Transcription
Quality Control Instrumentationfor Paint and Coating InstallationsWilliam Corbett, KTA-Tator, Inc.
Quality Control Instrumentation forPaint and Coating Installations
Learning Outcomes Identify organizations responsible forwriting inspection standards Identify inspection check points Describe basic inspection equipment Identify industry guides for verifyingsurface preparation and coating thickness
Purpose ofQuality Inspection Verify the quality of surfacepreparation and coatingapplication Help ensure the longevityof the paint/coating system
Causes of CoatingFailures Poor surface preparation Inadequate mixing and thinning Inadequate coating application Unfavorable environmentalconditions Incorrect selection of coating Manufacturing issue with coating
Prevention ofCoating Failures On-site quality assuranceand quality control(QA/QC) to verifyspecification compliance
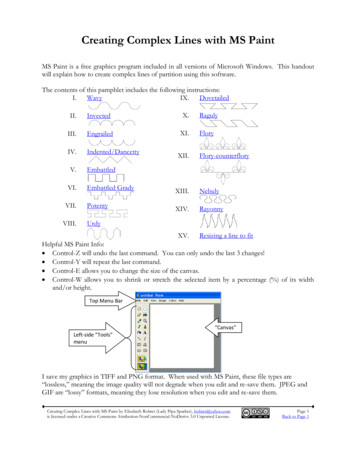
Industry Associations & Terms ASTM — ASTM International (formerly American Societyfor Testing and Materials) NACE — NACE International SSPC —The Society for Protective Coatings WFT — Wet Film Thickness DFT — Dry Film Thickness Mill Scale — Bluish-black oxide layer that forms on thesurface of hot-rolled carbon steel Mil — 0.001" Micron (micrometer) — 25.4 µm 1 mil
InspectionSequence Inspection Checkpoints Pre-surface preparation Measurement of ambientconditions Evaluation of compressed aircleanliness Surface preparation Witnessing coating mixing Inspection of coating application(continued)
InspectionSequence Inspection Checkpoints (continued) Determination of dry film thickness Evaluating cleanliness betweencoats Pinhole and holiday detection Evaluating cure/hardness Evaluating adhesion
Pre-SurfacePreparation Inspection Condition of the substrate Presence of grease, oil, dirt, etc. Presence of weld spatter Presence of sharp edges Presence of excessive pitting Installation of protectivecoverings
Ambient Conditions &Surface Temperature What are we measuring? Air Temperature Relative Humidity Dew Point Temperature Surface Temperature
Measuring Ambient Conditions Measuring Instruments Sling Psychrometers* Battery-poweredPsychrometers* Electronic Psychrometers*Used in conjunction withpsychrometric charts
Measuring SurfaceTemperature Dial-Type Thermometer Position & stabilize forminimum of 2 minutes Thermocouple-TypeThermometers Stabilize quickly Infrared (non-contact)thermometers
Electronic Psychrometers Measure/Record: Air Temperature Surface Temperature (ST) Relative Humidity Dew Point Temperature (DP) Spread between DP and STFeatures Auto-logging Data uploading using software Audio/visual alarm BlueTooth Data Output
Measurement ofAmbientConditions Measurements are obtained andrecorded every four hours, moreoften if conditions are worsening Measurements are obtainedwhere the work will be/is beingperformed Measurements may be obtainedautomatically
Relative Humidity: The amount ofmoisture in the air, as a percentage oftotal saturationMeasurementof AmbientConditions Dew Point: The temperature at whichmoisture in the air condenses on asurface A surface temperature at or below thedew point temperature will result incondensation
Measurement ofAmbientConditionsFinal surface preparation andcoating application should notbegin until the surfacetemperature is at least 5 F (3 C)above the dew pointtemperature.
