Transcription
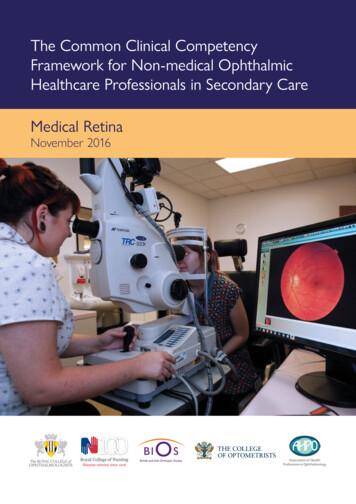
The Common Clinical CompetencyFramework for Non-medical OphthalmicHealthcare Professionals in Secondary CareMedical RetinaNovember 2016Association of HealthProfessions in Ophthalmology
General basic competences of non-medicaleye health care professionalsThe basic skill set of an ophthalmic non-medical healthcare professional (qualified optometrist, orthoptist,ophthalmic nurse or ophthalmic healthcare sciencepractitioner) is to: Perform basic clinical ophthalmic assessment Follow protocols within their scope of practiceunder appropriate supervision Detect abnormalities through assessment and acton these findings Not make a diagnosis or treatThis level of skills and competences is essential beforeundertaking further training and education for a Level1 expanded role; and some HCPs may need additionalophthalmic training (basic ophthalmic training courses)to obtain these skills.Possession of a competence indicates demonstrationof an understanding of the underlying principles,limitations and benefits of the skill, as well as beingable to elicit the appropriate information accurately.History taking B asic science knowledge about symptomatologyof eye disease Communication skills – ability to elicit relevantinformation Clinical knowledge about ophthalmic presentations Ability to take a general ophthalmic history Ability to take a social, family and drug history Ability to take a relevant systemic history, includingpast medical history Slit lamp examinationFundal examinationPupil reactionsEye movementsClinical assessment of visual fieldsUnderstand management of refractive errorInvestigations R ecognise roles of various investigations andunderstand their basisDealing with the needs ofophthalmic patients U nderstand the terminology and notation used forophthalmic examinations – including refractive status Communication skills- patients, relatives and colleagues- written, oral and non verbal Time management skills Patient as the focus of care Patient safety Infection control including equipmentdecontamination Knowledge of and adherence to local policies Team working Epidemiology of ophthalmic disease Understand basic drug principles Instil drops Administer drugs as prescribed Recognise allergies and common complicationsTeaching and educationOphthalmic examination Ophthalmic basic science knowledge- Anatomy- Physiology- Pathology- Optics- Microbiology Understanding of basic disease processes Ability to elicit and recognise the relevance of positiveand negative findings on examination Visual acuity measurement – understanding of variousmethods and notations External ocular examination2 Recognise own development needs Ability to share basic information with patients fortheir education and understandingPersonal development Self-learningReflective practiceRecognise and develop evidence based practice Recognise limitations of own practice andcompetences and works within this scope CPD – identify channels through which skills can bemaintained and developed
Competence in practice – Medical RetinaRelevant underlying knowledge in competence and behavioural skills.Level 1Level 2Level 3Participate in screening,under supervision, of medicalretina (MR) patients andparticipate in monitoring lowrisk patients with establisheddiagnoses in protocol driventreatment clinicsParticipate in triageand assessment ofnew patients. Performassessment, managementand monitoring underspecific protocolsParticipate in hospitalbased medical retina (MR)patient care, managing anddischarging patients underthe care of a consultantophthalmologistOphthalmic history takingLevel 1Level 2Level 3 As per general competencesAs per Level 1As per Level 2 Ability to: T ake a comprehensive historyrelevant to the patient with amedical retinal (MR) conditionwith particular emphasison relevant past medical,ophthalmic and drug history Ability to: R ecognise specific systemicconditions of relevance tomedical retinal (MR) diseases E licit specific informationin the differential diagnosisof MR and how thehistory may be helpful indetermining the differentconditions R ecognise history relevantto systemic conditions whichmay affect medical retinatreatment outcomes andrefer to ophthalmologistsas appropriate3
Ophthalmic examinationLevel 1Level 2Level 3As per general competencesAs per Level 1As per Level 2 Ability to: Ability to: Ability to: U nderstand the anatomy,physiology and pathophysiologyof the retina, with emphasison the macula U nderstand and recognisethe risk factors and differentialdiagnosis of disorders of retinaland macular pathology including :- AMD – dry, and wet(neovascular)- Central retinal vein occlusion(CRVO) / branch retinal veinocclusion (BRVO)- Diabetic retinopathy /maculopathy-C ystoid macular oedema(CMO)-C entral serous retinopathy(CSR)- Other differential diagnoses D etect the features neededto accurately grade diabeticretinopathy R ecognise and understandthe relevance of anteriorsegment changes associatedwith medical retinal diseaseeg APD, rubeosis, anteriorchamber activity U ndertake a competentophthalmic examinationwith regard to medicalretinal disorders U se a 3 mirror funduscontact lens as indicated andinterpret the results D etect the features neededto accurately grade diabeticretinopathy according tomodified Early TreatmentDiabetic Retinopathy Study(ETDRS) criteria includingpre-proliferative retinopathy,diabetic maculopathyand PDR with high riskcharacteristics D etect and classify diabeticretinal diseaseInvestigationsLevel 1Level 2Level 3 As per general competencesAs per Level 1As per Level 2 Ability to: Ability to: Ability to: P erform OCT imaging andfundus photography R ecognise basic pathologyon OCT images and fundusphotographs U nderstand diabetes, diabeticeye disease and its relevance toretinopathy screening4 R ecognise the use of fluoresceinand ICG angiography, andautofluorescence in medicalretina service delivery Use and interpret of ICG U se and interpret OCTimaging software and fundusphotographs to review dataand make accurate diagnosis S elect and interpret needfor specific tests for medicalretina conditions R ecognise and useelectrodiagnostics Recognise and use ultrasound
