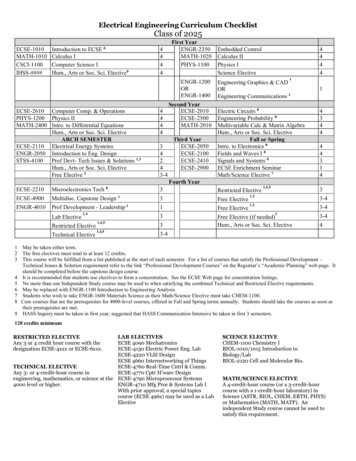
Transcription
Durability Growth throughHALT/HASS and Accelerated TestingElite Electronic EngineeringHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Topics Covered Review Your RequirementsOverview of Accelerated Stress TestingHALT HALT Equipment, Test Methods, ExpectationsHASSOther Accelerated TestsSummaryQ&AHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Test Requirements & Goals Is Testing Desired by Manufacturer toReduce Cost of Development,Manufacturing, and Warranty Obligations?Mandated by Manufacturer’s Client?What are your expectations and goals forthis testing?HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
New Product Development Testing ScreensNewProductHALT, HAST, ESD,Power Cycle, EMIRTCA DO-160MIL-810,SAE J1455Temp, Vibration, Shock,Waterproofness,Altitude, ve TestingQualificationTestingQual RetestQuantitative TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated TestingManufacturingScreen
Quantitative TestingSuccess Run TestingTest to Failure- WeibullReliability Block Diagrams.95.98.98.80.65HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing 0.73
Which Tests To Run Input from all departmentsDetermine failure modes (FMEA)Consider complete life cycle of productSuggest stresses that will precipitate failures Maximum Stress vs Time DependentDevelop test planExecute testHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Time Dependent Failure MechanismsFailure ModeFailure MechanismAccelerating FactorsLoss of signalSilicon DiffusionTemperaturePower FailureDielectric BreakdownElectric FieldLoss of signalElectromigrationTemperature & Power CyclingIntermittent OutputCorrosion & Oxidation ofFracturesHumidity, Voltage, TemperatureLoss of signalDendrite GrowthHumidity, TemperatureWater IntrusionSeal LeaksPressureCracked SolderJointFatigueThermal cycling & vibrationHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT Testing (Qualitative)Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT)Temperature and Thermal Shock (60C/min)Vibration 6 axis simultaneous (6 DOF)Very high stress levels to achieve time compression& quickly find the weakest links.Additional stresses likely to precipitate flaws can beused as a part of the HALT/HASS program. power cycling, voltage /electrical stressHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingDesign Optimization Provide data to designers for risk assessmentWeak links- opportunity to improve the product before the design is “locked in”.Build in lifetimes of use in its field environment, “very large margins”.Proactive technique focusing on the mode and mechanism of failure, not on thespecifications or the level of stress.No pass/fail criteria HALT specification. Some HALT specifications describe a“common method”Product Comparisons Side-by-side evaluation of various products and product revisions under similarextreme stressHASS Endpoints Large margins enables the use of high levels of stress in the HASS screen. Leaveseveral if not many lifetimes of use remaining in the product.Enables the use of HASS to quickly detect any slippage that might occur in themanufacturing process.HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT Testing Halt Chamber Workspace 42”x42”x40”Heating & Cooling -100C to 200C 60C/min dependingon product loading andtemperature rangeHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT Testing HeatingElements NichromeCoilsFLA 135AMin Service175A460VAC 3phAirflow4,000CFMHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT Testing LN2 Cooling 4.5GPM30 PSIGHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT Testing RS Vibration Table Multi-axis repetitive shock3 linear, 3 rotational Axes2Hz-10,000HzUp to 60GRMS(depending on loading)Table Size 30” x 30”Payload up to 400lbs(reduced vibration amplitude) Compressed Air 90PSIG, 48CFMHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT Testing RS ImpactorsHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT Testing1.E 01HALT PSD1.E 001.E-011.E-021.E-041.E-051.E-061.0E 00G 2/Hz1.E-03Frequency (Hz)1.0E 011.0E 021.0E 03HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing1.0E 041.0E 05
HALT TestingComponents on PWBCkt board resonant frequenciesChip capacitors and die bond wiresHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
RS vs. EDAcceleration ProfileAcceleration (G²/Hz)1 x 1 0 -1C ontrol1 x 1 0 -21 x 1 0 -32010010002000F requency (Hz)D emandFeb 11, 2005 10:23:11Level 1) 100%Output: 0 V RMSDemand: 6.061 GLevel T ime: 0:05:00Control: 6.06 GT otal T ime: 0:05:22Ice Corporation (33141)De-Icing Control Unit (9510 Rev T )End of T estHALT/HASS and Accelerated TestingY Axissn: C350-00057-SAC
RS vs. ED ED (Electrodynamic Vibration) Controllable Vibration Spectra5Hz-2000HzSingle Axis2” DisplacementRS Random Only6 Axis30Hz-10,000Hz10x -15x higher peak accel vs. EDHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Steps Involved with HALTSTEP 1: Pre-HALT Planning Discuss product with multi-functional teamDevelop test planBench test to confirm operation before starting HALTHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT ProcessSTEP 2: Preparing for the HALTSetup Design appropriate vibration fixtureTune chamber proportional & integral parametersConfigure air flow for maximum product temperaturechange rateApply thermocouples and accelerometers to deviceunder testSetup functional test equipmentHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT ProcessSTEP 3: Thermal Step Stressing Cold Begin at ambientStep