Evaluation ofCompressed AirCleanliness Compressed air must be clean and dry Indirect (automatic) requirement ofSSPC Surface Preparation Standards “Blotter test” (ASTM D4285) Exhaust compressed air at 18–24"for 1 minute onto “collector” Visually assess air cleanliness Assess prior to use and at frequentintervals
Abrasive Cleanliness What are we concerned about? Oil Water soluble contaminants
Why are we concerned aboutabrasive cleanliness?AbrasiveCleanliness Contamination on abrasive can betransferred to the surface SSPC Abrasive Specifications allrequire testing for cleanliness (oil &water soluble contaminants) SSPC/NACE joint surface preparationstandards for abrasive blast cleaninglist abrasive cleanliness as an indirectrequirement of the standards
Abrasive Cleanliness Vial test Oil film (ASTM D7393) Tap water Visual assessment No visually detectable oil Conductimetric Analysis (ASTMD4940) Deionized water Conductivity meter 1000 µS/cm
Surface Preparation Two-fold purpose ofsurface preparation Surface cleanliness Surface profile (anchorpattern)
Importanceof SurfacePreparation Surface preparation is the mostimportant factor affecting coatingsystem performance Surface conditions affectingcoating life: Presence of oil/grease Presence of salts or other chemicals Presence of dust/dirt Presence of corrosion products Presence of old coatings
Surface CleanlinessSSPC/NACE Surface Cleanliness Standards SSPC-SP1: Solvent Cleaning SSPC-SP2: Hand Tool Cleaning SSPC-SP3: Power Tool Cleaning SSPC-SP5/NACE 1: White Metal Blast Cleaning SSPC-SP6/NACE 3: Commercial Blast Cleaning SSPC-SP7/NACE 4: Brush-off Blast Cleaning(Continued)
Surface CleanlinessSSPC/NACE Surface Cleanliness Standards SSPC-SP10/NACE 2: Near-White Metal Blast Cleaning SSPC-SP11 & 15: Power Tool Cleaning SSPC-SP WJ-1/NACE WJ-1 thru WJ-4
Visual Guides for SurfaceCleanlinessSSPC VIS 1 “Guide and ReferencePhotographs for Steel SurfacesPrepared by Dry Abrasive BlastCleaning” Step 1: Assess initial condition(A, B, C, D, G1, G2, G3) Step 2: Locate photograph of levelof surface preparation(SP7, SP6, SP10, SP5), basedon initial condition E.g., C SP10
Visual Guides for SurfaceCleanliness SSPC VIS 3 “Guide and ReferencePhotographs for Steel SurfacesPrepared by Hand and Power ToolCleaning” Step 1: Assess initial condition(A,B,C,D,E,F,G) Step 2: Locate photograph oflevel of surface cleanliness(SP2, SP3, SP11, SP15), based on initialcondition E.g., G SP 15
Visual Guides forSurface Cleanliness Establish a project-specificsurface cleanlinessstandard (use visual guide) Verify removal of abrasiveand dust from surface priorto primer application
Surface Profile Measurement of surfaceroughness created bypower tool cleaning orabrasive blast cleaning Surface profile must bespecified separately fromsurface cleanliness
Surface Profile Standards ASTM D 4417Measurementof SurfaceProfile Method A (visual comparator) Method B (depth micrometer) Method C (replica tape) NACE SP02-87 (replica tape) SSPC-PA 17, “Procedure forDetermining Conformance toSteel Profile/Surface Roughness/Peak Count Requirements”
Measurement of SurfaceProfile Method B – Depth Micrometer Instrument base sets on peaks ofthe profile while a conical-shapedpoint projects into the valleys Features: Memory BlueTooth Data Transfer Statistical analysis of data andusing software
Measuring SurfaceProfile Method C – Replica Tape Replica tape used inconjunction with aspring-loadedmicrometer Digital RTR: Automatically deducts 2mils of Mylar thickness Can upload data via USBconnection of BlueTooth
No. of readings indicated in ASTMstandardsFrequency ofSurface ProfileMeasurements No. of locations not indicated in ASTMstandards No. of locations may be indicated bythe project specification SSPC-PA 17 provides no. of locationsto characterize the surface
Number ofReadings(todeterminelocationaverage) Based on Test Method (unlessotherwise specified) ASTM D 4417 “Sufficient” number of readings forMethod A (visual comparator) 10 readings per “location” forMethod B (depth micrometer) 2 readings per “location” for MethodC (replica tape)
Number of Locations(to characterize thesurface) SSPC-PA 17 Minimum of three 6” x 6”locations Per surface preparation“apparatus” Per work shift or 12-hourperiod (whichever isshorter)
SOLUBLE SALT (IONIC)CONTAMINATION Soluble salt contamination can bechlorides, sulfates, or nitrates. All canbe found in a soil environment. Soluble salts will increase soilconductivity and accelerate thecorrosion of the steel pipe. If the salts are not removed, theadhesion of the pipe coating may becompromised.
