn BUSA100, you used proprietorships as the form of business, in this class we use corporations. Themajor difference between the two for our purposes is in the Owner’s Equity section.Expanding the Accounting EquationREVENUE Amount the business charges customers for the products or services it sells. Revenuesincrease Assets and OEEXPENSES Amount expended as a result of the efforts made to produce revenues. Expenses will eitherdecrease assets or increase in liabilities. Expenses always reduce OE.(expenses do not always reduce cash - rent expense/rent payable)NET INCOME REVENUE Greater Than EXPENSES (increases OE)NET LOSS REVENUE Less Than EXPENSES (decreases OE)Page 2S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessNet Income or Loss is always determined OVER A DEFINED SPAN OF TIMEExample: Net Income for the 12 months ended December 31, 2017.DIVIDENDS & WITHDRAWALS (a.k.a. DRAWING) Reduction in OE as a result of cash or otherassets being distributed to the owners for their personal use. (the opposite of Owner Investment)ASSETS LIABILITIESITEMS OWNEDAMOUNTS OWEDCash, TrucksAccts PayableSTOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY OWNERS INVESTMENTCapital Stock RETAINED EARNINGSNet IncomeLess: DividendsRevenue - recognized when earned. Regardless if customer pays now or later.Expense - recognized when incurred, even if cash has not been paidIndicate whether each of the following is identified with (1) an asset, (2) a liability, or (3) stockholders'equity:a) accounts payableb) cashc) fees earnedd) lande) suppliesf) wages expenseAnalyzing Business Transactions1. What Happened2. Which Accounts Are Affected3. How is the Accounting Equation kept in balanceExamples:1. Owner contributes a building valued at 90,000 and Cash of 10,000 to the business2. Bought a PC for 5,0003. Financed a truck through the bank for 20,0004. Made his first Truck payment to the bank for 5005. The Owner Withdrew 1,000 from the business for personal usePage 3S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessPage 4S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessPage 5S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessFinancial Statements After transactions have been recorded and summarized, reports are prepared for users.The. accounting reports providing this information are called financial statements The primary financial statements of a corporation are the:- Income statement- Retained earnings statement- Balance sheet- Statement of cash flowsIndicate in the space provided by each item whether it would appear on the income statement(IS), balance sheet (BS), or retained earnings statement (RE):a. Service Revenueg.Accounts Receivableb. Utilities Expenseh.Common Stockc. Cashi.Equipmentd. Accounts Payablej.Advertising Expensee. Suppliesk.Dividendsf. Salaries and Wages Expensel.Notes PayablePage 6S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessOn October 1, Ebony Ernst organized Ernst Consulting;on October 3, the owner contributed 84,000 in assetsin exchange for its common stock to launch thebusiness. On October 31, the company’s records showthe following items and amounts. Use this informationto prepare an October income statement, retainedearnings statement, and balance sheet for the business.Income StatementExpenses:Total expensesNet incomeRetained Earnings StatementRetained earnings,Retained earnings,Page 7S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessBalance SheetAssetsLiabilitiesStockholders' EquityTotal stockholders'equityTotal liabilities and stockholders'equityTotal assetsPage 8S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessRivera Roofing Company, owned by Reyna Rivera, began operations in July andcompleted these transactions during that first month of operations.July12368101517232528303131Reyna Rivera invested 80,000 cash in the company in exchange for its common stock.The company rented office space and paid 700 cash for the July rent.The company purchased roofing equipment for 5,000 by paying 1,000 cash and agreeing to pay the 4,000 balance in 30 days.The company purchased office supplies for 600 cash.The company completed work for a customer and immediately collected 7,600 cash for the work.The company purchased 2,300 of office equipment on credit.The company completed work for a customer on credit in the amount of 8,200.The company purchased 3,100 of office supplies on credit.The company paid 2,300 cash for the office equipment purchased on July 10.The company billed a customer 5,000 for work completed; the balance is due in 30 days.The company received 8,200 cash for the work completed on July 15.The company paid an assistant’s salary of 1,560 cash for this month.The company paid 295 cash for this month’s utility bill.The company paid 1,800 cash in dividends to the owner (sole shareholder).1. Use additions and subtractions within the table to show the dollar effects of each transactionon individual items of the accounting equation. Show new balances after each transaction.2. Prepare an income statement for the month ended July 31.3. Prepare a retained earnings statement for the month ended July 31.4. Prepare a balance sheet as of July 31.5. What item appears on both the income statement and retained earnings statementPage 9S. Aviles
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessAssetsDateCash Liabilities CommonAccountsOfficeOfficeAccounts Roofing Receivable SuppliesEquipmentPayableStockEquipmentPage 10S. AvilesEquity- Dividends Revenues - Expenses
Accounting 1AClass NotesChapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and BusinessIncome StatementExpenses:Total expensesNet incomeRetained Earnings StatementRetained earnings,Retained earnings,Balance SheetAssetsLiabilitiesStockholders' EquityTotal stockholders'equityTotal liabilities and stockholders'equityTotal assetsPage 11S. Aviles
Chapter 1 – Introduction to Accounting and Business Page 2 S. Aviles All accounting is based on one simple formula ASSETS LIABILITIES OWNERS EQUITY (Owned) (owed) 3 WAYS A COMPANY GETS ASSETS 1. Contributed 2. Borrowed 3. Earned ASSETS items OWNED by a business that will provide FUTURE BENEFIT Examples: Money, merchandise, furniture, fixtures, machinery, buildings,