down in 5 C or 10 C incrementsUse caution as fundamental limit is approachedApproximate dwell time of 10 minutes at each temperatureAllow sufficient time to run functional testsFind and fix failuresVerify operation of thermal safetiesDisable safeties to determine actual operating & destruct limitsContinue until fundamental limit of technology is reachedPractice continuous failure monitoringHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT ProcessSTEP 4: Thermal Step Stressing Hot Begin at ambientStep up in 5 C or 10 C incrementsUse caution as fundamental limit is approachedApproximate dwell time of 10 minutes at each temperatureAllow sufficient time to run functional testsFind and fix failuresVerify operation of thermal safetiesDisable safeties to determine actual operating & destruct limitsContinue until fundamental limit of technology is reachedPractice continuous failure monitoringHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Limits Encountered in HALTData from Gregg Hobbs of Hobbs perUpperOperating rginMarginDestruct MarginDestruct MarginStressHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT ProcessSTEP 5: Rapid Thermal Cycling Transition temperature at maximum product temperature changeratesSelect temperatures 5 C inside upper and lower operational limitsReduce change rate by 10 C/min if product cannot withstandmaximum rateContinue thermal cycling until operating limit ( C/min) is foundContinue cycling for a minimum of 10 minutesApply functional testing and continuous failure monitoringDepending on the product or application, this step is sometimesomittedHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT ProcessSTEP 6: Vibration Step Stress Understand how product responds to vibration inputVibration is stepped-up in increments, normally 3-5Grms on the productDwell time of 10 minutes at each level is typicallysufficientStart dwell once product reaches vibration set pointContinue until operational or destruct limit is foundApply additional product stresses during processHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT ProcessSTEP 7: Combined Environments Develop thermal profileUse established thermal operating limits, dwell times and changeratesIncorporate functional tests and continuous failure monitoringBegin with constant vibration level of approximately 3-5 GrmsStep up in 3-5 Grms increments upon completion of each thermalcycleUse tickle vibration when higher Grms levels are reachedAdd 3-5 Grms tickle to determine if failures were precipitated athigh G level but only detectable at lower G levelHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Suggested HALT Process Per GMW 8287HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Other Stresses The Product Determines the StressPower CyclingOutput LoadingVoltage/Electrical StressesHumidity (HAST)PressureAltitudeCorrosionHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT ProcessSTEP 8: Lessons Learned Determine root cause of all failures that occurredMeet with design engineers to discuss HALT resultsManagement cost justification & risk assessmentDetermine and implement corrective actionPerform Verification HALTInsure problems are fixed and new problems were notintroducedPeriodically evaluate product as it is subjected to engineeringchangesHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingOther considerations Quantity of Samples Fixturing Product ImprovementPreparation for HASS/HASAComparison TestingStimulation vs. SimulationProduct and Fixture WeightTest UniformityHALT/HASS and Accelerated TestingLowerOperatingLimitOperatingMargin
HALT TestingCross Table Uniformity160.025.0136.3136.125 & 55 Grms Input 2.980.069.310.865.564.060.060.010.045.240.05 Grms Input Scale140.05.020.00.025 Grms Input55 Grms Input5 Grms Input0.01234Table Location5HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingResponse LevelTest LocationControl LevelGrms- 69.31MAX .450.364.02MAX .637.345.23MAX 44.560.04MAX .550.065.55MAX (55)157.4140.5110.5136.11520.517.912.116.81251MAX (55)HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing75.172.351.966.4158.1140.7112.8137.2
HALT TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingFailure Analysis ServicesHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingFailure Analysis Services“SEM photographs showing and overall view (top, 40x) and a typicalcloser view (bottom, 800x) showing some surface debris but nodamage to the integrated circuit from sample D4.”HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT TestingHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Other Uses of HALT Component Selection Did vendor perform HALT AND HASS?Use to verify products operating limits.Use to select most robust product.Vendor Selection If subcontracting, vendor needs to meet yourstandards (Halt and Hass equipment, shouldbe the same.)HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HASS- Highly Accelerated Stress Screening HASS is used as a production quality screenquickly identify any weaknesses that might enter theproduct due to changes or malfunctions in themanufacturing process.Each weakness detected, represents an opportunityto take corrective action prior to shipping largequantities of flawed product.The screen is “tuned” so that it detects weak productwhile still leaving several, if not many lifetimes offield use in the shipped product.HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HASS Testing HASS- 100% Production ScreeningHASA- 1-10% Production Auditing Safety