Transcription
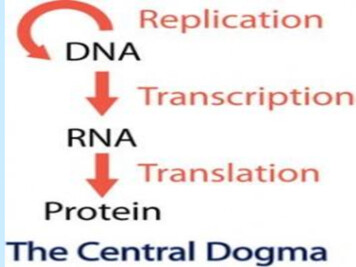
CHAPTER 13Transcription and TranslationCentral Dogma - ReviewTranscriptionIs the making of different types of RNA using DNA as a template. It requires many enzymes aswell as specific DNA sequences called promoters and enhancers.Main enzyme that makes RNA is the RNA Polymerase.Three main steps:1.-Initiation,2.-Elongation,3.-Termination1
CHAPTER 13Initiation: a small transcriptional factor attaches to the promoter regionThe segment in the promoter region in DNA that signals the start of transcription iscalled the TATA box. The small transcription factor helps RNA polymerase to attachDNA and begin transcription.2
CHAPTER 13Elongation:RNA elongates in the 5' 3' direction. The nucleotide sequence in the promoterdetermines which will be the strand used as a template. Only one of the strands ofDNA is used as a template and is called the sense strand.TerminationSpecific stop codons in DNA will signal for the release of the RNA being made.In prokaryotes happens immediately after the stop codon is transcribed; in eukaryotes,10-15 nucleotides could be transcribed until the RNA molecule is released.3
CHAPTER 13Processing of RNA molecules in Eukaryotes5’ Capping: guides with insertion of the RNA molecule into the ribosome and also withstabilityTranscriptionTranslationPoly-A tail: a series of Adenine nucleotides are added to the transcript. It helps withstability of RNA molecule.RNA splicing: RNA molecule is made of different regions called introns and exons.Introns are regions that are not used for protein coding, these are spliced (cut) out byspliceosomes of the final RNA molecule. Once the RNA molecule is ready in Eukaryotic cells, it is time for it to leave the nucleus,through the nuclear pores.TranslationTranslation is the making of protein or polypeptides using mRNA as a template.mRNA messenger RNArRNA ribosomal RNA (made in the nucleolus)tRNA transfer RNATransfer RNA consists of a RNA molecule of about 70-80 nucleotides long, it has aregion where an amino acid can attached to and a region with an anti-codon sequence.Ribosomal RNA consists of hundreds of nucleotides combined with 40% protein. It iscomposed of a large subunit and a small subunit.It has 3 sites:the A site the tRNA binding sitethe P site the Peptidyl tRNA-binding sitethe E site the exit site4
CHAPTER 13X-Ray crystallography of a ribosomeCharging of tRNAsThe enzyme in charge is Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, there are 20 different ones, one for eachamino acid.5
CHAPTER 13InitiationThe initiation of translation begins with the attachment of the small ribosomal subunitwith the start amino acid with the mRNA. The large subunit completes the complexElongationThis occurs in 3 steps:1-Codon recognition- the tRNA with the correct anti-codon will bind to the A site ofthe ribosome2-Peptide bond formation- a peptide bond is form between the amino acids in the PA site, while the peptide bond of the amino acid to tRNA in P site is broken.3-Translocation- movement of tRNA in P site is translocated to the E site where isreleased.6
CHAPTER 13TerminationA termination codon does not allow for attachment of a tRNA but for a terminationfactor which will hydrolyze the peptide bond between the growing chain and the tRNA inthe P-site.After Translation, proteins are processed either by modified in the cytosol or sent into the ERwith a signal peptide that allows it to get into the endoplasmic reticulumTranslation in a jiffy7
Transcription and Translation Central Dogma - Review Transcription Is the making of different types of RNA using DNA as a template. It requires many enzymes as well as specific DNA sequences called promoters and enhancers. Main enzyme that makes RNA is the RNA Polymerase. Three main steps: 1.-Initiation, 2.-Elongation, 3.-Termination 1