Investigations continued U nderstand the principles offluorescein, ICG angiographyand autofluorescence inmedical retina service delivery I nterpret fluorescein,ICG angiography andautofluorescence in medicalretina service delivery D etect the features neededto accurately grade diabeticretinopathy S elect and interpret need forspecific tests for medical retinaconditionsManagement and interventionsLevel 1Level 2Level 3 As per general competencesAs per Level 1As per Level 2Ability to:Ability to:Ability to: R ecognise acute retinalpathology, conduct appropriatetests and make appropriatereferrals, clearly stating thelevel of urgency R ecognise current nationalreferral guidelines and detailedknowledge of local referralpathways for patients withmedical retina disorders U nderstand the principles,processes and protocols ofnational diabetic retinopathyscreening programmes M ake re-treat decisions fornAMD within own level ofcompetence, according tolocal protocols in a consultantophthalmologist-led pathway,including the ability todetermine when to seekfurther advice D iagnose neovascular AMD(nAMD) with a provisionalrecommendation fortreatment M onitor the responseto treatment and modifymanagement plan ofreferred patients D ifferentially diagnose retinaland macular conditionsand manage or refer asappropriate R ecognise risks and benefitsof medical, laser and surgicalinterventions for differenttreatments for medicalretina conditions M ake re-treat decisions fornAMD according to localprotocols in a consultantophthalmologist led pathway,including the ability todetermine when furtherinvestigations are required inthe event of atypical or suboptimal responses to treatment Administer pharmacologicalinterventions, includingintravitreal injections inline with local policy andguidelines I ntegrate clinical data inorder to make differentialdiagnoses, and instigateappropriate managementplans according to protocoland supervision as required R ecognise a disease course thatis unusual C ommunicate with colleagueswithin a multidisciplinary setting5
Ability to deal with needs of ophthalmic patientsLevel 1Level 2Level 3 As per general competencesAs per Level 1As per Level 2Ability to:Ability to:Ability to: C ommunicate to patientsinformation about theirdiagnosis and potentialmanagement options includingreferral to rehabilitation servicesand eligibility for registration B e aware of the rapidlyevolving nature of medicalretina treatments that may berequested by patients B e part of the consentpathway C ommunicate with patientsabout their diagnosis,treatment plans and outcomes M anage patients fears andconcerns P rovide information andpsychological support for thepatient and carers U nderstand pharmacologyof anti-VEGF medications,to include possible contraindications, side effects anddrug interactions R ecognise the risks for patientsabout the natural history of thecondition and any therapeuticinterventions A dminister pharmacologicalinterventions in line withlocal policy and guidelines W ork in a team andcommunicate with relevantmembersTeaching and educationLevel 1Level 2Level 3 As per general competencesAs per Level 1As per Level 2Ability to:Ability to:Ability to: I nform and educate patients andcarers regarding medical retinadisorders and their management6 I nform/educate patients thereasons behind monitoring plan T each and train other groupsof professions
Personal developmentLevel 1Level 2Level 3 As per general competencesAs per Level 1As per Level 2Ability to: Direct self-learning Understand reflective practice R ecognise the need to workwithin own level of competence Seek advice where appropriate D emonstrate participationin CPD W ork within the clinicalgovernance framework service R ecognise NICE guidelinesand local protocols for AMD,diabetic macular oedema(DMO) and RVOsAbility to: K eep up to date with, applyand act upon the NICEguidelines and local protocolsfor AMD, diabetic macularoedema (DMO) and RVOsas part of the team R ecognise clinical trials whichmay influence current andfuture practice A udit own and serviceactivityNon-medical eye HCPs who participate in medical retina pathways must possess basic science knowledge ofthe epidemiology, clinical features, natural history and possible progression of the various types of disease.They will be familiar with evidence based guidelines and have a knowledge of basic principles and limitations ofrelevant equipment and tests along with the technical skills to employ it effectively.The Level 1 competences are in keeping with the Professional Certificate in medical retina currently availablefrom the University of Cardiff, City University of London and Ulster University.7
AbbreviationsAMDAge Related Macular DegenerationICGIndocyanine GreenAPDAfferent Pupillary DefectIOPIntra Ocular PressureBRVOBranch Retinal Vein OcclusionIPIndependent PrescriberCMOCystoid Macular OedemaLA/GALocal Anaesthetic/General AnaestheticCOAGChronic Open Angle GlaucomaMRMedical RetinaCPDContinuing Professional DevelopmentCRVOCentral Retinal Vein OcclusionnAMD Neovascular Age Related MacularDegeneration (wet AMD)CSRCentral Serous RetinopathyDMDiabetes MellitusDMODiabetic Macular OedemaDRDiabetic RetinopathyHCPsHealth Care ProfessionalsHEIsHigher Education InstitutionsHESHospital Eye ServiceContactProfessor Caroline MacEwenPresidentThe Royal College of Ophthalmologists18 Stephenson WayLondonNW1 2HDT. 020 7935 0702E. president@rcophth.ac.ukOCTOptical Coherence TomographyOHTOcular HypertensionPGDPatient Group DirectivePIPeripheal IridotomyRVORetinal Vein OcclusionSLTSelective Laser Trabeculoplasty
Medical Retina November 2016 The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care Association of Health Professions in Ophthalmology. 2 The basic skill set of an ophthalmic non-medical health care professional (qualified optometrist, orthoptist, ophthalmic nurse or ophthalmic healthcare science practitioner) is to: Perform