of of HASS Repeat screen a minimum of 20 timesAssuming remove less than 5% lifeFailures after less than 10 times, too harshRe-HALT- Confirm marginsHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Other Accelerated Stress Testing Acceleration FactorsTemperature Humidity Miner CriteriaVoltage Arrhenius-Peck ModelVibration Arrhenius ModelInverse Power LawProduct Life Cycling CALT TestingTest to Failure & Apply Weibull AnalysisHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Product Life Cycling Calibrated Accelerated Life Testing (CALT) Suggest primary fatigue mechanismSimulate loads at three stress levels 90% of foolish load (first test)80% of first test loadThird stress level Depends on first two and ultimate lifeTest all units to failurePlot S-N curve, Determine AF’sGenerate Weibull PlotHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Product Life CyclingAccelerated Life Testing “Accelerated Testing: StatisticalModels, Test Plans, and Data Analysis” By Wayne Nelson CALT GMW 8758 ExampleAutomatic Lubricating SystemHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
CALT Test Example Simulate loadsat three stresslevels Monitor testcounting cyclesto failureHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
CALT Test ExampleStress363636363131313125252525 Collect Failure Data AF (Saccel/Snormal)b100000Cycles to Failure Plot and determine InversePower RelationshipCycles To 925728723Pump S-N Curve100001000-5.93y 3050953219559.39x10010Determine AF'sConditionHigh StressMid StressConfirm StressNormal StressHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing100Applied Stress (PSI)Stress Value (PSI)36312515Accel Factor1807421N/A
CALT Test ExampleStress Level Sort and apply median ranksGenerate Weibull PlotHigh (IG)High (IG)High (IG)High (PP)Medium (PP)Medium (IG)Medium (PP)Medium (IG)Confirm (PP)Confirm (PP)Confirm (PP)Confirm (PP)Test 25728723Accel Factor1801801801807474747421212121Sorted Least to Most(Resort these numbers for eachchange to 2464905405609795940098431891698933HALT/HASS and Accelerated TestingMedian .3386.4094.39Cycles at 710
CALT Test ExampleReliaSoft W eibull 7 - www.ReliaSoft.comWeibull Plot Obtain distribution parametersData 1W eibull-2PRRX SRM MED FMF 12/ S 0Data PointsProbability Line50.000Unreliability, F(t) Reliability vs lifeProbability-W eibull90.000 Reliability metrics B1, B10Probability - Weibull99.00010.0005.000 Reliability Block Diagrams1.00010000.000100000.0001000000.000Time , (t ) HALT/HASS and Accelerated TestingSteve LayaElite Electronic Engineering6/ 12/ 20084:58:49 PM1.000E 7
HAST TestingAccelerated Humidity Testing HAST (Highly AcceleratedStress Testing) JESD22-A110 B Compress 1000 Hour 85/85Humidity to 96 Hours High Temperatures maystimulate uncorrelated failures Arrhenius-Peck AcceleratedModel for TemperatureHumidityHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HAST Testing“ Photographs showing environmental damage to the solderjoints of A8.”HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Instrumentation & Data Acquisition Yokagawa DL708 Scope Ten Systems In-House4, 8, and 16 ChannelLeCroy Digital Storage Scopes 1.5GHz Bandwidth, 8GS/s, 16M datapointsSeven Systems In-House 400MHz, 500Mhz scopesAgilent 34970A Data AcquisitionSystem 120 Single Ended or 60 Differential InputAC/DC, Volts, Amps, Frequency, OhmsHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Advanced Material CenterMaterials Testing and Failure Analysis Physical TestingThermal TestingChemical TestingLight & AppearanceExposure TestingProduct ComparisonsLocation: Ottawa, Illinoiswww.amc-testlabs.comHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Advanced Material CenterPhysical Testing Tensile Tear Dart Flextural Friction Surface Tension Specific Gravity Density COFHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Advanced Material Center Thermal Analysis Differential Scanning Calorimeter(DSC) Thermal Mechanical Analyzer (TMA) Melt rangePurityExpansion/ContractionThermal Gravimetric Analyzer (TGA) Thermal degradationAshHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Materials Engineering IncorporatedComplete Metallurgical Laboratory Failure AnalysisAnalysis of Processing ProblemsContamination IdentificationEngineering Support/ConsultingLaboratory TestingSpecialized TestingLitigation Support and Expert TestimonyLocation: Virgil, Illinoiswww.materials-engr.comHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Materials Engineering IncorporatedComplete Metallurgical Laboratory Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with EDS OES Chemical Composition Metallography and Microscopy Microhardness and Hardness Electrical Conductivity Density/Specific Gravity Surface Roughness (Ra) Pressure and Torque Testing Specialized Product and Component Testing ISO 17025 Accredited by A2LAHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Other Tests to FailureHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Other Tests to FailureHALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
Durability Growth to HALT HASSAny Questions?Thank You!HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing
HALT/HASS and Accelerated Testing HALT Testing (Qualitative) Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT) Temperature and Thermal Shock (60C/min) Vibration 6 axis simultaneous (6 DOF) Very high stress levels to achieve time compression & quickly find the weakest links. Additional stresses likely to precipitate flaws can be used as a part of the HALT/HASS program.