MEASUREMENT OF IONIC CONTAMINANTSConductivity Measurement(not ion-specific)Ion-Specific Test Kit
Verify product data and SDS on-site(most current versions)WitnessingCoatingMixing andThinning Verify correct coating materials andthinners on-site (manufacturer, productnumbers, colors, batch dates) Verify current shelf life Verify correct quantity and ratio ofcomponents (if multi-componentcoatings are specified)(Continued)
Witness mixing and thinning proceduresWitnessingCoatingMixing andThinning Verify induction or sweat-in (if required) Verify complete kits are mixed Verify correct type and quantity ofthinner addition Monitor pot life of mixed materials Verify that application equipment meetscoating manufacturer’s requirements
Measuring Dry FilmThickness Two standards that addressthe nondestructivemeasurement of coatingthickness on metals ASTM D7091 SSPC-PA 2
Describes a procedure for determiningshop/field conformance to a specified DFTrange on ferrous and non-ferrous metals Measurements are acquired usingcommercially available gages (two“types”)Scope ofSSPC-PA 2 Procedures for gage calibration,verification of accuracy and adjustmentare described Procedure for determining conformanceto specified thickness range overextended areas is described Contains 10 Non-mandatory Appendices
Definitions in SSPC-PA 2 Gage Reading: A single instrument reading Spot Measurement: The average of three or atleast three gage readings made within a 1 ½”diameter circle Area Measurement: The average of five spotmeasurements over each 100 square feet of coatedsurface
Gage TypesType 1 – Magnetic Pull-off GagesType 2 – Electronic Gages
Gage Types, continued Type 2 – Electronic Gages Electronic circuitry converts reference signal to coatingthickness
ASTM D7091 describes 3 operationalsteps to ensure accuratemeasurement:Calibration &Verificationof Accuracy Calibration Verification of Accuracy Adjustment Steps are required to be completedbefore coating thickness dataacquisition to determine conformanceto a specification Focus on Type 2 Gages today
Performed by the gage manufactureror an accredited calibration laboratoryGageCalibration Test certificate traceable to a NationalMetrology institution required No standard calibration interval(established based on experience &work environment) One year interval is common
Verification of Type2 Gage Accuracy Verify accuracy per manufacturerinstructions (use traceable coatedstandards or certified shims) Performed as described in ASTMD7091 Beginning and end of each workshift (minimum) During (e.g., hourly), if: Obtaining a large no. ofreadings Gage is dropped or readingsare suspect
Single Point VerificationVerificationof Type 2GageAccuracy Select one reference coated standardrepresenting the mid-range of theanticipated coating thickness E.g., 4-6 mils, select 5 mil referencestandard Two Point Verification Select reference coated standardsbelow and above the mediananticipated coating thickness E.g., 5 mils, select 3 mil and 7 milcoated standards
Adjustment of Type2 Gages Aligning a gage’s thicknessreadings to those of a knownthickness value to improve gageaccuracy on a specific surface orwithin a measuring range Corrects for: Surface Roughness Substrate Properties (metallurgy) Curvature Use Certified or Measured Shims
Measurement Frequency
Measurement Frequency For areas of coating: not exceeding 300 square feet, measure each 100square feet exceeding 300 square feet and not exceeding 1000square feet, arbitrarily select and measure 3 random100 square foot areas exceeding 1000 square feet, arbitrarily select andmeasure 3 - 100 square feet areas for the first 1000square feet, and 1 additional 100 square foot area foreach additional 1000 square feet, or portion thereof
Measurement Frequency ExampleSize of Coated Area:900 square feetNo. of Areas:3 areasNo. of Spots:3 Areas x 5 Spots/Area 15 SpotsMin. No. of Gage Readings:15 Spots x 3 Readings/Spot 45 Gage Readings
SSPC-PA 2, Appendix 7: Measuring Thickness onCoated Steel Pipe Exterior Pipe spools measured individually Table describes frequency Pipe spools 10 ft: 3 sets ofcircumferential spotmeasurementsTable A7Pipe DiameterCircumferential SpotMeasurementsInterval SpacingUp to 12 inch (30 cm)4 evenly spaced10 ft (3 m) apart14-24 inches (36-60 cm)6 evenly spaced10 ft (3 m) apart 24 inches (60 cm)8 evenly spaced10 ft (3 m) apart
Recoat Intervals/Cleanliness Verify minimum and maximumrecoat times are followed (seemanufacturer’s product datasheets) Verify surface is dry, clean, andfree of foreign matter beforeapplying subsequent coats
Final Inspection Holiday/Pinhole Detection Cure/Hardness Testing Adhesion Testing
Final Inspection Holiday/Pinhole Detection(“Jeeping”) Holiday - skip or miss Pinhole - tiny hole whichmay or may not be visibleto the unaided eye Mandatory for buriedpipe
Holiday/PinholeDetection NACE SP0188 Low Voltage (wet sponge) Non-conductive coatings overconductive substrates Up to 20 mils coating thickness Use wetting agent in water(e.g., Kodak Photo-Flo)
Holiday/PinholeDetection NACE SP0188 High Voltage (spark testing) Non-conductive coatings overconductive substrates Over 20 mils coating thickness
Determining the Proper Peak Voltage SettingV K* TWhere:V Peak voltage in voltsT Coating Thickness in MilsK Constant:Coatings 40 mils 525Coatings 40 mils 1250
Determining the Proper Peak Voltage SettingV K* TExample: 45 mil coating1250 x 451250 x 6.71 8388 volts (8.4 kV)
Determining the Proper Peak Voltage SettingNACE SP0188 – Table 1 (suggested settings only)MilsSuggested Voltages forHigh-Voltage Spark Testing8-111,500 V (1.5kV)12-152,000
SSPC-PA 17, “Procedure for Determining Conformance to Steel Profile/Surface Roughness/ Peak ount Requirements” Measurement of Surface Profile Method B –Depth Micrometer Instrument base sets on peaks of the profile while a conical-shaped point projects into the valleys Features: Memory BlueTooth Data Transfer Statistical analysis of data and using software Measurement of Surface .